
Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

digestion
The whole of the physical, chemical, and biochemical processes carried out by multicellular organisms to break down ingested nutrients into components that may be easily absorbed and directed into metabolism.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
all
This term is the most general term possible


calcium ion binding
Interacting selectively with calcium ions (Ca2+).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
serine-type endopeptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of internal, alpha-peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
endopeptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of internal, alpha-peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain.
serine-type peptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
peptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a peptide bond. A peptide bond is a covalent bond formed when the carbon atom from the carboxyl group of one amino acid shares electrons with the nitrogen atom from the amino group of a second amino acid.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
metal ion binding
Interacting selectively with any metal ion.
peptidase activity, acting on L-amino acid peptides
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds formed between L-amino acids.
hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. Hydrolase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 3.
serine hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a substrate by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
ion binding
Interacting selectively with ions, charged atoms or groups of atoms.
cation binding
Interacting selectively with cations, charged atoms or groups of atoms with a net positive charge.
all
This term is the most general term possible
calcium ion binding
Interacting selectively with calcium ions (Ca2+).
serine-type peptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
serine-type endopeptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of internal, alpha-peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04080 | 3.262e-02 | 0.1827 | 3 | 83 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction |
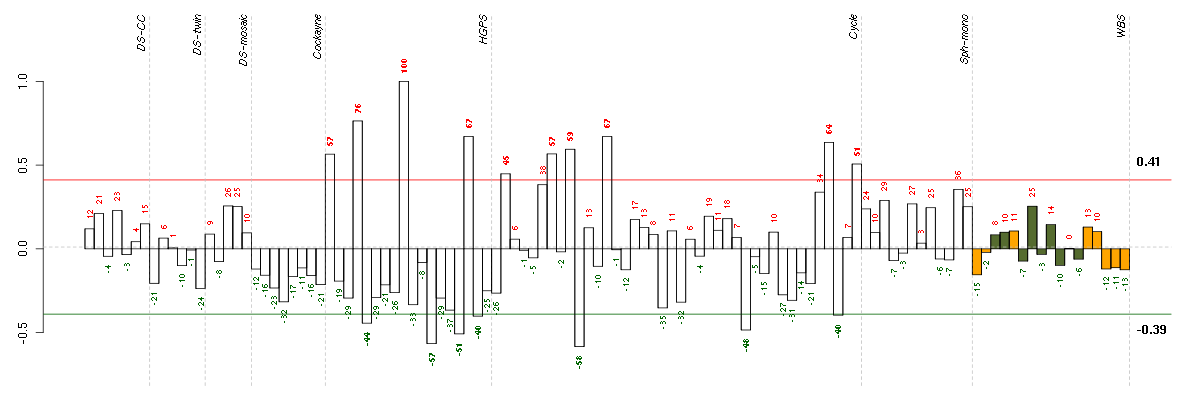
MFAP3Lmicrofibrillar-associated protein 3-like (205442_at), score: 0.75 NEFMneurofilament, medium polypeptide (205113_at), score: 1 NRXN3neurexin 3 (205795_at), score: 0.91 PCDH9protocadherin 9 (219737_s_at), score: 0.9 PRSS1protease, serine, 1 (trypsin 1) (216470_x_at), score: 0.85 PRSS2protease, serine, 2 (trypsin 2) (205402_x_at), score: 0.77 PRSS3protease, serine, 3 (207463_x_at), score: 0.9 TRY6trypsinogen C (215395_x_at), score: 0.81 UGDHUDP-glucose dehydrogenase (203343_at), score: 0.72
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485831.cel | 10 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690360.cel | 12 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690416.cel | 15 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486191.cel | 28 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690248.cel | 5 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11513 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690472.cel | 17 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM00038C |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486391.cel | 38 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485671.cel | 2 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486431.cel | 40 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690199.cel | 1 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485771.cel | 7 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485811.cel | 9 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486371.cel | 37 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485891.cel | 13 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690432.cel | 16 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG10750 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690231.cel | 4 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG10750 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690336.cel | 9 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG10750 |