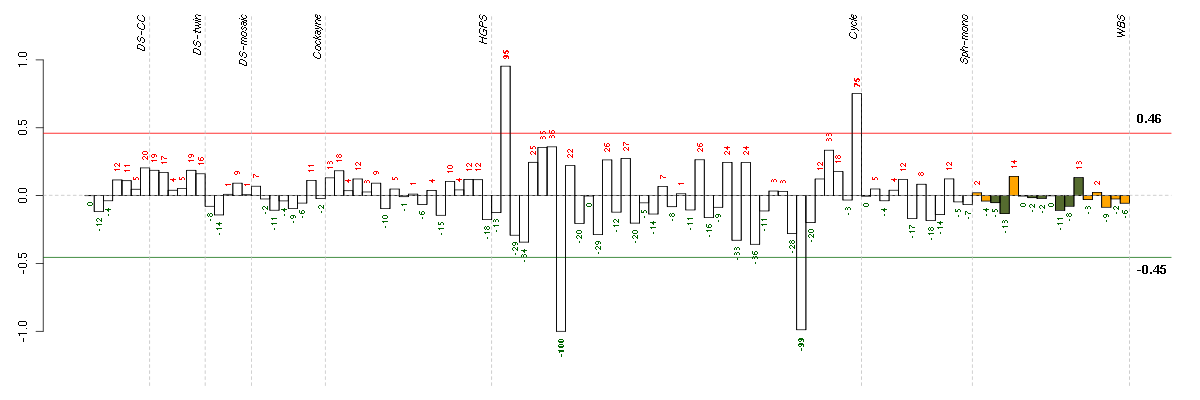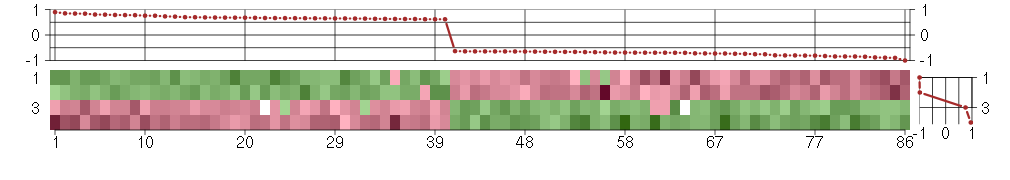

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
all
This term is the most general term possible
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intermediate filament
A cytoskeletal structure that forms a distinct elongated structure, characteristically 10 nm in diameter, that occurs in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Intermediate filaments form a fibrous system, composed of chemically heterogeneous subunits and involved in mechanically integrating the various components of the cytoplasmic space. Intermediate filaments may be divided into five chemically distinct classes: Type I, acidic keratins; Type II, basic keratins; Type III, including desmin, vimentin and others; Type IV, neurofilaments and related filaments; and Type V, lamins.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
neurofilament
A type of intermediate filament found in the core of neuronal axons. Neurofilaments are heteropolymers composed of three type IV polypeptides: NF-L, NF-M, and NF-H (for low, middle, and high molecular weight). Neurofilaments are responsible for the radial growth of an axon and determine axonal diameter.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
intermediate filament cytoskeleton
Cytoskeletal structure made from intermediate filaments, typically organized in the cytosol as an extended system that stretches from the nuclear envelope to the plasma membrane. Some intermediate filaments run parallel to the cell surface, while others traverse the cytosol; together they form an internal framework that helps support the shape and resilience of the cell.
neurofilament cytoskeleton
Intermediate filament cytoskeletal structure that is made up of neurofilaments. Neurofilaments are specialized intermediate filaments found in neurons.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
intermediate filament
A cytoskeletal structure that forms a distinct elongated structure, characteristically 10 nm in diameter, that occurs in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Intermediate filaments form a fibrous system, composed of chemically heterogeneous subunits and involved in mechanically integrating the various components of the cytoplasmic space. Intermediate filaments may be divided into five chemically distinct classes: Type I, acidic keratins; Type II, basic keratins; Type III, including desmin, vimentin and others; Type IV, neurofilaments and related filaments; and Type V, lamins.
neurofilament
A type of intermediate filament found in the core of neuronal axons. Neurofilaments are heteropolymers composed of three type IV polypeptides: NF-L, NF-M, and NF-H (for low, middle, and high molecular weight). Neurofilaments are responsible for the radial growth of an axon and determine axonal diameter.

ABCA7ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 7 (219577_s_at), score: 0.9 ABCA8ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 8 (204719_at), score: -0.88 ABLIM1actin binding LIM protein 1 (200965_s_at), score: -0.69 ADAadenosine deaminase (204639_at), score: 0.63 ADAMTS7ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 7 (220705_s_at), score: 0.8 AGBL2ATP/GTP binding protein-like 2 (220390_at), score: 0.66 AKR1B10aldo-keto reductase family 1, member B10 (aldose reductase) (206561_s_at), score: -0.65 APPamyloid beta (A4) precursor protein (214953_s_at), score: 0.63 BIRC3baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 3 (210538_s_at), score: -0.76 CD79BCD79b molecule, immunoglobulin-associated beta (205297_s_at), score: 0.85 CFIcomplement factor I (203854_at), score: -0.68 CYorf15Bchromosome Y open reading frame 15B (214131_at), score: 0.65 DCLK1doublecortin-like kinase 1 (205399_at), score: -0.69 DENND3DENN/MADD domain containing 3 (212975_at), score: -0.64 DMPKdystrophia myotonica-protein kinase (37996_s_at), score: -0.66 EFHC2EF-hand domain (C-terminal) containing 2 (220591_s_at), score: -0.72 EGR3early growth response 3 (206115_at), score: -0.72 ELAC1elaC homolog 1 (E. coli) (219325_s_at), score: 0.62 FKBP10FK506 binding protein 10, 65 kDa (219249_s_at), score: 0.84 FXYD2FXYD domain containing ion transport regulator 2 (207434_s_at), score: 0.69 GALNT12UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 12 (GalNAc-T12) (218885_s_at), score: -0.64 GATMglycine amidinotransferase (L-arginine:glycine amidinotransferase) (203178_at), score: -0.82 GPR56G protein-coupled receptor 56 (212070_at), score: -0.66 HGFhepatocyte growth factor (hepapoietin A; scatter factor) (209960_at), score: -1 HHIPL2HHIP-like 2 (220283_at), score: 0.64 HIST1H2AGhistone cluster 1, H2ag (207156_at), score: -0.74 HOXA4homeobox A4 (206289_at), score: 0.68 HSPA4Lheat shock 70kDa protein 4-like (205543_at), score: -0.69 INAinternexin neuronal intermediate filament protein, alpha (204465_s_at), score: -0.81 IRF1interferon regulatory factor 1 (202531_at), score: -0.7 KCTD15potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 15 (218553_s_at), score: 0.69 KIAA1305KIAA1305 (220911_s_at), score: -0.65 KRT8P12keratin 8 pseudogene 12 (222060_at), score: 0.63 LOC100128919similar to HSPC157 (219865_at), score: -0.7 LOC100133105hypothetical protein LOC100133105 (214237_x_at), score: 0.84 LOC100133748similar to GTF2IRD2 protein (215569_at), score: 0.62 LRP2low density lipoprotein-related protein 2 (205710_at), score: -0.67 LRP8low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 8, apolipoprotein e receptor (205282_at), score: 0.72 MAP7microtubule-associated protein 7 (202890_at), score: -0.85 MDM2Mdm2 p53 binding protein homolog (mouse) (205386_s_at), score: -0.84 MUC5ACmucin 5AC, oligomeric mucus/gel-forming (217182_at), score: 0.65 NDPNorrie disease (pseudoglioma) (206022_at), score: -0.73 NEBLnebulette (216882_s_at), score: 0.7 NEFMneurofilament, medium polypeptide (205113_at), score: 0.65 NFKBIAnuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha (201502_s_at), score: -0.63 NOL10nucleolar protein 10 (218591_s_at), score: 0.65 NXPH3neurexophilin 3 (221991_at), score: 0.67 OAS22'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase 2, 69/71kDa (204972_at), score: -0.84 PARD6Apar-6 partitioning defective 6 homolog alpha (C. elegans) (205245_at), score: 0.66 PHC3polyhomeotic homolog 3 (Drosophila) (215521_at), score: -0.64 PHF2PHD finger protein 2 (212726_at), score: -0.73 PIGLphosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis, class L (213889_at), score: -0.7 PIWIL1piwi-like 1 (Drosophila) (214868_at), score: 0.67 PKNOX1PBX/knotted 1 homeobox 1 (221883_at), score: 0.66 PROX1prospero homeobox 1 (207401_at), score: -0.7 RAB1ARAB1A, member RAS oncogene family (213440_at), score: 0.7 RAB40BRAB40B, member RAS oncogene family (217597_x_at), score: 0.64 RARRES1retinoic acid receptor responder (tazarotene induced) 1 (221872_at), score: -0.84 RASGRP2RAS guanyl releasing protein 2 (calcium and DAG-regulated) (214369_s_at), score: 0.62 RASSF2Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain family member 2 (203185_at), score: -0.8 RBM38RNA binding motif protein 38 (212430_at), score: 0.78 RCAN2regulator of calcineurin 2 (203498_at), score: -0.66 ROS1c-ros oncogene 1 , receptor tyrosine kinase (207569_at), score: 0.79 RPS6KA1ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 90kDa, polypeptide 1 (203379_at), score: 0.8 SECTM1secreted and transmembrane 1 (213716_s_at), score: -0.89 SELENBP1selenium binding protein 1 (214433_s_at), score: -0.66 SETD1ASET domain containing 1A (213202_at), score: 0.78 SLC15A1solute carrier family 15 (oligopeptide transporter), member 1 (211349_at), score: 0.68 SLC25A13solute carrier family 25, member 13 (citrin) (203775_at), score: 0.63 SNAI1snail homolog 1 (Drosophila) (219480_at), score: -0.74 SNAP25synaptosomal-associated protein, 25kDa (202508_s_at), score: -0.9 SYT1synaptotagmin I (203999_at), score: -0.8 SYT5synaptotagmin V (206161_s_at), score: 0.66 TBX2T-box 2 (40560_at), score: -0.64 TCP10t-complex 10 homolog (mouse) (207503_at), score: 0.73 THSD7Athrombospondin, type I, domain containing 7A (214920_at), score: -0.81 TLR3toll-like receptor 3 (206271_at), score: -0.69 TMPRSS6transmembrane protease, serine 6 (214955_at), score: 0.76 TRIM45tripartite motif-containing 45 (219923_at), score: 0.63 TRIM52tripartite motif-containing 52 (221897_at), score: -0.8 TSKUtsukushin (218245_at), score: -0.64 ULBP2UL16 binding protein 2 (221291_at), score: 0.68 YPEL1yippee-like 1 (Drosophila) (206063_x_at), score: 0.76 ZNF132zinc finger protein 132 (207402_at), score: -0.75 ZNF192zinc finger protein 192 (206579_at), score: -0.67 ZNF814zinc finger protein 814 (60794_f_at), score: -0.65
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485791.cel | 8 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486311.cel | 34 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486431.cel | 40 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485671.cel | 2 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |