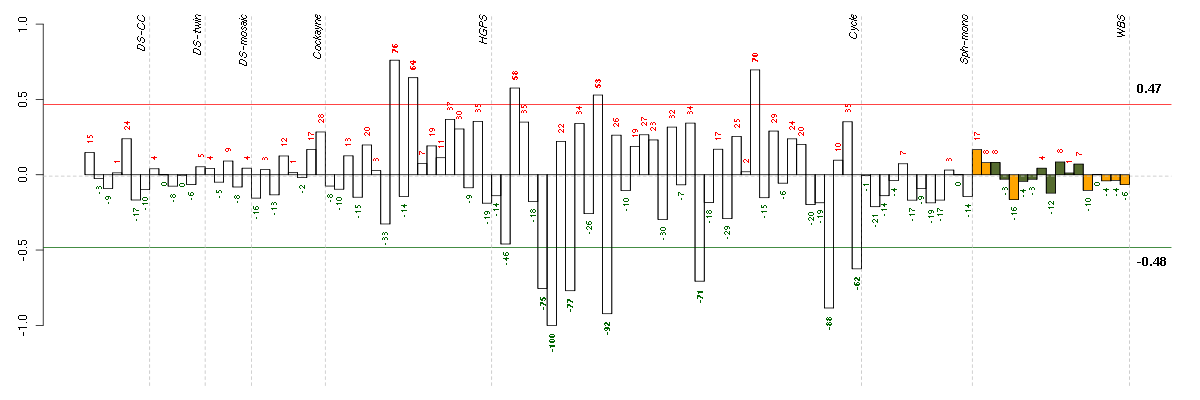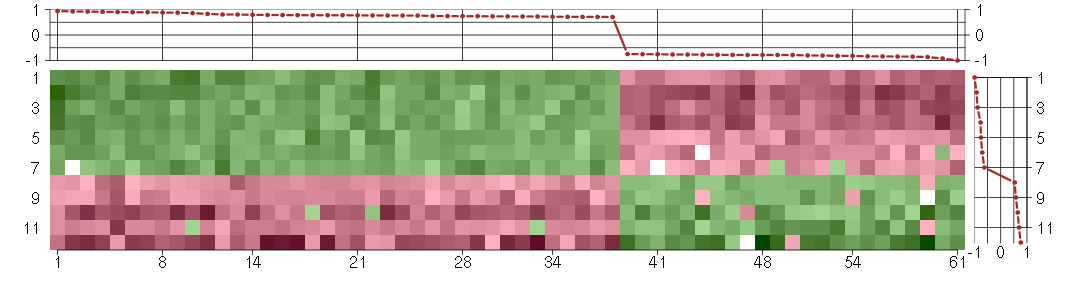

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

cell morphogenesis
The developmental process by which the size or shape of a cell is generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation
The change in form (cell shape and size) that occurs when relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history.
cell adhesion
The attachment of a cell, either to another cell or to an underlying substrate such as the extracellular matrix, via cell adhesion molecules.
homophilic cell adhesion
The attachment of an adhesion molecule in one cell to an identical molecule in an adjacent cell.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
cell-cell adhesion
The attachment of one cell to another cell via adhesion molecules.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
biological adhesion
The attachment of a cell or organism to a substrate or other organism.
cell projection organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
neurite development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the neurite over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The neurite is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
cellular structure morphogenesis
The process by which cellular structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cell part morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell part are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
neuron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation
The process by which the structures of a neuron are generated and organized. This process occurs while the initially relatively unspecialized cell is acquiring the specialized features of a neuron.
generation of neurons
The process by which nerve cells are generated. This includes the production of neuroblasts and their differentiation into neurons.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
neurite morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of neurites are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. A neurite is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cell projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell adhesion
The attachment of a cell, either to another cell or to an underlying substrate such as the extracellular matrix, via cell adhesion molecules.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
cellular structure morphogenesis
The process by which cellular structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cellular structure morphogenesis
The process by which cellular structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation
The process by which the structures of a neuron are generated and organized. This process occurs while the initially relatively unspecialized cell is acquiring the specialized features of a neuron.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation
The change in form (cell shape and size) that occurs when relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history.
cell projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
neurite morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of neurites are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. A neurite is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites.
neuron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
neurite development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the neurite over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The neurite is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites.
cell projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
neurite morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of neurites are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. A neurite is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites.


ATN1atrophin 1 (40489_at), score: 0.73 BTBD2BTB (POZ) domain containing 2 (207722_s_at), score: 0.74 C4orf43chromosome 4 open reading frame 43 (218513_at), score: -0.84 CASC3cancer susceptibility candidate 3 (207842_s_at), score: 0.73 CDC42BPBCDC42 binding protein kinase beta (DMPK-like) (217849_s_at), score: 0.77 CDH13cadherin 13, H-cadherin (heart) (204726_at), score: -0.78 CDH6cadherin 6, type 2, K-cadherin (fetal kidney) (205532_s_at), score: -0.75 CICcapicua homolog (Drosophila) (212784_at), score: 0.8 CITcitron (rho-interacting, serine/threonine kinase 21) (212801_at), score: 0.77 CIZ1CDKN1A interacting zinc finger protein 1 (205516_x_at), score: 0.76 CNOT3CCR4-NOT transcription complex, subunit 3 (203239_s_at), score: 0.79 CRTC3CREB regulated transcription coactivator 3 (218648_at), score: 0.94 DNAJB9DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily B, member 9 (202843_at), score: -0.78 FAM18Bfamily with sequence similarity 18, member B (218446_s_at), score: -0.81 FLJ12529pre-mRNA cleavage factor I, 59 kDa subunit (217866_at), score: 0.88 FOXK2forkhead box K2 (203064_s_at), score: 0.8 GMCL1germ cell-less homolog 1 (Drosophila) (218458_at), score: -0.82 HNRNPH2heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein H2 (H') (201132_at), score: -0.78 HNRNPUL1heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U-like 1 (209675_s_at), score: 0.76 HSD17B6hydroxysteroid (17-beta) dehydrogenase 6 homolog (mouse) (37512_at), score: -0.78 HSPA12Aheat shock 70kDa protein 12A (214434_at), score: 0.86 KAL1Kallmann syndrome 1 sequence (205206_at), score: -0.92 LARP4La ribonucleoprotein domain family, member 4 (214155_s_at), score: -0.77 LOC100132540similar to LOC339047 protein (214870_x_at), score: 0.89 LOC339047hypothetical protein LOC339047 (221501_x_at), score: 0.92 LOC391132similar to hCG2041276 (216177_at), score: -0.77 LOC399491LOC399491 protein (214035_x_at), score: 0.75 LRDDleucine-rich repeats and death domain containing (221640_s_at), score: 0.71 LRRN3leucine rich repeat neuronal 3 (209841_s_at), score: -0.86 MAP1Smicrotubule-associated protein 1S (218522_s_at), score: 0.78 MAP7D1MAP7 domain containing 1 (217943_s_at), score: 0.71 MAST2microtubule associated serine/threonine kinase 2 (211593_s_at), score: 0.78 MFAP3Lmicrofibrillar-associated protein 3-like (205442_at), score: -0.84 NBL1neuroblastoma, suppression of tumorigenicity 1 (37005_at), score: 0.83 NEFMneurofilament, medium polypeptide (205113_at), score: -1 NFATC4nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 4 (205897_at), score: 0.72 NPIPnuclear pore complex interacting protein (204538_x_at), score: 0.92 NRXN3neurexin 3 (205795_at), score: -0.77 OLFML2Bolfactomedin-like 2B (213125_at), score: 0.9 PCDH9protocadherin 9 (219737_s_at), score: -0.78 PCDHGA1protocadherin gamma subfamily A, 1 (209079_x_at), score: 0.77 PIP5K1Cphosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase, type I, gamma (212518_at), score: 0.79 POLSpolymerase (DNA directed) sigma (202466_at), score: 0.73 POM121POM121 membrane glycoprotein (rat) (212178_s_at), score: 0.74 PRMT3protein arginine methyltransferase 3 (213320_at), score: -0.82 REREarginine-glutamic acid dipeptide (RE) repeats (200940_s_at), score: 0.77 RNF11ring finger protein 11 (208924_at), score: -0.78 RNF220ring finger protein 220 (219988_s_at), score: 0.89 RPL18AP6ribosomal protein L18a pseudogene 6 (216383_at), score: -0.84 RPS17P5ribosomal protein S17 pseudogene 5 (216348_at), score: -0.8 SCAMP4secretory carrier membrane protein 4 (213244_at), score: 0.91 SF1splicing factor 1 (208313_s_at), score: 0.88 SLC33A1solute carrier family 33 (acetyl-CoA transporter), member 1 (203165_s_at), score: -0.76 SOLHsmall optic lobes homolog (Drosophila) (204275_at), score: 0.76 STRN4striatin, calmodulin binding protein 4 (217903_at), score: 0.73 TICAM2toll-like receptor adaptor molecule 2 (214658_at), score: -0.85 TXLNAtaxilin alpha (212300_at), score: 0.74 VPS37Bvacuolar protein sorting 37 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (221704_s_at), score: 0.71 WDR6WD repeat domain 6 (217734_s_at), score: 0.78 WDR62WD repeat domain 62 (215218_s_at), score: 0.71 YTHDC2YTH domain containing 2 (213077_at), score: -0.75
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485771.cel | 7 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485891.cel | 13 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486371.cel | 37 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485811.cel | 9 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485751.cel | 6 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486091.cel | 23 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486431.cel | 40 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485871.cel | 12 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485691.cel | 3 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690344.cel | 10 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM00038C |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486211.cel | 29 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690304.cel | 8 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GMO8398C |