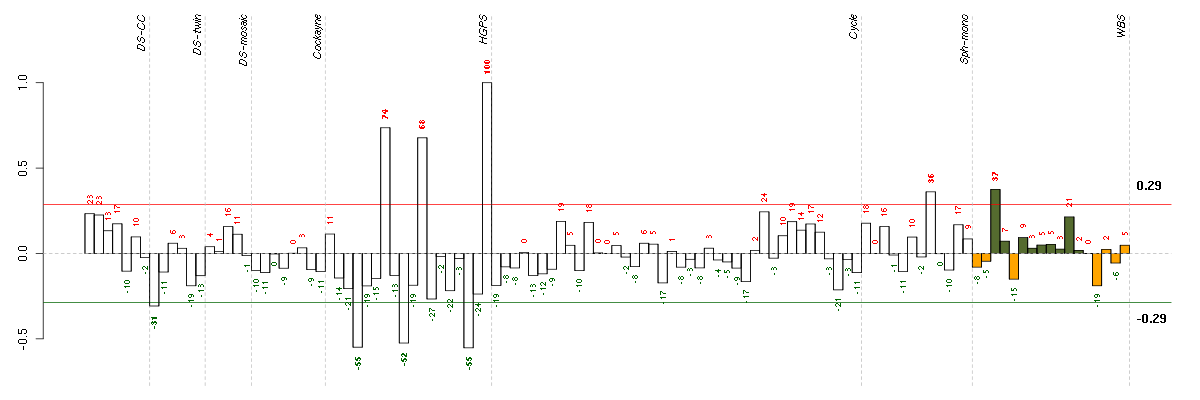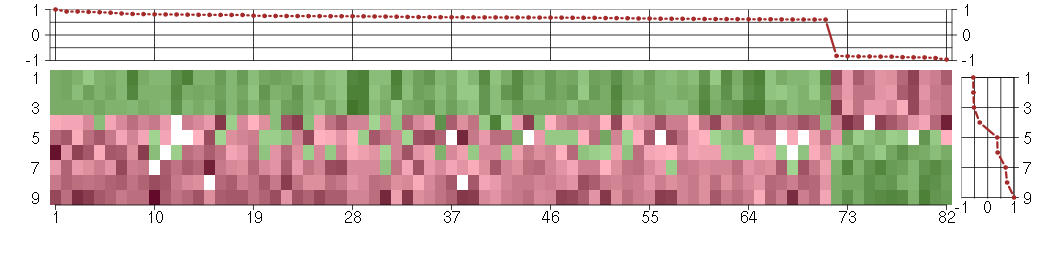

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

angiogenesis
Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
blood vessel development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the blood vessel over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood.
temperature homeostasis
A homeostatic process by which an organism modulates its internal body temperature.
fever
A rise in body temperature above the normal, often as a response to infection.
cytokine production
The appearance of a cytokine due to biosynthesis or secretion following a cellular stimulus, resulting in an increase in its intracellular or extracellular levels.
vasculature development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the vasculature over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
immune effector process
Any process of the immune system that occurs as part of an immune response.
activation of immune response
Any process that initiates an immune response.
immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
acute inflammatory response
Inflammation which comprises a rapid, short-lived, relatively uniform response to acute injury or antigenic challenge and is characterized by accumulations of fluid, plasma proteins, and granulocytic leukocytes. An acute inflammatory response occurs within a matter of minutes or hours, and either resolves within a few days or becomes a chronic inflammatory response.
activation of plasma proteins during acute inflammatory response
Any process activating plasma proteins via proteolysis during an acute inflammatory response.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
defense response
Reactions, triggered in response to the presence of a foreign body or the occurrence of an injury, which result in restriction of damage to the organism attacked or prevention/recovery from the infection caused by the attack.
acute-phase response
Process involving non-antibody proteins whose concentrations in the plasma increase in response to infection or injury of homeothermic animals.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
proteolysis
The hydrolysis of a peptide bond or bonds within a protein.
cell motion
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell.
chemotaxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism, or the directed growth of a cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis).
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
humoral immune response
An immune response mediated through a body fluid.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
cell surface receptor linked signal transduction
Any series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of an extracellular ligand to a receptor on the surface of the target cell.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
behavior
The specific actions or reactions of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Patterned activity of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions.
locomotory behavior
The specific movement from place to place of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Locomotion of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cell proliferation
The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
response to external stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an external stimulus.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cell migration
The orderly movement of cells from one site to another, often during the development of a multicellular organism or multicellular structure.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
neutrophil chemotaxis
The directed movement of a neutrophil cell, the most numerous polymorphonuclear leukocyte found in the blood, in response to an external stimulus, usually an infection or wounding.
leukocyte chemotaxis
The movement of a leukocyte in response to an external stimulus.
heat generation
Any homeostatic process by which an organism produces heat, thereby raising its internal temperature.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
interleukin-2 production
The appearance of interleukin-2 due to biosynthesis or secretion following a cellular stimulus, resulting in an increase in its intracellular or extracellular levels.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
locomotion
Self-propelled movement of a cell or organism from one location to another.
cytokine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cytokines, any of a group of proteins that function to control the survival, growth and differentiation of tissues and cells, and which have autocrine and paracrine activity.
interleukin-2 biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of interleukin-2.
cytokine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving cytokines, any of a group of proteins that function to control the survival, growth and differentiation of tissues and cells, and which have autocrine and paracrine activity.
regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation.
response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
taxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to an external stimulus.
homeostatic process
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal equilibrium.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
blood vessel morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of blood vessels are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
anatomical structure formation
The process pertaining to the initial formation of an anatomical structure from unspecified parts. This process begins with the specific processes that contribute to the appearance of the discrete structure and ends when the structural rudiment is recognizable. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cell motility
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell that results in translocation of the cell from one place to another.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
leukocyte migration
The movement of leukocytes within or between different tissues and organs of the body.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
localization of cell
Any process by which a cell is transported to, and/or maintained in, a specific location.
cell chemotaxis
The directed movement of a motile cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis).
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
immune effector process
Any process of the immune system that occurs as part of an immune response.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
cell motility
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell that results in translocation of the cell from one place to another.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation.
anatomical structure formation
The process pertaining to the initial formation of an anatomical structure from unspecified parts. This process begins with the specific processes that contribute to the appearance of the discrete structure and ends when the structural rudiment is recognizable. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
taxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to an external stimulus.
chemotaxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism, or the directed growth of a cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis).
cell motion
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
activation of immune response
Any process that initiates an immune response.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.
interleukin-2 biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of interleukin-2.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
cell chemotaxis
The directed movement of a motile cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis).
leukocyte migration
The movement of leukocytes within or between different tissues and organs of the body.
leukocyte chemotaxis
The movement of a leukocyte in response to an external stimulus.
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
taxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to an external stimulus.
temperature homeostasis
A homeostatic process by which an organism modulates its internal body temperature.
cytokine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cytokines, any of a group of proteins that function to control the survival, growth and differentiation of tissues and cells, and which have autocrine and paracrine activity.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
cytokine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cytokines, any of a group of proteins that function to control the survival, growth and differentiation of tissues and cells, and which have autocrine and paracrine activity.
angiogenesis
Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels.
blood vessel morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of blood vessels are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood.
activation of plasma proteins during acute inflammatory response
Any process activating plasma proteins via proteolysis during an acute inflammatory response.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.
fever
A rise in body temperature above the normal, often as a response to infection.

extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
all
This term is the most general term possible
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.

protein binding
Interacting selectively with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
pattern binding
Interacting selectively with a repeating or polymeric structure, such as a polysaccharide or peptidoglycan.
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
receptor binding
Interacting selectively with one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function.
cytokine activity
Functions to control the survival, growth, differentiation and effector function of tissues and cells.
interleukin-1 receptor binding
Interacting selectively with the interleukin-1 receptor.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
growth factor activity
The function that stimulates a cell to grow or proliferate. Most growth factors have other actions besides the induction of cell growth or proliferation.
all
This term is the most general term possible
ABCA8ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 8 (204719_at), score: 1 ADAMTSL3ADAMTS-like 3 (213974_at), score: 0.61 ADMadrenomedullin (202912_at), score: -0.83 AKR1C3aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C3 (3-alpha hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, type II) (209160_at), score: 0.75 ANXA3annexin A3 (209369_at), score: 0.68 ARHGAP29Rho GTPase activating protein 29 (203910_at), score: 0.62 BMP6bone morphogenetic protein 6 (206176_at), score: 0.68 BNC2basonuclin 2 (220272_at), score: 0.8 C3complement component 3 (217767_at), score: 0.79 C8orf84chromosome 8 open reading frame 84 (214725_at), score: 0.67 CD200CD200 molecule (209583_s_at), score: 0.92 CD34CD34 molecule (209543_s_at), score: 0.64 CD55CD55 molecule, decay accelerating factor for complement (Cromer blood group) (201925_s_at), score: 0.8 CFHcomplement factor H (213800_at), score: 0.91 CFHR1complement factor H-related 1 (215388_s_at), score: 0.87 CHRDL1chordin-like 1 (209763_at), score: 0.7 CLDN1claudin 1 (218182_s_at), score: 0.61 CMAHcytidine monophosphate-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase (CMP-N-acetylneuraminate monooxygenase) pseudogene (205518_s_at), score: 0.74 COL15A1collagen, type XV, alpha 1 (203477_at), score: 0.69 CUGBP2CUG triplet repeat, RNA binding protein 2 (202158_s_at), score: 0.79 CXCL1chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (melanoma growth stimulating activity, alpha) (204470_at), score: 0.89 CXCL6chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 6 (granulocyte chemotactic protein 2) (206336_at), score: 0.74 DPYSL3dihydropyrimidinase-like 3 (201430_s_at), score: 0.69 DSG2desmoglein 2 (217901_at), score: 0.74 EDN1endothelin 1 (218995_s_at), score: 0.66 EIF1AYeukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A, Y-linked (204409_s_at), score: 0.63 ENPEPglutamyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase A) (204844_at), score: -0.84 ERGv-ets erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogene homolog (avian) (213541_s_at), score: 0.74 FBLN1fibulin 1 (202995_s_at), score: 0.69 FGL2fibrinogen-like 2 (204834_at), score: 0.81 FOXO1forkhead box O1 (202724_s_at), score: 0.67 FUT8fucosyltransferase 8 (alpha (1,6) fucosyltransferase) (203988_s_at), score: 0.63 GALNT12UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 12 (GalNAc-T12) (218885_s_at), score: 0.68 GPR116G protein-coupled receptor 116 (212950_at), score: -0.88 GPR126G protein-coupled receptor 126 (213094_at), score: 0.79 GPR4G protein-coupled receptor 4 (206236_at), score: 0.74 GPRC5BG protein-coupled receptor, family C, group 5, member B (203632_s_at), score: 0.66 GSTT2glutathione S-transferase theta 2 (205439_at), score: 0.65 HGFhepatocyte growth factor (hepapoietin A; scatter factor) (209960_at), score: 0.69 HRH1histamine receptor H1 (205579_at), score: 0.62 HSPB8heat shock 22kDa protein 8 (221667_s_at), score: -0.84 IFI27interferon, alpha-inducible protein 27 (202411_at), score: 0.82 IL18interleukin 18 (interferon-gamma-inducing factor) (206295_at), score: 0.62 IL1Ainterleukin 1, alpha (210118_s_at), score: 0.72 IL1Binterleukin 1, beta (39402_at), score: 0.64 IL8interleukin 8 (202859_x_at), score: 0.7 ITGA8integrin, alpha 8 (214265_at), score: -0.82 KCTD12potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 12 (212192_at), score: 0.83 KIAA0247KIAA0247 (202181_at), score: 0.69 KLF5Kruppel-like factor 5 (intestinal) (209212_s_at), score: 0.62 LAMA4laminin, alpha 4 (202202_s_at), score: 0.74 LAMC2laminin, gamma 2 (202267_at), score: 0.84 LIPGlipase, endothelial (219181_at), score: 0.81 LTBP2latent transforming growth factor beta binding protein 2 (204682_at), score: 0.72 MMP2matrix metallopeptidase 2 (gelatinase A, 72kDa gelatinase, 72kDa type IV collagenase) (201069_at), score: 0.62 MYH10myosin, heavy chain 10, non-muscle (212372_at), score: 0.73 MYLKmyosin light chain kinase (202555_s_at), score: -0.88 NFIBnuclear factor I/B (209289_at), score: 0.69 NOX4NADPH oxidase 4 (219773_at), score: 0.92 PARP3poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase family, member 3 (209940_at), score: -0.9 PDZRN4PDZ domain containing ring finger 4 (220595_at), score: 0.62 PID1phosphotyrosine interaction domain containing 1 (219093_at), score: 0.65 PLXNA2plexin A2 (213030_s_at), score: 0.75 PPM1Hprotein phosphatase 1H (PP2C domain containing) (212686_at), score: 0.61 PTGESprostaglandin E synthase (210367_s_at), score: 0.7 RAC2ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 2 (rho family, small GTP binding protein Rac2) (213603_s_at), score: -0.85 RPP25ribonuclease P/MRP 25kDa subunit (219143_s_at), score: -0.96 SCRN1secernin 1 (201462_at), score: -0.85 SERPINF1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade F (alpha-2 antiplasmin, pigment epithelium derived factor), member 1 (202283_at), score: 0.7 SLC39A8solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 8 (209267_s_at), score: 0.79 SOX17SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 17 (219993_at), score: 0.74 SOX4SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 4 (201417_at), score: 0.6 THBS2thrombospondin 2 (203083_at), score: 0.64 TLR4toll-like receptor 4 (221060_s_at), score: 0.69 TNFAIP6tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 6 (206026_s_at), score: 0.73 TNFAIP8tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 8 (210260_s_at), score: 0.76 TPK1thiamin pyrophosphokinase 1 (221218_s_at), score: 0.61 TSPYL5TSPY-like 5 (213122_at), score: 0.66 UAP1L1UDP-N-acteylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase 1-like 1 (214755_at), score: -0.87 ZFHX4zinc finger homeobox 4 (219779_at), score: 0.79 ZFPM2zinc finger protein, multitype 2 (219778_at), score: 0.68 ZNF323zinc finger protein 323 (222016_s_at), score: 0.71
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690432.cel | 16 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG10750 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690231.cel | 4 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG10750 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690336.cel | 9 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG10750 |
| 1Twin.CEL | 1 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956418.cel | 13 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| 1104_CNTL.CEL | 3 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | none | WBS 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690352.cel | 11 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11498 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690272.cel | 7 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11498 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690480.cel | 18 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11498 |