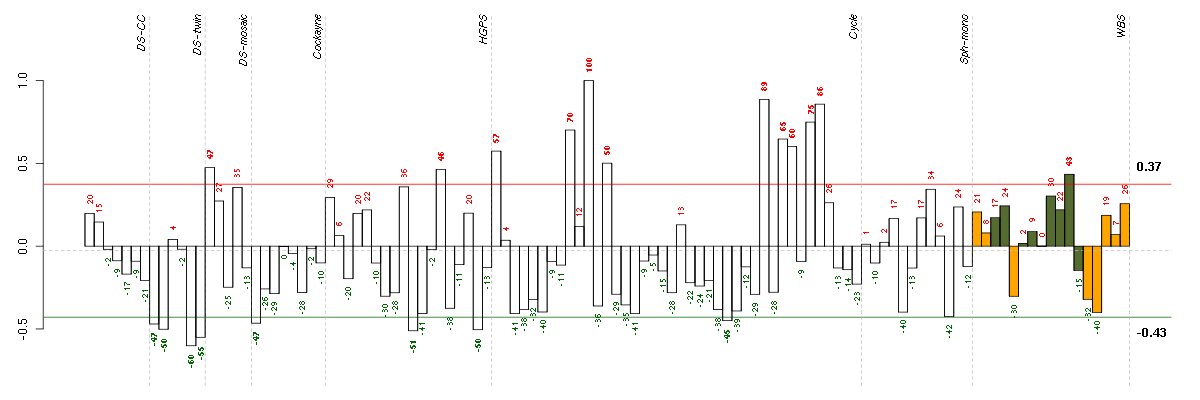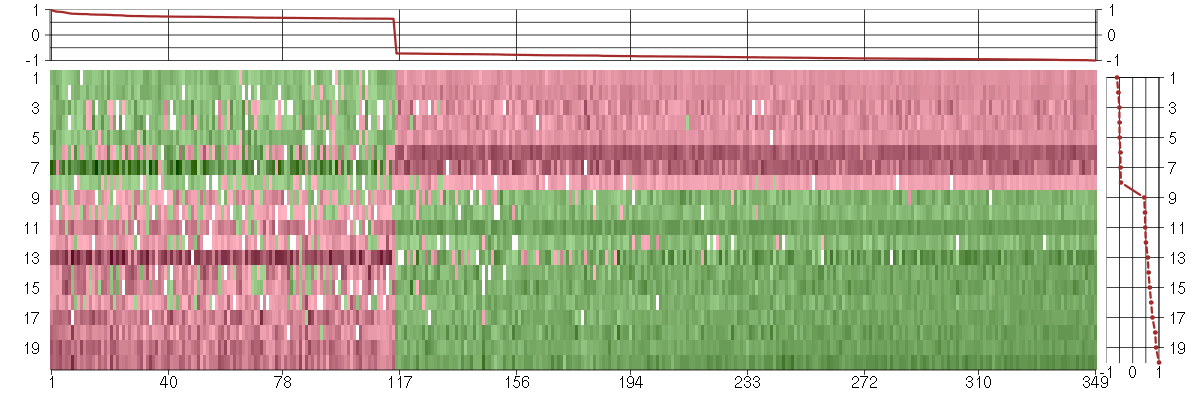

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

DNA replication
The process whereby new strands of DNA are synthesized. The template for replication can either be an existing DNA molecule or RNA.
chromosome segregation
The process by which genetic material, in the form of chromosomes, is organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets.
chromosome organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level that results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of chromosomes, structures composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins that carries hereditary information.
mitotic sister chromatid segregation
The cell cycle process whereby replicated homologous chromosomes are organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two sets during the mitotic cell cycle. Each replicated chromosome, composed of two sister chromatids, aligns at the cell equator, paired with its homologous partner. One homolog of each morphologic type goes into each of the resulting chromosome sets.
cell cycle checkpoint
The cell cycle regulatory process by which progression through the cycle can be halted until conditions are suitable for the cell to proceed to the next stage.
DNA replication checkpoint
A signal transduction based surveillance mechanism that prevents the initiation of mitosis until DNA replication is complete, thereby ensuring that progeny inherit a full complement of the genome.
regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of CDK activity.
S phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through S phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which DNA synthesis takes place.
M phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which mitosis takes place.
microtubule cytoskeleton organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising microtubules and their associated proteins.
mitotic cell cycle
Progression through the phases of the mitotic cell cycle, the most common eukaryotic cell cycle, which canonically comprises four successive phases called G1, S, G2, and M and includes replication of the genome and the subsequent segregation of chromosomes into daughter cells. In some variant cell cycles nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division, or G1 and G2 phases may be absent.
M phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the cell cycle comprising nuclear division.
nuclear division
A process by which a cell nucleus is divided into two nuclei, with DNA and other nuclear contents distributed between the daughter nuclei.
double-strand break repair via homologous recombination
The error-free repair of a double-strand break in DNA in which the broken DNA molecule is repaired using homologous sequences. A strand in the broken DNA searches for a homologous region in an intact chromosome to serve as the template for DNA synthesis. The restoration of two intact DNA molecules results in the exchange, reciprocal or nonreciprocal, of genetic material between the intact DNA molecule and the broken DNA molecule.
recombinational repair
The repair of damaged DNA that involves the exchange, reciprocal or nonreciprocal, of genetic material between the broken DNA molecule and a homologous region of DNA.
DNA synthesis during DNA repair
Synthesis of DNA that proceeds from the broken 3' single-strand DNA end uses the homologous intact duplex as the template.
sister chromatid segregation
The process by which sister chromatids are organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets.
cytokinesis
A cellular process resulting in the division of the cytoplasm of a cell and its separation into two daughter cells. Cytokinesis usually occurs after growth, replication, and segregation of cellular components.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
regulation of cell cycle
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progression through the cell cycle.
cytoskeleton organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
DNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
DNA-dependent DNA replication
The process whereby new strands of DNA are synthesized, using parental DNA as a template for the DNA-dependent DNA polymerases that synthesize the new strands.
DNA unwinding during replication
The process by which interchain hydrogen bonds between two strands of DNA are broken or 'melted', generating unpaired template strands for DNA replication.
DNA replication initiation
The process by which DNA replication is started; this involves the separation of a stretch of the DNA double helix, the recruitment of DNA polymerases and the initiation of polymerase action.
DNA strand elongation during DNA replication
The process by which a DNA strand is synthesized from template DNA during replication by the action of polymerases, which add nucleotides to the 3' end of the nascent DNA strand.
regulation of DNA replication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication.
DNA repair
The process of restoring DNA after damage. Genomes are subject to damage by chemical and physical agents in the environment (e.g. UV and ionizing radiations, chemical mutagens, fungal and bacterial toxins, etc.) and by free radicals or alkylating agents endogenously generated in metabolism. DNA is also damaged because of errors during its replication. A variety of different DNA repair pathways have been reported that include direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, photoreactivation, bypass, double-strand break repair pathway, and mismatch repair pathway.
nucleotide-excision repair
In nucleotide excision repair a small region of the strand surrounding the damage is removed from the DNA helix as an oligonucleotide. The small gap left in the DNA helix is filled in by the sequential action of DNA polymerase and DNA ligase. Nucleotide excision repair recognizes a wide range of substrates, including damage caused by UV irradiation (pyrimidine dimers and 6-4 photoproducts) and chemicals (intrastrand cross-links and bulky adducts).
nucleotide-excision repair, DNA gap filling
Repair of the gap in the DNA helix by DNA polymerase and DNA ligase after the portion of the strand containing the lesion has been removed by pyrimidine-dimer repair enzymes.
double-strand break repair
The repair of double-strand breaks in DNA via homologous and nonhomologous mechanisms to reform a continuous DNA helix.
DNA recombination
Any process by which a new genotype is formed by reassortment of genes resulting in gene combinations different from those that were present in the parents. In eukaryotes genetic recombination can occur by chromosome assortment, intrachromosomal recombination, or nonreciprocal interchromosomal recombination. Intrachromosomal recombination occurs by crossing over. In bacteria it may occur by genetic transformation, conjugation, transduction, or F-duction.
DNA packaging
Any process by which DNA and associated proteins are formed into a compact, orderly structure.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
response to DNA damage stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
microtubule-based process
Any cellular process that depends upon or alters the microtubule cytoskeleton, that part of the cytoskeleton comprising microtubules and their associated proteins.
microtubule-based movement
Movement of organelles, other microtubules and other particles along microtubules, mediated by motor proteins.
cell cycle
The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division.
spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the spindle, the array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during DNA segregation and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
mitotic spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the microtubule spindle during a mitotic cell cycle.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
mitotic chromosome condensation
The cell cycle process whereby chromatin structure is compacted prior to mitosis in eukaryotic cells.
regulation of mitosis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of mitosis.
mitotic cell cycle checkpoint
A signal transduction-based surveillance mechanism that ensures accurate chromosome replication and segregation by preventing progression through a mitotic cell cycle until conditions are suitable for the cell to proceed to the next stage.
centrosome cycle
The cell cycle process whereby centrosome duplication and separation takes place. The centrosome cycle can operate with a considerable degree of independence from other processes of the cell cycle.
meiosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the nuclear division phase of a meiotic cell cycle, the specialized nuclear and cell division in which a single diploid cell undergoes two nuclear divisions following a single round of DNA replication in order to produce four daughter cells that contain half the number of chromosomes as the diploid cell. Meiotic division occurs during the formation of gametes from diploid organisms and at the beginning of haplophase in those organisms that alternate between diploid and haploid generations.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
intracellular signaling cascade
A series of reactions within the cell that occur as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
regulation of mitotic cell cycle
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progress through the mitotic cell cycle.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
negative regulation of DNA replication
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication.
cell proliferation
The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
negative regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the rate of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
negative regulation of metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cell cycle process
Any process that modulates a cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
second-messenger-mediated signaling
A series of molecular signals in which an ion or small molecule is formed or released into the cytosol, thereby helping relay the signal within the cell.
phosphoinositide-mediated signaling
A series of molecular signals in which a cell uses a phosphoinositide to convert an extracellular signal into a response.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
cell cycle phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through one of the biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
DNA strand elongation
The DNA metabolic process by which a DNA strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of an existing DNA stand.
regulation of DNA replication initiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of initiation of DNA replication; the process by which DNA becomes competent to replicate. In eukaryotes, replication competence is established in early G1 and lost during the ensuing S phase.
chromosome condensation
The progressive compaction of dispersed interphase chromatin into threadlike chromosomes prior to mitotic or meiotic nuclear division, or during apoptosis, in eukaryotic cells.
cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport
The directed movement of substances along cytoskeletal elements such as microfilaments or microtubules within a cell.
microtubule organizing center organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a microtubule organizing center, a structure from which microtubules grow.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
negative regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
negative regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
DNA integrity checkpoint
Any cell cycle checkpoint that delays or arrests cell cycle progression in response to changes in DNA structure.
negative regulation of DNA replication initiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of initiation of DNA replication.
DNA geometric change
The process by which a transformation is induced in the geometry of a DNA double helix, resulting in a change in twist, writhe, or both, but with no change in linking number. Includes the unwinding of double-stranded DNA by helicases.
DNA duplex unwinding
The process by which interchain hydrogen bonds between two strands of DNA are broken or 'melted', generating a region of unpaired single strands.
cellular response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating the organism is under stress. The stress is usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular response to DNA damage stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
regulation of kinase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of kinase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of protein kinase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase activity.
negative regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
intracellular transport
The directed movement of substances within a cell.
organelle fission
The creation of two or more organelles by division of one organelle.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of catalytic activity
Any process that modulates the activity of an enzyme.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
negative regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
centrosome organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a centrosome, a structure comprised of a pair of centrioles and peri-centriolar material from which a microtubule spindle apparatus is organized.
cell division
The process resulting in the physical partitioning and separation of a cell into daughter cells.
S phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through S phase, the part of the cell cycle during which DNA synthesis takes place.
meiotic cell cycle
Progression through the phases of the meiotic cell cycle, in which canonically a cell replicates to produce four offspring with half the chromosomal content of the progenitor cell.
interphase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through interphase, the stage of cell cycle between successive rounds of chromosome segregation. Canonically, interphase is the stage of the cell cycle during which the biochemical and physiologic functions of the cell are performed and replication of chromatin occurs.
M phase of meiotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the meiotic cell cycle during which meiosis takes place.
interphase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through interphase, the stage of cell cycle between successive rounds of mitosis. Canonically, interphase is the stage of the cell cycle during which the biochemical and physiologic functions of the cell are performed and replication of chromatin occurs.
regulation of transferase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transferase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from one compound (generally regarded as the donor) to another compound (generally regarded as the acceptor). Transferase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 2.
cellular localization
Any process by which a substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in, a specific location within or in the membrane of a cell.
establishment of localization in cell
The directed movement of a substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location within, or in the membrane of, a cell.
cellular response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of molecular function
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of molecular functions. Molecular functions are elemental biological activities occurring at the molecular level, such as catalysis or binding.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
negative regulation of metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
cellular localization
Any process by which a substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in, a specific location within or in the membrane of a cell.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the rate of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
negative regulation of metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
negative regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
sister chromatid segregation
The process by which sister chromatids are organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets.
negative regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cell cycle
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progression through the cell cycle.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
establishment of localization in cell
The directed movement of a substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location within, or in the membrane of, a cell.
cellular response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating the organism is under stress. The stress is usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
intracellular transport
The directed movement of substances within a cell.
negative regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the rate of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
negative regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
negative regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
negative regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
mitotic spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the microtubule spindle during a mitotic cell cycle.
regulation of mitotic cell cycle
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progress through the mitotic cell cycle.
regulation of cell cycle process
Any process that modulates a cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
microtubule organizing center organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a microtubule organizing center, a structure from which microtubules grow.
cellular response to DNA damage stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism.
negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of DNA replication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication.
negative regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
negative regulation of DNA replication
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication.
negative regulation of DNA replication
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication.
negative regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
negative regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
regulation of DNA replication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication.
negative regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
DNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
negative regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
mitotic chromosome condensation
The cell cycle process whereby chromatin structure is compacted prior to mitosis in eukaryotic cells.
mitotic spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the microtubule spindle during a mitotic cell cycle.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
regulation of mitosis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of mitosis.
mitotic cell cycle checkpoint
A signal transduction-based surveillance mechanism that ensures accurate chromosome replication and segregation by preventing progression through a mitotic cell cycle until conditions are suitable for the cell to proceed to the next stage.
meiosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the nuclear division phase of a meiotic cell cycle, the specialized nuclear and cell division in which a single diploid cell undergoes two nuclear divisions following a single round of DNA replication in order to produce four daughter cells that contain half the number of chromosomes as the diploid cell. Meiotic division occurs during the formation of gametes from diploid organisms and at the beginning of haplophase in those organisms that alternate between diploid and haploid generations.
mitotic chromosome condensation
The cell cycle process whereby chromatin structure is compacted prior to mitosis in eukaryotic cells.
sister chromatid segregation
The process by which sister chromatids are organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets.
chromosome condensation
The progressive compaction of dispersed interphase chromatin into threadlike chromosomes prior to mitotic or meiotic nuclear division, or during apoptosis, in eukaryotic cells.
microtubule cytoskeleton organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising microtubules and their associated proteins.
M phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which mitosis takes place.
spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the spindle, the array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during DNA segregation and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
M phase of meiotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the meiotic cell cycle during which meiosis takes place.
mitotic sister chromatid segregation
The cell cycle process whereby replicated homologous chromosomes are organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two sets during the mitotic cell cycle. Each replicated chromosome, composed of two sister chromatids, aligns at the cell equator, paired with its homologous partner. One homolog of each morphologic type goes into each of the resulting chromosome sets.
regulation of mitosis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of mitosis.
S phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through S phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which DNA synthesis takes place.
S phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through S phase, the part of the cell cycle during which DNA synthesis takes place.
interphase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through interphase, the stage of cell cycle between successive rounds of mitosis. Canonically, interphase is the stage of the cell cycle during which the biochemical and physiologic functions of the cell are performed and replication of chromatin occurs.
DNA repair
The process of restoring DNA after damage. Genomes are subject to damage by chemical and physical agents in the environment (e.g. UV and ionizing radiations, chemical mutagens, fungal and bacterial toxins, etc.) and by free radicals or alkylating agents endogenously generated in metabolism. DNA is also damaged because of errors during its replication. A variety of different DNA repair pathways have been reported that include direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, photoreactivation, bypass, double-strand break repair pathway, and mismatch repair pathway.
microtubule-based movement
Movement of organelles, other microtubules and other particles along microtubules, mediated by motor proteins.
negative regulation of DNA replication
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication.
DNA replication
The process whereby new strands of DNA are synthesized. The template for replication can either be an existing DNA molecule or RNA.
regulation of DNA replication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication.
negative regulation of DNA replication
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication.
regulation of DNA replication initiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of initiation of DNA replication; the process by which DNA becomes competent to replicate. In eukaryotes, replication competence is established in early G1 and lost during the ensuing S phase.
negative regulation of DNA replication initiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of initiation of DNA replication.
DNA synthesis during DNA repair
Synthesis of DNA that proceeds from the broken 3' single-strand DNA end uses the homologous intact duplex as the template.
recombinational repair
The repair of damaged DNA that involves the exchange, reciprocal or nonreciprocal, of genetic material between the broken DNA molecule and a homologous region of DNA.
centrosome cycle
The cell cycle process whereby centrosome duplication and separation takes place. The centrosome cycle can operate with a considerable degree of independence from other processes of the cell cycle.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
negative regulation of DNA replication initiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of initiation of DNA replication.
DNA replication checkpoint
A signal transduction based surveillance mechanism that prevents the initiation of mitosis until DNA replication is complete, thereby ensuring that progeny inherit a full complement of the genome.
DNA replication initiation
The process by which DNA replication is started; this involves the separation of a stretch of the DNA double helix, the recruitment of DNA polymerases and the initiation of polymerase action.
DNA strand elongation during DNA replication
The process by which a DNA strand is synthesized from template DNA during replication by the action of polymerases, which add nucleotides to the 3' end of the nascent DNA strand.
nucleotide-excision repair, DNA gap filling
Repair of the gap in the DNA helix by DNA polymerase and DNA ligase after the portion of the strand containing the lesion has been removed by pyrimidine-dimer repair enzymes.
double-strand break repair via homologous recombination
The error-free repair of a double-strand break in DNA in which the broken DNA molecule is repaired using homologous sequences. A strand in the broken DNA searches for a homologous region in an intact chromosome to serve as the template for DNA synthesis. The restoration of two intact DNA molecules results in the exchange, reciprocal or nonreciprocal, of genetic material between the intact DNA molecule and the broken DNA molecule.
DNA unwinding during replication
The process by which interchain hydrogen bonds between two strands of DNA are broken or 'melted', generating unpaired template strands for DNA replication.
regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of CDK activity.

nuclear chromosome
A chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
condensed chromosome
A highly compacted molecule of DNA and associated proteins resulting in a cytologically distinct structure.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a chromosome that includes the centromere and associated proteins. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
condensed chromosome kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of a condensed chromosome and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
condensed chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a condensed chromosome that includes the centromere and associated proteins, including the kinetochore. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
condensin complex
A multisubunit protein complex that plays a central role in chromosome condensation.
spindle pole
Either of the ends of a spindle, where spindle microtubules are organized; usually contains a microtubule organizing center and accessory molecules, spindle microtubules and astral microtubules.
outer kinetochore of condensed chromosome
The region of a condensed chromosome kinetochore most external to centromeric DNA; this outer region mediates kinetochore-microtubule interactions.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
nucleus
A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
nucleoplasm
That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus.
replication fork
The Y-shaped region of a replicating DNA molecule, resulting from the separation of the DNA strands and in which the synthesis of new strands takes place. Also includes associated protein complexes.
alpha DNA polymerase:primase complex
A complex of four polypeptides, comprising large and small DNA polymerase alpha subunits and two primase subunits, which catalyzes the synthesis of an RNA primer on the lagging strand of replicating DNA; the smaller of the two primase subunits alone can catalyze oligoribonucleotide synthesis.
chromosome
A structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
centrosome
A structure comprised of a core structure (in most organisms, a pair of centrioles) and peripheral material from which a microtubule-based structure, such as a spindle apparatus, is organized. Centrosomes occur close to the nucleus during interphase in many eukaryotic cells, though in animal cells it changes continually during the cell-division cycle.
microtubule organizing center
A region in a eukaryotic cell, such as a centrosome or basal body, from which microtubules grow.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
microtubule
Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle.
microtubule associated complex
Any multimeric complex connected to a microtubule.
spindle microtubule
Any microtubule that is part of a mitotic or meiotic spindle; anchored at one spindle pole.
microtubule cytoskeleton
The part of the cytoskeleton (the internal framework of a cell) composed of microtubules and associated proteins.
replisome
A multi-component enzymatic machine at the replication fork which mediates DNA replication. Includes DNA primase, one or more DNA polymerases, DNA helicases, and other proteins.
membrane-enclosed lumen
The enclosed volume within a sealed membrane or between two sealed membranes. Encompasses the volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the space between the two lipid bilayers of a double membrane surrounding an organelle, e.g. nuclear envelope lumen.
nuclear lumen
The volume enclosed by the nuclear inner membrane.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
protein-DNA complex
A macromolecular complex containing both protein and DNA molecules.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
organelle lumen
The internal volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle; includes the volume enclosed by a single organelle membrane, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the volume enclosed by the innermost of the two lipid bilayers of an organelle envelope, e.g. nuclear lumen.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or carbohydrate groups.
nuclear replication fork
The Y-shaped region of a nuclear replicating DNA molecule, resulting from the separation of the DNA strands and in which the synthesis of new strands takes place. Also includes associated protein complexes.
nuclear replisome
A multi-component enzymatic machine at the nuclear replication fork, which mediates DNA replication. Includes DNA primase, one or more DNA polymerases, DNA helicases, and other proteins.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
nuclear part
Any constituent part of the nucleus, a membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
nuclear chromosome part
Any constituent part of a nuclear chromosome, a chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
intracellular organelle lumen
An organelle lumen that is part of an intracellular organelle.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle lumen
The internal volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle; includes the volume enclosed by a single organelle membrane, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the volume enclosed by the innermost of the two lipid bilayers of an organelle envelope, e.g. nuclear lumen.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle lumen
An organelle lumen that is part of an intracellular organelle.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
condensin complex
A multisubunit protein complex that plays a central role in chromosome condensation.
outer kinetochore of condensed chromosome
The region of a condensed chromosome kinetochore most external to centromeric DNA; this outer region mediates kinetochore-microtubule interactions.
replisome
A multi-component enzymatic machine at the replication fork which mediates DNA replication. Includes DNA primase, one or more DNA polymerases, DNA helicases, and other proteins.
nuclear lumen
The volume enclosed by the nuclear inner membrane.
nuclear chromosome part
Any constituent part of a nuclear chromosome, a chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
microtubule associated complex
Any multimeric complex connected to a microtubule.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
microtubule organizing center
A region in a eukaryotic cell, such as a centrosome or basal body, from which microtubules grow.
nucleoplasm
That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus.
alpha DNA polymerase:primase complex
A complex of four polypeptides, comprising large and small DNA polymerase alpha subunits and two primase subunits, which catalyzes the synthesis of an RNA primer on the lagging strand of replicating DNA; the smaller of the two primase subunits alone can catalyze oligoribonucleotide synthesis.
outer kinetochore of condensed chromosome
The region of a condensed chromosome kinetochore most external to centromeric DNA; this outer region mediates kinetochore-microtubule interactions.
nuclear part
Any constituent part of the nucleus, a membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated.
nuclear chromosome
A chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
spindle pole
Either of the ends of a spindle, where spindle microtubules are organized; usually contains a microtubule organizing center and accessory molecules, spindle microtubules and astral microtubules.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
replisome
A multi-component enzymatic machine at the replication fork which mediates DNA replication. Includes DNA primase, one or more DNA polymerases, DNA helicases, and other proteins.
alpha DNA polymerase:primase complex
A complex of four polypeptides, comprising large and small DNA polymerase alpha subunits and two primase subunits, which catalyzes the synthesis of an RNA primer on the lagging strand of replicating DNA; the smaller of the two primase subunits alone can catalyze oligoribonucleotide synthesis.
nuclear replication fork
The Y-shaped region of a nuclear replicating DNA molecule, resulting from the separation of the DNA strands and in which the synthesis of new strands takes place. Also includes associated protein complexes.
nuclear replisome
A multi-component enzymatic machine at the nuclear replication fork, which mediates DNA replication. Includes DNA primase, one or more DNA polymerases, DNA helicases, and other proteins.
nuclear chromosome part
Any constituent part of a nuclear chromosome, a chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
centrosome
A structure comprised of a core structure (in most organisms, a pair of centrioles) and peripheral material from which a microtubule-based structure, such as a spindle apparatus, is organized. Centrosomes occur close to the nucleus during interphase in many eukaryotic cells, though in animal cells it changes continually during the cell-division cycle.
spindle microtubule
Any microtubule that is part of a mitotic or meiotic spindle; anchored at one spindle pole.
condensed chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a condensed chromosome that includes the centromere and associated proteins, including the kinetochore. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
condensin complex
A multisubunit protein complex that plays a central role in chromosome condensation.
microtubule organizing center
A region in a eukaryotic cell, such as a centrosome or basal body, from which microtubules grow.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
microtubule
Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle.
microtubule associated complex
Any multimeric complex connected to a microtubule.
condensed chromosome kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of a condensed chromosome and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
nuclear replisome
A multi-component enzymatic machine at the nuclear replication fork, which mediates DNA replication. Includes DNA primase, one or more DNA polymerases, DNA helicases, and other proteins.

nucleotide binding
Interacting selectively with a nucleotide, any compound consisting of a nucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the ribose or deoxyribose moiety.
protein binding
Interacting selectively with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
nucleic acid binding
Interacting selectively with any nucleic acid.
DNA binding
Interacting selectively with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
DNA helicase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: NTP + H2O = NDP + phosphate to drive the unwinding of a DNA helix.
chromatin binding
Interacting selectively with chromatin, the network of fibers of DNA and protein that make up the chromosomes of the eukaryotic nucleus during interphase.
ATPase activity, coupled
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate to directly drive some other reaction, for example ion transport across a membrane.
motor activity
Catalysis of movement along a polymeric molecule such as a microfilament or microtubule, coupled to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate.
microtubule motor activity
Catalysis of movement along a microtubule, coupled to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate (usually ATP).
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: deoxynucleoside triphosphate + DNA(n) = diphosphate + DNA(n+1); the synthesis of DNA from deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates in the presence of a DNA template and primer.
nucleoside-triphosphatase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: a nucleoside triphosphate + H2O = nucleoside diphosphate + phosphate.
helicase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: NTP + H2O = NDP + phosphate to drive the unwinding of a DNA or RNA helix.
nuclease activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of ester linkages within nucleic acids.
exonuclease activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of ester linkages within nucleic acids by removing nucleotide residues from the 3' or 5' end.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
ATP binding
Interacting selectively with ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator.
DNA-dependent ATPase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate in the presence of single- or double-stranded DNA; drives another reaction.
ATPase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate. May or may not be coupled to another reaction.
pyrophosphatase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a pyrophosphate bond between two phosphate groups, leaving one phosphate on each of the two fragments.
transferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from one compound (generally regarded as the donor) to another compound (generally regarded as the acceptor). Transferase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 2.
transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphorus-containing group from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor).
nucleotidyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a nucleotidyl group to a reactant.
hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. Hydrolase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 3.
hydrolase activity, acting on ester bonds
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of any ester bond.
hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of any acid anhydride.
hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, in phosphorus-containing anhydrides
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of any acid anhydride which contains phosphorus.
purine nucleotide binding
Interacting selectively with purine nucleotides, any compound consisting of a purine nucleoside esterified with (ortho)phosphate.
adenyl nucleotide binding
Interacting selectively with adenyl nucleotides, any compound consisting of adenosine esterified with (ortho)phosphate.
ribonucleotide binding
Interacting selectively with a ribonucleotide, any compound consisting of a ribonucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the ribose moiety.
purine ribonucleotide binding
Interacting selectively with a purine ribonucleotide, any compound consisting of a purine ribonucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the ribose moiety.
adenyl ribonucleotide binding
Interacting selectively with an adenyl ribonucleotide, any compound consisting of adenosine esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the ribose moiety.
DNA polymerase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: deoxynucleoside triphosphate + DNA(n) = diphosphate + DNA(n+1); the synthesis of DNA from deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates in the presence of a nucleic acid template and primer.
all
This term is the most general term possible
purine ribonucleotide binding
Interacting selectively with a purine ribonucleotide, any compound consisting of a purine ribonucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the ribose moiety.
adenyl ribonucleotide binding
Interacting selectively with an adenyl ribonucleotide, any compound consisting of adenosine esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the ribose moiety.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04110 | 6.538e-17 | 4.422 | 32 | 98 | Cell cycle |
| 03030 | 3.639e-16 | 1.489 | 20 | 33 | DNA replication |
| 03410 | 7.161e-05 | 1.354 | 10 | 30 | Base excision repair |
| 03430 | 4.558e-04 | 0.9927 | 8 | 22 | Mismatch repair |
| 03440 | 1.133e-03 | 1.128 | 8 | 25 | Homologous recombination |
| 03420 | 2.233e-02 | 1.805 | 8 | 40 | Nucleotide excision repair |
| 00240 | 4.754e-02 | 3.113 | 10 | 69 | Pyrimidine metabolism |
ACDadrenocortical dysplasia homolog (mouse) (204617_s_at), score: -0.72 ANGPTL4angiopoietin-like 4 (221009_s_at), score: 0.67 ANK2ankyrin 2, neuronal (202920_at), score: 0.77 APOBEC3Bapolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 3B (206632_s_at), score: -0.76 ARHGAP11ARho GTPase activating protein 11A (204492_at), score: -0.95 ARHGAP19Rho GTPase activating protein 19 (212738_at), score: -0.79 ARL6IP1ADP-ribosylation factor-like 6 interacting protein 1 (211935_at), score: -0.73 ASF1BASF1 anti-silencing function 1 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (218115_at), score: -0.93 ASPMasp (abnormal spindle) homolog, microcephaly associated (Drosophila) (219918_s_at), score: -0.95 ATP13A3ATPase type 13A3 (219558_at), score: 0.65 ATP2A2ATPase, Ca++ transporting, cardiac muscle, slow twitch 2 (212361_s_at), score: 0.69 AURKAaurora kinase A (208079_s_at), score: -0.86 AURKBaurora kinase B (209464_at), score: -1 BARD1BRCA1 associated RING domain 1 (205345_at), score: -0.89 BBS1Bardet-Biedl syndrome 1 (218471_s_at), score: 0.71 BIRC5baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 5 (202095_s_at), score: -0.95 BLMBloom syndrome (205733_at), score: -0.94 BMP6bone morphogenetic protein 6 (206176_at), score: 0.66 BRCA1breast cancer 1, early onset (204531_s_at), score: -0.89 BRCA2breast cancer 2, early onset (208368_s_at), score: -0.91 BUB1budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 1 homolog (yeast) (209642_at), score: -0.95 BUB1Bbudding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 1 homolog beta (yeast) (203755_at), score: -0.92 C12orf48chromosome 12 open reading frame 48 (220060_s_at), score: -0.82 C14orf1chromosome 14 open reading frame 1 (202562_s_at), score: 0.65 C14orf143chromosome 14 open reading frame 143 (214264_s_at), score: -0.72 C17orf91chromosome 17 open reading frame 91 (214696_at), score: 0.91 C18orf24chromosome 18 open reading frame 24 (217640_x_at), score: -0.99 C1orf112chromosome 1 open reading frame 112 (220840_s_at), score: -0.79 C1Rcomplement component 1, r subcomponent (212067_s_at), score: 0.64 C1RLcomplement component 1, r subcomponent-like (218983_at), score: 0.66 C21orf45chromosome 21 open reading frame 45 (219004_s_at), score: -0.98 C4orf18chromosome 4 open reading frame 18 (219872_at), score: 0.82 C9orf40chromosome 9 open reading frame 40 (218904_s_at), score: -0.74 CBR3carbonyl reductase 3 (205379_at), score: -0.88 CCDC15coiled-coil domain containing 15 (220466_at), score: -0.88 CCL2chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (216598_s_at), score: 0.69 CCNA2cyclin A2 (203418_at), score: -0.92 CCNB1cyclin B1 (214710_s_at), score: -0.78 CCNB2cyclin B2 (202705_at), score: -0.94 CCNE1cyclin E1 (213523_at), score: -0.73 CCNE2cyclin E2 (205034_at), score: -0.84 CCNFcyclin F (204826_at), score: -0.87 CD302CD302 molecule (203799_at), score: 0.64 CDC2cell division cycle 2, G1 to S and G2 to M (203213_at), score: -0.84 CDC20cell division cycle 20 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (202870_s_at), score: -0.93 CDC25Acell division cycle 25 homolog A (S. pombe) (204695_at), score: -0.8 CDC25Bcell division cycle 25 homolog B (S. pombe) (201853_s_at), score: -0.76 CDC25Ccell division cycle 25 homolog C (S. pombe) (205167_s_at), score: -0.79 CDC45LCDC45 cell division cycle 45-like (S. cerevisiae) (204126_s_at), score: -0.94 CDC6cell division cycle 6 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (203967_at), score: -0.84 CDC7cell division cycle 7 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (204510_at), score: -0.89 CDCA3cell division cycle associated 3 (221436_s_at), score: -0.96 CDCA8cell division cycle associated 8 (221520_s_at), score: -0.96 CDK2cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (204252_at), score: -0.9 CDKN2Dcyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2D (p19, inhibits CDK4) (210240_s_at), score: -0.81 CDKN3cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 3 (209714_s_at), score: -0.85 CDT1chromatin licensing and DNA replication factor 1 (209832_s_at), score: -0.93 CDYLchromodomain protein, Y-like (203100_s_at), score: 0.7 CENPAcentromere protein A (204962_s_at), score: -0.88 CENPC1centromere protein C 1 (204739_at), score: -0.74 CENPEcentromere protein E, 312kDa (205046_at), score: -0.95 CENPFcentromere protein F, 350/400ka (mitosin) (207828_s_at), score: -0.96 CENPIcentromere protein I (214804_at), score: -0.9 CENPMcentromere protein M (218741_at), score: -0.99 CEP110centrosomal protein 110kDa (205642_at), score: -0.8 CEP152centrosomal protein 152kDa (215170_s_at), score: -0.76 CEP192centrosomal protein 192kDa (218827_s_at), score: -0.75 CEP55centrosomal protein 55kDa (218542_at), score: -0.91 CEP72centrosomal protein 72kDa (219531_at), score: -0.81 CEP97centrosomal protein 97kDa (219886_at), score: -0.74 CHAF1Achromatin assembly factor 1, subunit A (p150) (214426_x_at), score: -0.94 CHAF1Bchromatin assembly factor 1, subunit B (p60) (204775_at), score: -0.93 CITcitron (rho-interacting, serine/threonine kinase 21) (212801_at), score: -0.92 CKAP2cytoskeleton associated protein 2 (218252_at), score: -0.97 CKS1BCDC28 protein kinase regulatory subunit 1B (201897_s_at), score: -0.83 CKS2CDC28 protein kinase regulatory subunit 2 (204170_s_at), score: -0.77 COL14A1collagen, type XIV, alpha 1 (212865_s_at), score: 0.73 COL15A1collagen, type XV, alpha 1 (203477_at), score: 0.79 CORINcorin, serine peptidase (220356_at), score: 0.64 CP110CP110 protein (204662_at), score: -0.75 CPA3carboxypeptidase A3 (mast cell) (205624_at), score: 0.82 CREG1cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes 1 (201200_at), score: 0.74 CTSOcathepsin O (203758_at), score: 0.65 CYP51A1cytochrome P450, family 51, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (216607_s_at), score: 0.72 DACT1dapper, antagonist of beta-catenin, homolog 1 (Xenopus laevis) (219179_at), score: 0.66 DCLRE1BDNA cross-link repair 1B (PSO2 homolog, S. cerevisiae) (219490_s_at), score: -0.75 DCP1ADCP1 decapping enzyme homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (218508_at), score: 0.67 DDX11DEAD/H (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp/His) box polypeptide 11 (CHL1-like helicase homolog, S. cerevisiae) (208149_x_at), score: -0.95 DDX12DEAD/H (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp/His) box polypeptide 12 (CHL1-like helicase homolog, S. cerevisiae) (213378_s_at), score: -0.83 DEKDEK oncogene (200934_at), score: -0.8 DEPDC1DEP domain containing 1 (220295_x_at), score: -0.98 DHCR77-dehydrocholesterol reductase (201790_s_at), score: 0.89 DHFRdihydrofolate reductase (202533_s_at), score: -0.8 DLEU2deleted in lymphocytic leukemia 2 (non-protein coding) (216870_x_at), score: -0.89 DLEU2Ldeleted in lymphocytic leukemia 2-like (215629_s_at), score: -0.8 DLGAP5discs, large (Drosophila) homolog-associated protein 5 (203764_at), score: -0.93 DMC1DMC1 dosage suppressor of mck1 homolog, meiosis-specific homologous recombination (yeast) (208382_s_at), score: -0.87 DMDdystrophin (203881_s_at), score: 0.64 DNA2DNA replication helicase 2 homolog (yeast) (213647_at), score: -0.83 DNASE2deoxyribonuclease II, lysosomal (214992_s_at), score: 0.67 DPP4dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (211478_s_at), score: 0.68 DPY19L2P2dpy-19-like 2 pseudogene 2 (C. elegans) (215143_at), score: -0.8 DRAMdamage-regulated autophagy modulator (218627_at), score: 0.74 DSCC1defective in sister chromatid cohesion 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (219000_s_at), score: -0.8 DSN1DSN1, MIND kinetochore complex component, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (219512_at), score: -0.94 DTLdenticleless homolog (Drosophila) (218585_s_at), score: -0.88 DTYMKdeoxythymidylate kinase (thymidylate kinase) (203270_at), score: -0.73 DVL3dishevelled, dsh homolog 3 (Drosophila) (201908_at), score: 0.74 E2F8E2F transcription factor 8 (219990_at), score: -0.87 ECT2epithelial cell transforming sequence 2 oncogene (219787_s_at), score: -0.73 ENTPD7ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 7 (220153_at), score: 0.78 ERCC6Lexcision repair cross-complementing rodent repair deficiency, complementation group 6-like (219650_at), score: -0.95 ERI2exoribonuclease 2 (213365_at), score: -0.74 ESPL1extra spindle pole bodies homolog 1 (S. cerevisiae) (38158_at), score: -0.82 EXO1exonuclease 1 (204603_at), score: -0.91 EXOSC9exosome component 9 (205061_s_at), score: -0.78 EZH2enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (Drosophila) (203358_s_at), score: -0.93 F10coagulation factor X (205620_at), score: 0.64 FABP3fatty acid binding protein 3, muscle and heart (mammary-derived growth inhibitor) (214285_at), score: 0.87 FAM111Afamily with sequence similarity 111, member A (218248_at), score: -0.77 FAM64Afamily with sequence similarity 64, member A (221591_s_at), score: -0.86 FAM8A1family with sequence similarity 8, member A1 (203420_at), score: 0.67 FANCAFanconi anemia, complementation group A (203805_s_at), score: -0.83 FANCGFanconi anemia, complementation group G (203564_at), score: -0.93 FANCIFanconi anemia, complementation group I (213007_at), score: -0.94 FBXO5F-box protein 5 (218875_s_at), score: -0.8 FCGRTFc fragment of IgG, receptor, transporter, alpha (218831_s_at), score: 0.68 FEN1flap structure-specific endonuclease 1 (204767_s_at), score: -0.75 FGF7fibroblast growth factor 7 (keratinocyte growth factor) (205782_at), score: 0.72 FN3KRPfructosamine 3 kinase related protein (218210_at), score: -0.75 FOXM1forkhead box M1 (202580_x_at), score: -0.93 FRYfurry homolog (Drosophila) (204072_s_at), score: 0.69 GABARAPL1GABA(A) receptor-associated protein like 1 (208868_s_at), score: 0.72 GALNAC4S-6STB cell RAG associated protein (203066_at), score: 0.64 GCH1GTP cyclohydrolase 1 (204224_s_at), score: 0.64 GEMGTP binding protein overexpressed in skeletal muscle (204472_at), score: 0.66 GFPT2glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase 2 (205100_at), score: 0.64 GINS1GINS complex subunit 1 (Psf1 homolog) (206102_at), score: -0.92 GINS2GINS complex subunit 2 (Psf2 homolog) (221521_s_at), score: -0.97 GINS3GINS complex subunit 3 (Psf3 homolog) (45633_at), score: -0.87 GINS4GINS complex subunit 4 (Sld5 homolog) (211767_at), score: -0.84 GMNNgeminin, DNA replication inhibitor (218350_s_at), score: -0.86 GNPTABN-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate transferase, alpha and beta subunits (212959_s_at), score: 0.77 GPR183G protein-coupled receptor 183 (205419_at), score: 0.83 GPSM2G-protein signaling modulator 2 (AGS3-like, C. elegans) (221922_at), score: -0.77 GRAMD1CGRAM domain containing 1C (219313_at), score: -0.75 GTSE1G-2 and S-phase expressed 1 (204318_s_at), score: -0.98 HBEGFheparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (203821_at), score: 0.67 HELLShelicase, lymphoid-specific (220085_at), score: -0.85 HIRIP3HIRA interacting protein 3 (204504_s_at), score: -0.8 HIVEP1human immunodeficiency virus type I enhancer binding protein 1 (204512_at), score: 0.8 HJURPHolliday junction recognition protein (218726_at), score: -0.94 HMGB1L10high-mobility group box 1-like 10 (216508_x_at), score: -0.73 HMGB2high-mobility group box 2 (208808_s_at), score: -0.89 HMGB3high-mobility group box 3 (203744_at), score: -0.84 HMGB3L1high-mobility group box 3-like 1 (216548_x_at), score: -0.81 HMMRhyaluronan-mediated motility receptor (RHAMM) (207165_at), score: -0.93 ICAM1intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (202638_s_at), score: 0.98 IL6interleukin 6 (interferon, beta 2) (205207_at), score: 0.94 IL8interleukin 8 (202859_x_at), score: 0.69 INSIG1insulin induced gene 1 (201627_s_at), score: 0.72 ITGA1integrin, alpha 1 (214660_at), score: 0.68 ITGB3BPintegrin beta 3 binding protein (beta3-endonexin) (205176_s_at), score: -0.87 KIAA0101KIAA0101 (202503_s_at), score: -0.74 KIAA0247KIAA0247 (202181_at), score: 0.67 KIAA0586KIAA0586 (205631_at), score: -0.86 KIF11kinesin family member 11 (204444_at), score: -0.95 KIF14kinesin family member 14 (206364_at), score: -0.92 KIF15kinesin family member 15 (219306_at), score: -0.97 KIF18Bkinesin family member 18B (222039_at), score: -0.98 KIF20Akinesin family member 20A (218755_at), score: -0.84 KIF20Bkinesin family member 20B (205235_s_at), score: -0.94 KIF22kinesin family member 22 (202183_s_at), score: -0.97 KIF23kinesin family member 23 (204709_s_at), score: -0.88 KIF2Ckinesin family member 2C (209408_at), score: -0.92 KIF4Akinesin family member 4A (218355_at), score: -0.99 KIFC1kinesin family member C1 (209680_s_at), score: -0.84 KNTC1kinetochore associated 1 (206316_s_at), score: -0.96 LIFleukemia inhibitory factor (cholinergic differentiation factor) (205266_at), score: 0.72 LIG1ligase I, DNA, ATP-dependent (202726_at), score: -0.97 LMBRD1LMBR1 domain containing 1 (218191_s_at), score: 0.73 LMCD1LIM and cysteine-rich domains 1 (218574_s_at), score: 0.83 LMNB1lamin B1 (203276_at), score: -0.94 LMNB2lamin B2 (216952_s_at), score: -0.79 LOC81691exonuclease NEF-sp (208107_s_at), score: -0.81 LYSTlysosomal trafficking regulator (203518_at), score: 0.65 MAD2L1MAD2 mitotic arrest deficient-like 1 (yeast) (203362_s_at), score: -0.98 MAGI2membrane associated guanylate kinase, WW and PDZ domain containing 2 (209737_at), score: 0.67 MAN1C1mannosidase, alpha, class 1C, member 1 (218918_at), score: 0.67 MARCH2membrane-associated ring finger (C3HC4) 2 (210075_at), score: 0.72 MCM10minichromosome maintenance complex component 10 (220651_s_at), score: -0.97 MCM2minichromosome maintenance complex component 2 (202107_s_at), score: -0.96 MCM3minichromosome maintenance complex component 3 (201555_at), score: -0.9 MCM4minichromosome maintenance complex component 4 (212141_at), score: -0.92 MCM5minichromosome maintenance complex component 5 (216237_s_at), score: -0.98 MCM6minichromosome maintenance complex component 6 (201930_at), score: -0.75 MCM7minichromosome maintenance complex component 7 (210983_s_at), score: -0.93 MEIS3P1Meis homeobox 3 pseudogene 1 (214077_x_at), score: 0.64 MELKmaternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase (204825_at), score: -0.84 MFAP3microfibrillar-associated protein 3 (213123_at), score: 0.72 MFAP4microfibrillar-associated protein 4 (212713_at), score: 0.7 MKI67antigen identified by monoclonal antibody Ki-67 (212022_s_at), score: -0.92 MLF1IPMLF1 interacting protein (218883_s_at), score: -0.89 MLXIPMLX interacting protein (202519_at), score: 0.66 MNS1meiosis-specific nuclear structural 1 (219703_at), score: -0.75 MRE11AMRE11 meiotic recombination 11 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (205395_s_at), score: -0.8 MSH2mutS homolog 2, colon cancer, nonpolyposis type 1 (E. coli) (209421_at), score: -0.85 MTSS1metastasis suppressor 1 (203037_s_at), score: 0.73 MYBL1v-myb myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog (avian)-like 1 (213906_at), score: -0.78 MYBL2v-myb myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog (avian)-like 2 (201710_at), score: -0.78 MYO19myosin XIX (219320_at), score: -0.85 NADSYN1NAD synthetase 1 (218840_s_at), score: 0.67 NAMPTnicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (217738_at), score: 0.71 NASPnuclear autoantigenic sperm protein (histone-binding) (201970_s_at), score: -0.84 NCAPD2non-SMC condensin I complex, subunit D2 (201774_s_at), score: -0.9 NCAPD3non-SMC condensin II complex, subunit D3 (212789_at), score: -0.91 NCAPGnon-SMC condensin I complex, subunit G (218663_at), score: -0.93 NCAPG2non-SMC condensin II complex, subunit G2 (219588_s_at), score: -0.94 NCAPHnon-SMC condensin I complex, subunit H (212949_at), score: -0.96 NDC80NDC80 homolog, kinetochore complex component (S. cerevisiae) (204162_at), score: -0.93 NEDD9neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally down-regulated 9 (202149_at), score: 0.7 NEIL3nei endonuclease VIII-like 3 (E. coli) (219502_at), score: -0.89 NEK2NIMA (never in mitosis gene a)-related kinase 2 (204641_at), score: -0.92 NFIL3nuclear factor, interleukin 3 regulated (203574_at), score: 0.65 NFKB1nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1 (209239_at), score: 0.71 NINJ1ninjurin 1 (203045_at), score: 0.72 NR4A3nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 3 (209959_at), score: 0.68 NUDT1nudix (nucleoside diphosphate linked moiety X)-type motif 1 (204766_s_at), score: -0.76 NUP107nucleoporin 107kDa (218768_at), score: -0.8 NUSAP1nucleolar and spindle associated protein 1 (218039_at), score: -0.95 OIP5Opa interacting protein 5 (213599_at), score: -0.96 OLFML2Aolfactomedin-like 2A (213075_at), score: 0.74 ORC1Lorigin recognition complex, subunit 1-like (yeast) (205085_at), score: -0.83 ORC6Lorigin recognition complex, subunit 6 like (yeast) (219105_x_at), score: -0.9 P2RX4purinergic receptor P2X, ligand-gated ion channel, 4 (204088_at), score: 0.68 PARP2poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 2 (214086_s_at), score: -0.75 PASKPAS domain containing serine/threonine kinase (216945_x_at), score: -0.74 PBKPDZ binding kinase (219148_at), score: -0.92 PCNTpericentrin (203660_s_at), score: -0.81 PDGFAplatelet-derived growth factor alpha polypeptide (205463_s_at), score: 0.73 PDGFDplatelet derived growth factor D (219304_s_at), score: 0.75 PIGBphosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis, class B (214151_s_at), score: 0.8 PIK3CDphosphoinositide-3-kinase, catalytic, delta polypeptide (203879_at), score: 0.68 PIONpigeon homolog (Drosophila) (222150_s_at), score: 0.64 PKMYT1protein kinase, membrane associated tyrosine/threonine 1 (204267_x_at), score: -0.85 PLK1polo-like kinase 1 (Drosophila) (202240_at), score: -0.82 PLK4polo-like kinase 4 (Drosophila) (204887_s_at), score: -0.9 PLSCR4phospholipid scramblase 4 (218901_at), score: 0.7 PMEPA1prostate transmembrane protein, androgen induced 1 (217875_s_at), score: 0.7 POLA1polymerase (DNA directed), alpha 1, catalytic subunit (204835_at), score: -0.96 POLA2polymerase (DNA directed), alpha 2 (70kD subunit) (204441_s_at), score: -0.86 POLD1polymerase (DNA directed), delta 1, catalytic subunit 125kDa (203422_at), score: -0.94 POLD3polymerase (DNA-directed), delta 3, accessory subunit (212836_at), score: -0.82 POLEpolymerase (DNA directed), epsilon (216026_s_at), score: -0.95 POLE2polymerase (DNA directed), epsilon 2 (p59 subunit) (205909_at), score: -0.85 POLQpolymerase (DNA directed), theta (219510_at), score: -0.91 PPLperiplakin (203407_at), score: 0.64 PRC1protein regulator of cytokinesis 1 (218009_s_at), score: -0.87 PRIM1primase, DNA, polypeptide 1 (49kDa) (205053_at), score: -0.92 PRKG1protein kinase, cGMP-dependent, type I (207119_at), score: 0.69 PRR11proline rich 11 (219392_x_at), score: -0.76 PSMC3IPPSMC3 interacting protein (213951_s_at), score: -0.95 PSRC1proline/serine-rich coiled-coil 1 (201896_s_at), score: -0.89 PTHLHparathyroid hormone-like hormone (211756_at), score: 0.71 PTTG1pituitary tumor-transforming 1 (203554_x_at), score: -0.93 PTTG3pituitary tumor-transforming 3 (208511_at), score: -0.8 RAB33ARAB33A, member RAS oncogene family (206039_at), score: 0.73 RACGAP1Rac GTPase activating protein 1 (222077_s_at), score: -0.85 RAD51AP1RAD51 associated protein 1 (204146_at), score: -0.92 RAD51L1RAD51-like 1 (S. cerevisiae) (210255_at), score: -0.78 RAD54BRAD54 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (219494_at), score: -0.91 RAD54LRAD54-like (S. cerevisiae) (204558_at), score: -0.93 RAD9ARAD9 homolog A (S. pombe) (204828_at), score: -0.73 RBL1retinoblastoma-like 1 (p107) (205296_at), score: -0.84 RFC2replication factor C (activator 1) 2, 40kDa (203696_s_at), score: -0.74 RFC3replication factor C (activator 1) 3, 38kDa (204127_at), score: -1 RFC4replication factor C (activator 1) 4, 37kDa (204023_at), score: -0.85 RFWD3ring finger and WD repeat domain 3 (218564_at), score: -0.8 RNASEH2Aribonuclease H2, subunit A (203022_at), score: -0.96 RPL39Lribosomal protein L39-like (210115_at), score: -0.85 RRM2ribonucleotide reductase M2 polypeptide (209773_s_at), score: -0.85 RUNX1runt-related transcription factor 1 (209360_s_at), score: 0.82 RWDD2ARWD domain containing 2A (213555_at), score: 0.71 SAP30Sin3A-associated protein, 30kDa (204900_x_at), score: -0.82 SC4MOLsterol-C4-methyl oxidase-like (209146_at), score: 0.8 SCARA3scavenger receptor class A, member 3 (219416_at), score: -0.87 SH3TC2SH3 domain and tetratricopeptide repeats 2 (219710_at), score: -0.73 SHCBP1SHC SH2-domain binding protein 1 (219493_at), score: -0.87 SHMT1serine hydroxymethyltransferase 1 (soluble) (209980_s_at), score: -0.88 SKILSKI-like oncogene (206675_s_at), score: 0.66 SLC19A2solute carrier family 19 (thiamine transporter), member 2 (209681_at), score: 0.8 SLC2A14solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 14 (222088_s_at), score: 0.66 SLC2A3P1solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 3 pseudogene 1 (221751_at), score: 0.66 SLC33A1solute carrier family 33 (acetyl-CoA transporter), member 1 (203165_s_at), score: 0.65 SLC43A3solute carrier family 43, member 3 (213113_s_at), score: -0.76 SMC2structural maintenance of chromosomes 2 (204240_s_at), score: -0.95 SMC4structural maintenance of chromosomes 4 (201663_s_at), score: -0.82 SOX9SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 9 (202935_s_at), score: 0.68 SPAG5sperm associated antigen 5 (203145_at), score: -0.87 SPATA2Lspermatogenesis associated 2-like (214965_at), score: 0.74 SPC25SPC25, NDC80 kinetochore complex component, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (209891_at), score: -0.94 SPRED2sprouty-related, EVH1 domain containing 2 (212458_at), score: 0.64 SQLEsqualene epoxidase (213562_s_at), score: 0.85 SREBF2sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 2 (201247_at), score: 0.75 SRFserum response factor (c-fos serum response element-binding transcription factor) (202401_s_at), score: 0.69 ST3GAL1ST3 beta-galactoside alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase 1 (208322_s_at), score: 0.66 STILSCL/TAL1 interrupting locus (205339_at), score: -0.9 STK38Lserine/threonine kinase 38 like (212572_at), score: 0.91 STMN1stathmin 1/oncoprotein 18 (200783_s_at), score: -0.8 STX6syntaxin 6 (212799_at), score: 0.72 SUV39H1suppressor of variegation 3-9 homolog 1 (Drosophila) (218619_s_at), score: -0.83 SVEP1sushi, von Willebrand factor type A, EGF and pentraxin domain containing 1 (213247_at), score: 0.82 TACC3transforming, acidic coiled-coil containing protein 3 (218308_at), score: -0.97 TGFBR1transforming growth factor, beta receptor 1 (206943_at), score: 0.7 TIMELESStimeless homolog (Drosophila) (203046_s_at), score: -0.98 TK1thymidine kinase 1, soluble (202338_at), score: -0.84 TM6SF1transmembrane 6 superfamily member 1 (219892_at), score: 0.8 TM7SF2transmembrane 7 superfamily member 2 (210130_s_at), score: 0.71 TMEM194Atransmembrane protein 194A (212621_at), score: -0.98 TMEM39Atransmembrane protein 39A (218615_s_at), score: 0.77 TMPOthymopoietin (209754_s_at), score: -0.73 TOM1target of myb1 (chicken) (202807_s_at), score: 0.7 TOP2Atopoisomerase (DNA) II alpha 170kDa (201291_s_at), score: -0.85 TP53BP2tumor protein p53 binding protein, 2 (203120_at), score: 0.7 TPD52L1tumor protein D52-like 1 (203786_s_at), score: 0.72 TPX2TPX2, microtubule-associated, homolog (Xenopus laevis) (210052_s_at), score: -0.91 TRAF3TNF receptor-associated factor 3 (221571_at), score: 0.64 TRIB1tribbles homolog 1 (Drosophila) (202241_at), score: 0.72 TRIP13thyroid hormone receptor interactor 13 (204033_at), score: -0.95 TRMT5TRM5 tRNA methyltransferase 5 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (221952_x_at), score: -0.78 TROAPtrophinin associated protein (tastin) (204649_at), score: -0.84 TTC17tetratricopeptide repeat domain 17 (218972_at), score: 0.68 TTKTTK protein kinase (204822_at), score: -0.96 UBE2Cubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2C (202954_at), score: -0.88 UNGuracil-DNA glycosylase (202330_s_at), score: -0.74 VCLvinculin (200930_s_at), score: 0.8 VEGFAvascular endothelial growth factor A (211527_x_at), score: 0.66 VRK1vaccinia related kinase 1 (203856_at), score: -0.78 WDHD1WD repeat and HMG-box DNA binding protein 1 (216228_s_at), score: -0.84 WDR62WD repeat domain 62 (215218_s_at), score: -0.83 WDR76WD repeat domain 76 (205519_at), score: -0.94 WEE1WEE1 homolog (S. pombe) (212533_at), score: -0.76 WHSC1Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome candidate 1 (209053_s_at), score: -0.89 WRAP53WD repeat containing, antisense to TP53 (44563_at), score: -0.88 WWTR1WW domain containing transcription regulator 1 (202132_at), score: 0.66 YRDCyrdC domain containing (E. coli) (218647_s_at), score: 0.77 ZNF85zinc finger protein 85 (206572_x_at), score: -0.78 ZWILCHZwilch, kinetochore associated, homolog (Drosophila) (218349_s_at), score: -0.75 ZWINTZW10 interactor (204026_s_at), score: -0.85
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5CTwin.CEL | 5 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 5 |
| 6Twin.CEL | 6 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 6 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690344.cel | 10 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM00038C |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690472.cel | 17 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM00038C |
| 2Twin.CEL | 2 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 2 |
| 1Twin.CEL | 1 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 1 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949557.cel | 1 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486151.cel | 26 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| 9118_CNTL.CEL | 11 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | none | WBS 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690376.cel | 13 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11513 |
| 46A.CEL | 1 | 3 | DS-mosaic | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-mosaic 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485891.cel | 13 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485651.cel | 1 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486291.cel | 33 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486271.cel | 32 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485811.cel | 9 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486331.cel | 35 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486351.cel | 36 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486231.cel | 30 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485851.cel | 11 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |