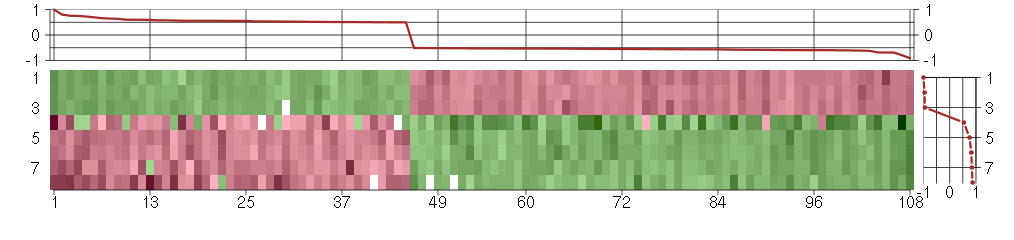

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

cell morphogenesis
The developmental process by which the size or shape of a cell is generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation
The change in form (cell shape and size) that occurs when relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
cellular aldehyde metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving aldehydes, any organic compound with the formula R-CH=O, as carried out by individual cells.
cell motion
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state.
axonogenesis
Generation of a long process of a neuron, that carries efferent (outgoing) action potentials from the cell body towards target cells.
axon guidance
The process by which the migration of an axon growth cone is directed to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
cell projection organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
neurite development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the neurite over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The neurite is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
cellular structure morphogenesis
The process by which cellular structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cell part morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell part are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
neuron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation
The process by which the structures of a neuron are generated and organized. This process occurs while the initially relatively unspecialized cell is acquiring the specialized features of a neuron.
generation of neurons
The process by which nerve cells are generated. This includes the production of neuroblasts and their differentiation into neurons.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
neurite morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of neurites are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. A neurite is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cell projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
localization of cell
Any process by which a cell is transported to, and/or maintained in, a specific location.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
cellular structure morphogenesis
The process by which cellular structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cellular structure morphogenesis
The process by which cellular structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
cell motion
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell.
cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation
The process by which the structures of a neuron are generated and organized. This process occurs while the initially relatively unspecialized cell is acquiring the specialized features of a neuron.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation
The change in form (cell shape and size) that occurs when relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history.
cell projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
neurite morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of neurites are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. A neurite is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites.
neuron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
neurite development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the neurite over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The neurite is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites.
cell projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
neurite morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of neurites are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. A neurite is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites.
axon guidance
The process by which the migration of an axon growth cone is directed to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues.


molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
aldehyde dehydrogenase (NAD) activity
Catalysis of the reaction: an aldehyde + NAD+ + H2O = an acid + NADH + H+.
aldo-keto reductase activity
Catalysis of the NADPH-dependent reduction of carbonyl compounds.
oxidoreductase activity
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction, a reversible chemical reaction in which the oxidation state of an atom or atoms within a molecule is altered. One substrate acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and becomes oxidized, while the other acts as hydrogen or electron acceptor and becomes reduced.
steroid dehydrogenase activity
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which one substrate is a sterol derivative.
oxidoreductase activity, acting on CH-OH group of donors
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-OH group act as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces a hydrogen or electron acceptor.
oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-OH group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces NAD+ or NADP.
oxidoreductase activity, acting on the aldehyde or oxo group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which an aldehyde or ketone (oxo) group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces NAD or NADP.
oxidoreductase activity, acting on the aldehyde or oxo group of donors
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which an aldehyde or ketone (oxo) group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces a hydrogen or electron acceptor.
oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-CH group of donors
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-CH group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces a hydrogen or electron acceptor.
oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-CH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-CH group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces NAD or NADP.
steroid dehydrogenase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-OH group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces NAD+ or NADP, and in which one substrate is a sterol derivative.
trans-1,2-dihydrobenzene-1,2-diol dehydrogenase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: NADP+ + trans-1,2-dihydrobenzene-1,2-diol = NADPH + catechol.
all
This term is the most general term possible
steroid dehydrogenase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-OH group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces NAD+ or NADP, and in which one substrate is a sterol derivative.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00980 | 1.282e-02 | 0.5293 | 5 | 37 | Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 |
ABLIM1actin binding LIM protein 1 (200965_s_at), score: -0.52 AEBP1AE binding protein 1 (201792_at), score: -0.56 AKAP12A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein 12 (210517_s_at), score: -0.52 AKAP2A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein 2 (202759_s_at), score: -0.55 AKR1B10aldo-keto reductase family 1, member B10 (aldose reductase) (206561_s_at), score: 0.8 AKR1C1aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C1 (dihydrodiol dehydrogenase 1; 20-alpha (3-alpha)-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase) (204151_x_at), score: 0.52 AKR1C2aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C2 (dihydrodiol dehydrogenase 2; bile acid binding protein; 3-alpha hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, type III) (209699_x_at), score: 0.55 AKR1C3aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C3 (3-alpha hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, type II) (209160_at), score: 0.55 ALDH1A1aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family, member A1 (212224_at), score: -0.51 ALDH3A1aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, memberA1 (205623_at), score: 0.53 ALDH3A2aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, member A2 (202053_s_at), score: 0.53 ARHGAP5Rho GTPase activating protein 5 (217936_at), score: -0.54 ARMCX1armadillo repeat containing, X-linked 1 (218694_at), score: -0.55 BMP7bone morphogenetic protein 7 (209590_at), score: 0.6 C14orf169chromosome 14 open reading frame 169 (219526_at), score: -0.59 C20orf39chromosome 20 open reading frame 39 (219310_at), score: 0.56 CAND2cullin-associated and neddylation-dissociated 2 (putative) (213547_at), score: -0.56 CD24CD24 molecule (209771_x_at), score: 0.53 CD248CD248 molecule, endosialin (219025_at), score: -0.54 CDKN1Acyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (p21, Cip1) (202284_s_at), score: -0.54 CELSR1cadherin, EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 1 (flamingo homolog, Drosophila) (41660_at), score: 0.66 CELSR3cadherin, EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 3 (flamingo homolog, Drosophila) (40020_at), score: 0.69 COL3A1collagen, type III, alpha 1 (215076_s_at), score: -0.59 DGKDdiacylglycerol kinase, delta 130kDa (208072_s_at), score: 0.64 DLX4distal-less homeobox 4 (208216_at), score: 0.51 DNAJC7DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 7 (202416_at), score: 0.51 EIF4A1eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A, isoform 1 (211787_s_at), score: 0.51 EMP1epithelial membrane protein 1 (201325_s_at), score: -0.59 EPHX1epoxide hydrolase 1, microsomal (xenobiotic) (202017_at), score: 0.5 FAM174Bfamily with sequence similarity 174, member B (51158_at), score: -0.69 FAM65Bfamily with sequence similarity 65, member B (209829_at), score: -0.58 FCGR2AFc fragment of IgG, low affinity IIa, receptor (CD32) (203561_at), score: 0.57 FGF13fibroblast growth factor 13 (205110_s_at), score: 0.56 FLT1fms-related tyrosine kinase 1 (vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor receptor) (222033_s_at), score: -0.56 FOXG1forkhead box G1 (206018_at), score: 0.55 GAL3ST4galactose-3-O-sulfotransferase 4 (219815_at), score: -0.62 GALCgalactosylceramidase (204417_at), score: -0.59 GAS1growth arrest-specific 1 (204457_s_at), score: -0.52 GCLCglutamate-cysteine ligase, catalytic subunit (202923_s_at), score: 0.5 GRAMD3GRAM domain containing 3 (218706_s_at), score: -0.58 GREM1gremlin 1, cysteine knot superfamily, homolog (Xenopus laevis) (218469_at), score: -0.91 HEY1hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif 1 (44783_s_at), score: 0.52 HHIPL2HHIP-like 2 (220283_at), score: 0.5 HSD17B12hydroxysteroid (17-beta) dehydrogenase 12 (217869_at), score: -0.55 HYPKHuntingtin interacting protein K (218680_x_at), score: 0.5 IGSF3immunoglobulin superfamily, member 3 (202421_at), score: 0.73 IL23Ainterleukin 23, alpha subunit p19 (211796_s_at), score: -0.55 IPWimprinted in Prader-Willi syndrome (non-protein coding) (221974_at), score: -0.56 ISL1ISL LIM homeobox 1 (206104_at), score: -0.53 KYNUkynureninase (L-kynurenine hydrolase) (217388_s_at), score: 1 LAPTM5lysosomal multispanning membrane protein 5 (201721_s_at), score: 0.5 LEF1lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (221558_s_at), score: 0.75 LMO7LIM domain 7 (202674_s_at), score: -0.53 LOC728855hypothetical LOC728855 (222001_x_at), score: 0.56 LPPR4plasticity related gene 1 (213496_at), score: -0.53 LTBP2latent transforming growth factor beta binding protein 2 (204682_at), score: -0.53 LUMlumican (201744_s_at), score: -0.79 MEIS3P1Meis homeobox 3 pseudogene 1 (214077_x_at), score: -0.53 MLLT3myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia (trithorax homolog, Drosophila); translocated to, 3 (204918_s_at), score: -0.56 MOXD1monooxygenase, DBH-like 1 (209708_at), score: -0.53 MPPED2metallophosphoesterase domain containing 2 (205413_at), score: 0.75 MYO1Bmyosin IB (212364_at), score: -0.69 NEK7NIMA (never in mitosis gene a)-related kinase 7 (212530_at), score: -0.52 NPTX1neuronal pentraxin I (204684_at), score: 0.63 OXTRoxytocin receptor (206825_at), score: -0.53 PCLOpiccolo (presynaptic cytomatrix protein) (213558_at), score: 0.56 PCTK2PCTAIRE protein kinase 2 (221918_at), score: -0.52 PDGFRAplatelet-derived growth factor receptor, alpha polypeptide (203131_at), score: -0.59 PEX5peroxisomal biogenesis factor 5 (203244_at), score: 0.51 PFDN2prefoldin subunit 2 (218336_at), score: 0.56 PLAGL1pleiomorphic adenoma gene-like 1 (209318_x_at), score: -0.53 PLCB1phospholipase C, beta 1 (phosphoinositide-specific) (213222_at), score: -0.56 PLCG1phospholipase C, gamma 1 (202789_at), score: 0.5 PLK2polo-like kinase 2 (Drosophila) (201939_at), score: 0.51 PSTPIP2proline-serine-threonine phosphatase interacting protein 2 (219938_s_at), score: -0.59 RARBretinoic acid receptor, beta (205080_at), score: 0.53 RECKreversion-inducing-cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs (205407_at), score: -0.56 RGS4regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (204337_at), score: -0.53 RIPK4receptor-interacting serine-threonine kinase 4 (221215_s_at), score: 0.6 RP2retinitis pigmentosa 2 (X-linked recessive) (205191_at), score: -0.53 SAMD4Asterile alpha motif domain containing 4A (212845_at), score: -0.58 SCRIBscribbled homolog (Drosophila) (212556_at), score: -0.53 SERPINB7serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 7 (206421_s_at), score: -0.51 SERPINB9serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 9 (209723_at), score: -0.56 SH3BGRSH3 domain binding glutamic acid-rich protein (204979_s_at), score: 0.51 SLC30A1solute carrier family 30 (zinc transporter), member 1 (212907_at), score: -0.6 SLC38A4solute carrier family 38, member 4 (220786_s_at), score: -0.58 SPANXCSPANX family, member C (220217_x_at), score: 0.6 SULF1sulfatase 1 (212353_at), score: -0.59 SULT1A1sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1A, phenol-preferring, member 1 (203615_x_at), score: 0.58 SULT1A2sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1A, phenol-preferring, member 2 (207122_x_at), score: 0.54 SYNGR1synaptogyrin 1 (210613_s_at), score: -0.6 TBXA2Rthromboxane A2 receptor (336_at), score: -0.61 TCF7L2transcription factor 7-like 2 (T-cell specific, HMG-box) (212761_at), score: -0.56 TEStestis derived transcript (3 LIM domains) (202720_at), score: -0.68 TGFB2transforming growth factor, beta 2 (220407_s_at), score: 0.57 TGIF2TGFB-induced factor homeobox 2 (216262_s_at), score: 0.51 THBS2thrombospondin 2 (203083_at), score: -0.58 TMEM30Atransmembrane protein 30A (217743_s_at), score: -0.55 TNS1tensin 1 (221748_s_at), score: -0.59 TRPC3transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 3 (210814_at), score: 0.56 TSPYL5TSPY-like 5 (213122_at), score: -0.61 TUBB6tubulin, beta 6 (209191_at), score: -0.51 ULK2unc-51-like kinase 2 (C. elegans) (204062_s_at), score: -0.55 VAV3vav 3 guanine nucleotide exchange factor (218807_at), score: 0.59 VGLL3vestigial like 3 (Drosophila) (220327_at), score: -0.57 ZNF215zinc finger protein 215 (220214_at), score: -0.54 ZNF518Azinc finger protein 518A (204291_at), score: -0.54
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956178.cel | 6 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956824.cel | 24 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956358.cel | 10 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
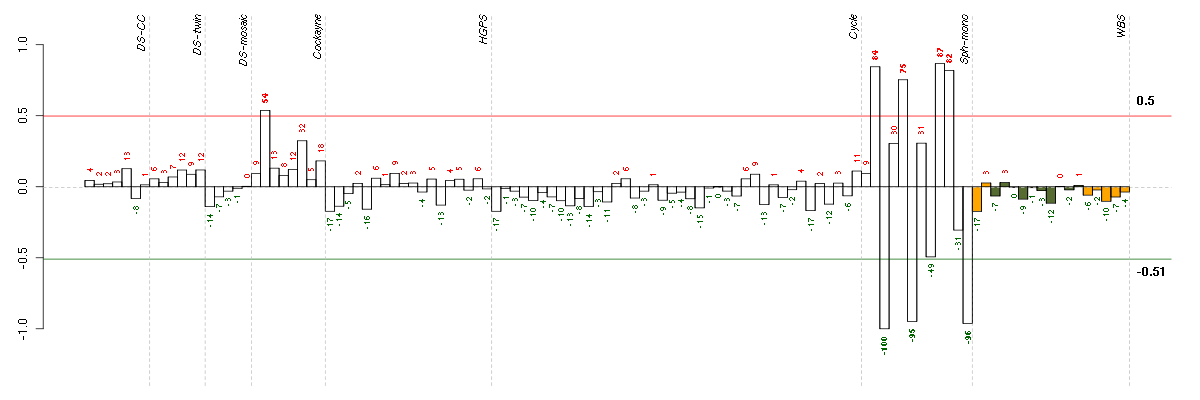
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949579.cel | 2 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | none | CSB |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956321.cel | 9 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956614.cel | 18 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956138.cel | 4 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956457.cel | 14 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |