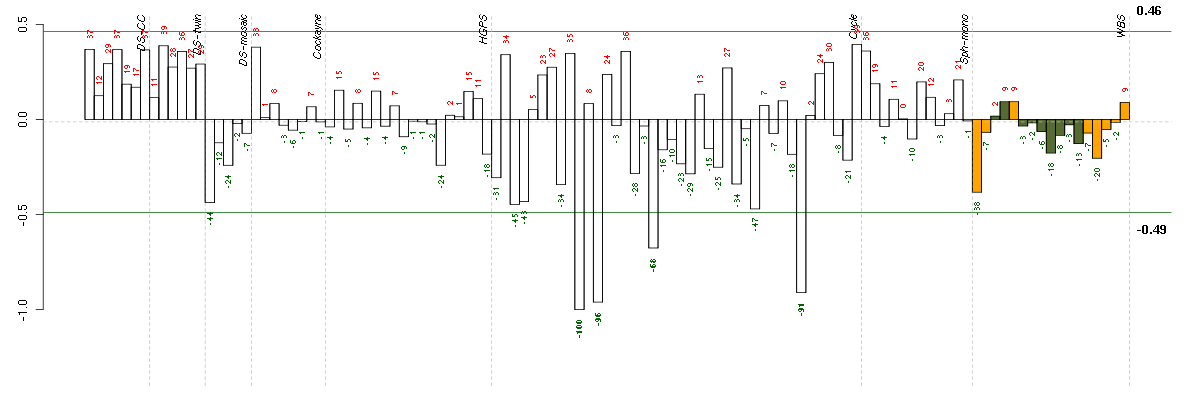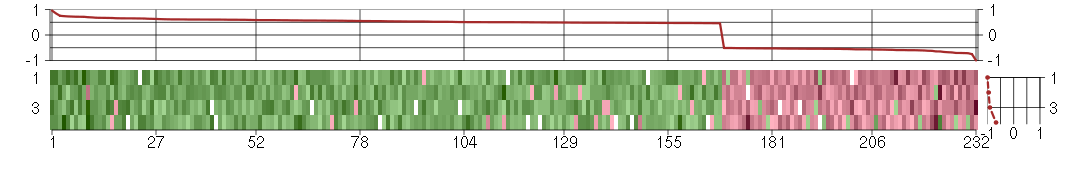

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
embryonic development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an embryo from its formation until the end of its embryonic life stage. The end of the embryonic stage is organism-specific. For example, for mammals, the process would begin with zygote formation and end with birth. For insects, the process would begin at zygote formation and end with larval hatching. For plant zygotic embryos, this would be from zygote formation to the end of seed dormancy. For plant vegetative embryos, this would be from the initial determination of the cell or group of cells to form an embryo until the point when the embryo becomes independent of the parent plant.
sensory organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of sensory organs over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
heart development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the heart over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
embryonic heart tube development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the embryonic heart tube over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
tube development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tube over time, from its initial formation to a mature structure. Epithelial and endothelial tubes transport gases, liquids and cells from one site to another and form the basic structure of many organs and tissues including lung and trachea, kidney, the mammary gland, the vascular system and the gastrointestinal and urinary-genital tracts.
ear development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the ear over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The ear is the sense organ in vertebrates that is specialized for the detection of sound, and the maintenance of balance. Includes the outer ear and middle ear, which collect and transmit sound waves; and the inner ear, which contains the organs of balance and (except in fish) hearing. Also includes the pinna, the visible part of the outer ear, present in some mammals.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
inner ear development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the inner ear over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
all
This term is the most general term possible
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
embryonic development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an embryo from its formation until the end of its embryonic life stage. The end of the embryonic stage is organism-specific. For example, for mammals, the process would begin with zygote formation and end with birth. For insects, the process would begin at zygote formation and end with larval hatching. For plant zygotic embryos, this would be from zygote formation to the end of seed dormancy. For plant vegetative embryos, this would be from the initial determination of the cell or group of cells to form an embryo until the point when the embryo becomes independent of the parent plant.
tube development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tube over time, from its initial formation to a mature structure. Epithelial and endothelial tubes transport gases, liquids and cells from one site to another and form the basic structure of many organs and tissues including lung and trachea, kidney, the mammary gland, the vascular system and the gastrointestinal and urinary-genital tracts.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
embryonic heart tube development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the embryonic heart tube over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic heart tube development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the embryonic heart tube over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
inner ear development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the inner ear over time, from its formation to the mature structure.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
actin cytoskeleton
The part of the cytoskeleton (the internal framework of a cell) composed of actin and associated proteins. Includes actin cytoskeleton-associated complexes.
myosin complex
A protein complex, formed of one or more myosin heavy chains plus associated light chains and other proteins, that functions as a molecular motor; uses the energy of ATP hydrolysis to move actin filaments or to move vesicles or other cargo on fixed actin filaments; has magnesium-ATPase activity and binds actin. Myosin classes are distinguished based on sequence features of the motor, or head, domain, but also have distinct tail regions that are believed to bind specific cargoes.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or carbohydrate groups.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
myosin complex
A protein complex, formed of one or more myosin heavy chains plus associated light chains and other proteins, that functions as a molecular motor; uses the energy of ATP hydrolysis to move actin filaments or to move vesicles or other cargo on fixed actin filaments; has magnesium-ATPase activity and binds actin. Myosin classes are distinguished based on sequence features of the motor, or head, domain, but also have distinct tail regions that are believed to bind specific cargoes.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
myosin complex
A protein complex, formed of one or more myosin heavy chains plus associated light chains and other proteins, that functions as a molecular motor; uses the energy of ATP hydrolysis to move actin filaments or to move vesicles or other cargo on fixed actin filaments; has magnesium-ATPase activity and binds actin. Myosin classes are distinguished based on sequence features of the motor, or head, domain, but also have distinct tail regions that are believed to bind specific cargoes.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
metal ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of metal ions from one side of a membrane to the other.
nicotinic acetylcholine-activated cation-selective channel activity
NA
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a channel that opens when a specific extracellular ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
excitatory extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity
NA
cation channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of cation from one side of the membrane to the other.
ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
ligand-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a channel that opens when a specific ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
passive transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of the membrane to the other, down the solute's concentration gradient.
ligand-gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel that opens when a specific ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel that opens in response to a specific stimulus.
substrate specific channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a specific solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
all
This term is the most general term possible
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
cation channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
cation channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
ligand-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a channel that opens when a specific ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
nicotinic acetylcholine-activated cation-selective channel activity
NA
ABCD1ATP-binding cassette, sub-family D (ALD), member 1 (205142_x_at), score: -0.57 ABOABO blood group (transferase A, alpha 1-3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase; transferase B, alpha 1-3-galactosyltransferase) (216716_at), score: 0.73 ACP6acid phosphatase 6, lysophosphatidic (218795_at), score: -0.52 ACSL5acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 5 (218322_s_at), score: 0.68 ADORA1adenosine A1 receptor (216220_s_at), score: 0.49 AGMATagmatine ureohydrolase (agmatinase) (219792_at), score: 0.67 AIPL1aryl hydrocarbon receptor interacting protein-like 1 (219977_at), score: 0.56 ALDH1L1aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family, member L1 (215798_at), score: 0.65 ANKFY1ankyrin repeat and FYVE domain containing 1 (219868_s_at), score: -0.56 APOC4apolipoprotein C-IV (206738_at), score: 0.52 APPamyloid beta (A4) precursor protein (214953_s_at), score: 0.57 ARL15ADP-ribosylation factor-like 15 (219842_at), score: 0.61 ATP6V0A1ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal V0 subunit a1 (205095_s_at), score: -0.62 B9D1B9 protein domain 1 (210534_s_at), score: -0.7 BAI2brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 2 (204966_at), score: 0.56 BCL2A1BCL2-related protein A1 (205681_at), score: 0.61 BCL2L11BCL2-like 11 (apoptosis facilitator) (222343_at), score: 0.96 BCL3B-cell CLL/lymphoma 3 (204908_s_at), score: -0.51 BDH13-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, type 1 (211715_s_at), score: 0.55 BDH23-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, type 2 (218285_s_at), score: -0.55 BFSP1beaded filament structural protein 1, filensin (206746_at), score: -0.6 BTBD2BTB (POZ) domain containing 2 (207722_s_at), score: -0.51 C11orf1chromosome 11 open reading frame 1 (218925_s_at), score: 0.49 C11orf30chromosome 11 open reading frame 30 (219012_s_at), score: 0.46 C11orf71chromosome 11 open reading frame 71 (218789_s_at), score: -0.57 C19orf40chromosome 19 open reading frame 40 (214816_x_at), score: 0.58 C7orf28Achromosome 7 open reading frame 28A (201974_s_at), score: 0.46 CA3carbonic anhydrase III, muscle specific (204865_at), score: 0.6 CACNA1Gcalcium channel, voltage-dependent, T type, alpha 1G subunit (211315_s_at), score: 0.72 CAMK2Bcalcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II beta (34846_at), score: 0.48 CCDC9coiled-coil domain containing 9 (206257_at), score: 0.6 CCL11chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 11 (210133_at), score: 0.58 CD79BCD79b molecule, immunoglobulin-associated beta (205297_s_at), score: 0.48 CD83CD83 molecule (204440_at), score: 0.66 CEACAM1carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 (biliary glycoprotein) (211883_x_at), score: 0.49 CELSR2cadherin, EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 2 (flamingo homolog, Drosophila) (204029_at), score: 0.7 CFHcomplement factor H (213800_at), score: -0.52 CHRDL1chordin-like 1 (209763_at), score: 0.57 CHRNA10cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 10 (220210_at), score: 0.48 CHRNA6cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 6 (207568_at), score: 0.58 CHRNA9cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 9 (221107_at), score: 0.46 CHRNB2cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, beta 2 (neuronal) (206635_at), score: 0.48 CLCA2chloride channel accessory 2 (217528_at), score: 0.85 CPEB3cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein 3 (205773_at), score: 0.54 CR1complement component (3b/4b) receptor 1 (Knops blood group) (217484_at), score: 0.54 CROPcisplatin resistance-associated overexpressed protein (208835_s_at), score: 0.49 CTSEcathepsin E (205927_s_at), score: 0.6 CXorf21chromosome X open reading frame 21 (220252_x_at), score: 0.52 CYCSP52cytochrome c, somatic pseudogene 52 (217206_at), score: 0.6 CYP3A4cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, polypeptide 4 (205998_x_at), score: 0.55 DAOD-amino-acid oxidase (206878_at), score: 0.57 DCP2DCP2 decapping enzyme homolog (S. cerevisiae) (212919_at), score: 0.49 DGCR2DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 2 (214198_s_at), score: 0.51 DKFZP564O0823DKFZP564O0823 protein (204687_at), score: 0.48 DMPKdystrophia myotonica-protein kinase (37996_s_at), score: -0.53 DNAJC2DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 2 (213097_s_at), score: 0.5 DUSP9dual specificity phosphatase 9 (205777_at), score: 0.6 EBPemopamil binding protein (sterol isomerase) (202735_at), score: 0.53 EHMT2euchromatic histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2 (202326_at), score: -0.54 ELK1ELK1, member of ETS oncogene family (210376_x_at), score: -0.52 ELK4ELK4, ETS-domain protein (SRF accessory protein 1) (206919_at), score: 0.47 ELSPBP1epididymal sperm binding protein 1 (220366_at), score: 0.5 EMCNendomucin (219436_s_at), score: -0.64 ENTPD1ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 1 (209473_at), score: 0.59 ETFDHelectron-transferring-flavoprotein dehydrogenase (205530_at), score: -0.51 F11coagulation factor XI (206610_s_at), score: 0.72 FA2Hfatty acid 2-hydroxylase (219429_at), score: 0.53 FABP3fatty acid binding protein 3, muscle and heart (mammary-derived growth inhibitor) (214285_at), score: 0.53 FAM75A3family with sequence similarity 75, member A3 (215935_at), score: 0.48 FBXO17F-box protein 17 (220233_at), score: -0.52 FBXO2F-box protein 2 (219305_x_at), score: 0.5 FETUBfetuin B (214417_s_at), score: 0.55 FGF12fibroblast growth factor 12 (207501_s_at), score: 0.61 FGF9fibroblast growth factor 9 (glia-activating factor) (206404_at), score: -0.6 FKBP10FK506 binding protein 10, 65 kDa (219249_s_at), score: 0.57 FOXC2forkhead box C2 (MFH-1, mesenchyme forkhead 1) (214520_at), score: -0.54 G6PC2glucose-6-phosphatase, catalytic, 2 (221453_at), score: 0.5 GEMIN4gem (nuclear organelle) associated protein 4 (205527_s_at), score: 0.5 GFOD1glucose-fructose oxidoreductase domain containing 1 (219821_s_at), score: 0.72 GK2glycerol kinase 2 (215430_at), score: 0.6 GNALguanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), alpha activating activity polypeptide, olfactory type (206355_at), score: 0.49 GPATCH4G patch domain containing 4 (220596_at), score: 0.63 GPLD1glycosylphosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase D1 (206264_at), score: 0.48 GRPgastrin-releasing peptide (206326_at), score: -0.54 GZMMgranzyme M (lymphocyte met-ase 1) (207460_at), score: 0.65 HAB1B1 for mucin (215778_x_at), score: 0.48 HAND1heart and neural crest derivatives expressed 1 (220138_at), score: 0.62 HDAC5histone deacetylase 5 (202455_at), score: -0.54 HES1hairy and enhancer of split 1, (Drosophila) (203394_s_at), score: -0.64 HHEXhematopoietically expressed homeobox (215933_s_at), score: -0.52 HIP1Rhuntingtin interacting protein 1 related (209558_s_at), score: 0.61 HIST1H2BGhistone cluster 1, H2bg (210387_at), score: -0.6 HIST1H4Ghistone cluster 1, H4g (208551_at), score: 0.51 HPNhepsin (204934_s_at), score: 0.67 HSPA6heat shock 70kDa protein 6 (HSP70B') (117_at), score: 0.58 IFI30interferon, gamma-inducible protein 30 (201422_at), score: -0.53 IL18interleukin 18 (interferon-gamma-inducing factor) (206295_at), score: -0.53 IL22RA1interleukin 22 receptor, alpha 1 (220056_at), score: 0.57 IL2RBinterleukin 2 receptor, beta (205291_at), score: 0.65 INE1inactivation escape 1 (non-protein coding) (207252_at), score: 0.56 IP6K2inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 2 (218192_at), score: -0.53 IRS4insulin receptor substrate 4 (207403_at), score: 0.5 JAK2Janus kinase 2 (a protein tyrosine kinase) (205842_s_at), score: -0.59 JMJD7jumonji domain containing 7 (60528_at), score: 0.53 JUNBjun B proto-oncogene (201473_at), score: -0.52 JUPjunction plakoglobin (201015_s_at), score: -0.59 KAL1Kallmann syndrome 1 sequence (205206_at), score: 0.48 KIAA1009KIAA1009 (206005_s_at), score: 0.48 KIAA1305KIAA1305 (220911_s_at), score: -0.71 KPNA6karyopherin alpha 6 (importin alpha 7) (212101_at), score: -0.58 LAX1lymphocyte transmembrane adaptor 1 (207734_at), score: 0.67 LINS1lines homolog 1 (Drosophila) (220121_at), score: 0.5 LOC100129064hypothetical LOC100129064 (220764_at), score: 0.48 LOC100188945cell division cycle associated 4 pseudogene (215109_at), score: 0.61 LOC202181hypothetical protein LOC202181 (220609_at), score: 0.61 LOC391132similar to hCG2041276 (216177_at), score: 0.55 LPGAT1lysophosphatidylglycerol acyltransferase 1 (202651_at), score: 0.48 LRP8low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 8, apolipoprotein e receptor (205282_at), score: 0.47 LRRC37B2leucine rich repeat containing 37, member B2 (216149_at), score: 0.53 LSM14BLSM14B, SCD6 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (219653_at), score: 0.48 LY6Hlymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus H (206773_at), score: 0.47 MAFKv-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog K (avian) (206750_at), score: 0.5 MAGEB2melanoma antigen family B, 2 (206218_at), score: 0.48 MAN2A2mannosidase, alpha, class 2A, member 2 (219999_at), score: 0.51 MCF2L2MCF.2 cell line derived transforming sequence-like 2 (215112_x_at), score: 0.47 MDM2Mdm2 p53 binding protein homolog (mouse) (205386_s_at), score: -0.7 MFNGMFNG O-fucosylpeptide 3-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (204153_s_at), score: 0.64 MGC5590hypothetical protein MGC5590 (220931_at), score: 0.55 MLYCDmalonyl-CoA decarboxylase (218869_at), score: -0.51 MPP1membrane protein, palmitoylated 1, 55kDa (202974_at), score: -0.54 MPP3membrane protein, palmitoylated 3 (MAGUK p55 subfamily member 3) (206186_at), score: 0.47 MUC1mucin 1, cell surface associated (207847_s_at), score: -0.75 MUC13mucin 13, cell surface associated (218687_s_at), score: 0.5 MUC5ACmucin 5AC, oligomeric mucus/gel-forming (217182_at), score: 0.6 MYBPC1myosin binding protein C, slow type (214087_s_at), score: 0.5 MYH15myosin, heavy chain 15 (215331_at), score: 0.65 MYL4myosin, light chain 4, alkali; atrial, embryonic (210088_x_at), score: 0.54 MYO15Amyosin XVA (220288_at), score: 0.54 MYO5Cmyosin VC (218966_at), score: 0.49 NDRG4NDRG family member 4 (209159_s_at), score: -0.59 NFKBIAnuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha (201502_s_at), score: -0.62 NOL10nucleolar protein 10 (218591_s_at), score: 0.69 NOS1nitric oxide synthase 1 (neuronal) (207309_at), score: 0.5 NOVA1neuro-oncological ventral antigen 1 (205794_s_at), score: 0.65 NSUN5BNOL1/NOP2/Sun domain family, member 5B (214100_x_at), score: 0.51 OCLMoculomedin (208274_at), score: 0.74 OR7E47Polfactory receptor, family 7, subfamily E, member 47 pseudogene (216698_x_at), score: 0.5 P2RY4pyrimidinergic receptor P2Y, G-protein coupled, 4 (221466_at), score: 0.56 PACS1phosphofurin acidic cluster sorting protein 1 (220557_s_at), score: -0.56 PAPPA2pappalysin 2 (213332_at), score: 0.52 PARD6Apar-6 partitioning defective 6 homolog alpha (C. elegans) (205245_at), score: 0.52 PCDHGA3protocadherin gamma subfamily A, 3 (216352_x_at), score: -0.52 PCNXpecanex homolog (Drosophila) (213173_at), score: 0.48 PDE5Aphosphodiesterase 5A, cGMP-specific (206757_at), score: -0.55 PIPOXpipecolic acid oxidase (221605_s_at), score: 0.53 PLA2G6phospholipase A2, group VI (cytosolic, calcium-independent) (215938_s_at), score: 0.61 PLXDC1plexin domain containing 1 (219700_at), score: 0.61 PPP1R13Bprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 13B (216347_s_at), score: 0.57 PRKCBprotein kinase C, beta (209685_s_at), score: 0.55 PRSS1protease, serine, 1 (trypsin 1) (216470_x_at), score: 0.49 PTPN20Bprotein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 20B (215172_at), score: -0.57 PTPRDprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, D (214043_at), score: 0.47 PTPRUprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, U (211320_s_at), score: 0.71 RAB11BRAB11B, member RAS oncogene family (34478_at), score: -0.61 RAP1GAPRAP1 GTPase activating protein (203911_at), score: 0.75 RAPGEF4Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 4 (205651_x_at), score: 0.47 RASGRP3RAS guanyl releasing protein 3 (calcium and DAG-regulated) (205801_s_at), score: -0.54 REEP1receptor accessory protein 1 (204364_s_at), score: 0.59 RLN1relaxin 1 (211753_s_at), score: 0.58 RNF24ring finger protein 24 (204669_s_at), score: -0.54 ROS1c-ros oncogene 1 , receptor tyrosine kinase (207569_at), score: 0.55 RP3-377H14.5hypothetical LOC285830 (222279_at), score: 0.47 RPGRIP1retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator interacting protein 1 (206608_s_at), score: 0.65 RPL10Lribosomal protein L10-like (217559_at), score: 0.58 RXRBretinoid X receptor, beta (215099_s_at), score: -0.52 S100A14S100 calcium binding protein A14 (218677_at), score: 0.48 SAA4serum amyloid A4, constitutive (207096_at), score: 0.63 SCAMP4secretory carrier membrane protein 4 (213244_at), score: -0.56 SCAMP5secretory carrier membrane protein 5 (212699_at), score: 0.62 SCML1sex comb on midleg-like 1 (Drosophila) (218793_s_at), score: 0.52 SCN11Asodium channel, voltage-gated, type XI, alpha subunit (220791_x_at), score: 0.57 SDPRserum deprivation response (phosphatidylserine binding protein) (218711_s_at), score: -0.6 SEMA3Dsema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), short basic domain, secreted, (semaphorin) 3D (215324_at), score: 0.5 SEMA3Fsema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), short basic domain, secreted, (semaphorin) 3F (35666_at), score: 0.49 SEPT5septin 5 (209767_s_at), score: 0.53 SERPINB13serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 13 (211362_s_at), score: 0.47 SIGLEC6sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin 6 (210796_x_at), score: 0.65 SLC14A1solute carrier family 14 (urea transporter), member 1 (Kidd blood group) (205856_at), score: -0.54 SLC15A1solute carrier family 15 (oligopeptide transporter), member 1 (211349_at), score: 0.57 SLC38A4solute carrier family 38, member 4 (220786_s_at), score: -0.54 SLC4A7solute carrier family 4, sodium bicarbonate cotransporter, member 7 (209884_s_at), score: 0.46 SLC9A3R2solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 3 regulator 2 (209830_s_at), score: -0.58 SLFN12schlafen family member 12 (219885_at), score: -0.56 SNAP25synaptosomal-associated protein, 25kDa (202508_s_at), score: -1 SORBS1sorbin and SH3 domain containing 1 (218087_s_at), score: 0.61 SPAG8sperm associated antigen 8 (206816_s_at), score: 0.59 STK17Bserine/threonine kinase 17b (205214_at), score: -0.54 SULT1B1sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1B, member 1 (207601_at), score: 0.47 SUOXsulfite oxidase (204067_at), score: -0.67 SYN2synapsin II (210247_at), score: 0.48 SYT1synaptotagmin I (203999_at), score: -0.56 TAF4BTAF4b RNA polymerase II, TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factor, 105kDa (216226_at), score: 0.58 TAL1T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia 1 (206283_s_at), score: 0.56 TCP10t-complex 10 homolog (mouse) (207503_at), score: 0.61 TGFBR2transforming growth factor, beta receptor II (70/80kDa) (207334_s_at), score: -0.53 TGIF2TGFB-induced factor homeobox 2 (216262_s_at), score: 0.47 TIAF1TGFB1-induced anti-apoptotic factor 1 (202039_at), score: -0.71 TLE3transducin-like enhancer of split 3 (E(sp1) homolog, Drosophila) (206472_s_at), score: -0.68 TMCC2transmembrane and coiled-coil domain family 2 (213096_at), score: 0.5 TMSB4Ythymosin beta 4, Y-linked (206769_at), score: 0.6 TNFRSF9tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 9 (207536_s_at), score: 0.48 TNFSF10tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 10 (214329_x_at), score: 0.67 TNK1tyrosine kinase, non-receptor, 1 (217149_x_at), score: 0.6 TRIM45tripartite motif-containing 45 (219923_at), score: 0.57 TRMT2ATRM2 tRNA methyltransferase 2 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (91617_at), score: 0.52 TSPAN2tetraspanin 2 (214606_at), score: 0.5 UBTD1ubiquitin domain containing 1 (219172_at), score: -0.54 UGT1A8UDP glucuronosyltransferase 1 family, polypeptide A8 (221304_at), score: 0.5 URB2URB2 ribosome biogenesis 2 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (205284_at), score: 0.55 VEGFBvascular endothelial growth factor B (203683_s_at), score: -0.53 VENTXP1VENT homeobox (Xenopus laevis) pseudogene 1 (216722_at), score: -0.68 WDR4WD repeat domain 4 (221632_s_at), score: 0.5 WDR42AWD repeat domain 42A (202249_s_at), score: -0.57 WFDC8WAP four-disulfide core domain 8 (215276_at), score: 0.53 ZBTB40zinc finger and BTB domain containing 40 (203958_s_at), score: 0.58 ZNF117zinc finger protein 117 (207605_x_at), score: 0.61 ZNF132zinc finger protein 132 (207402_at), score: -0.53 ZNF193zinc finger protein 193 (205181_at), score: 0.53 ZNF202zinc finger protein 202 (204327_s_at), score: 0.49 ZNF224zinc finger protein 224 (216983_s_at), score: 0.47 ZNF254zinc finger protein 254 (206862_at), score: 0.5 ZNF783zinc finger family member 783 (221876_at), score: 0.47
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485831.cel | 10 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485871.cel | 12 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486311.cel | 34 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485991.cel | 18 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |