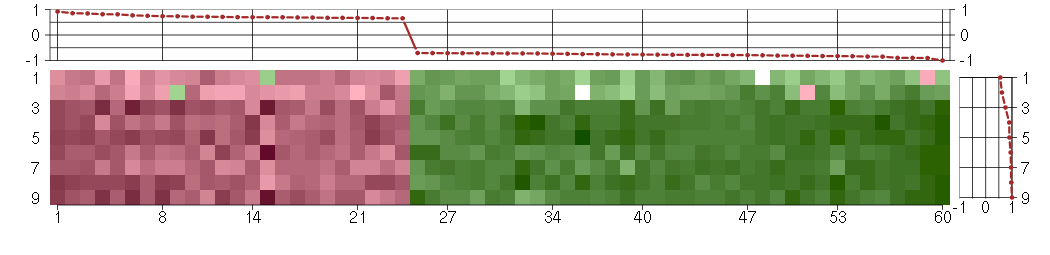

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

skeletal system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the skeleton over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The skeleton is the bony framework of the body in vertebrates (endoskeleton) or the hard outer envelope of insects (exoskeleton or dermoskeleton).
ossification
The formation of bone or of a bony substance, or the conversion of fibrous tissue or of cartilage into bone or a bony substance.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tissue over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
regulation of ossification
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of bone formation.
bone mineralization
The deposition of calcium phosphate in bone tissue.
regulation of bone mineralization
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of bone mineralization.
biomineral formation
Formation of hard tissues that consist mainly of inorganic compounds, and also contain a small amounts of organic matrices that are believed to play important roles in their formation.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of tissue remodeling
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of tissue remodeling.
bone remodeling
The continuous turnover of bone matrix and mineral that involves first, an increase in resorption (osteoclastic activity) and later, reactive bone formation (osteoblastic activity). The process of bone remodeling takes place in the adult skeleton at discrete foci. The process ensures the mechanical integrity of the skeleton throughout life and plays an important role in calcium homeostasis. An imbalance in the regulation of bone resorption and bone formation results in many of the metabolic bone diseases, such as osteoporosis.
regulation of bone remodeling
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of bone remodeling, the processes of bone formation and resorption that combine to maintain skeletal integrity.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
tissue remodeling
The reorganization or renovation of existing tissues. This process can either change the characteristics of a tissue such as in blood vessel remodeling, or result in the dynamic equilibrium of a tissue such as in bone remodeling.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
bone development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of bone over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Bone is the hard skeletal connective tissue consisting of both mineral and cellular components.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biomineral formation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of biomineral formation, the formation of hard tissues that consist mainly of inorganic compounds.
all
This term is the most general term possible
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of tissue remodeling
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of tissue remodeling.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
regulation of ossification
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of bone formation.
regulation of biomineral formation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of biomineral formation, the formation of hard tissues that consist mainly of inorganic compounds.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
regulation of bone remodeling
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of bone remodeling, the processes of bone formation and resorption that combine to maintain skeletal integrity.
regulation of bone mineralization
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of bone mineralization.
regulation of bone mineralization
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of bone mineralization.
tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tissue over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
ossification
The formation of bone or of a bony substance, or the conversion of fibrous tissue or of cartilage into bone or a bony substance.
bone development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of bone over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Bone is the hard skeletal connective tissue consisting of both mineral and cellular components.
regulation of ossification
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of bone formation.
bone mineralization
The deposition of calcium phosphate in bone tissue.
regulation of biomineral formation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of biomineral formation, the formation of hard tissues that consist mainly of inorganic compounds.

extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
all
This term is the most general term possible

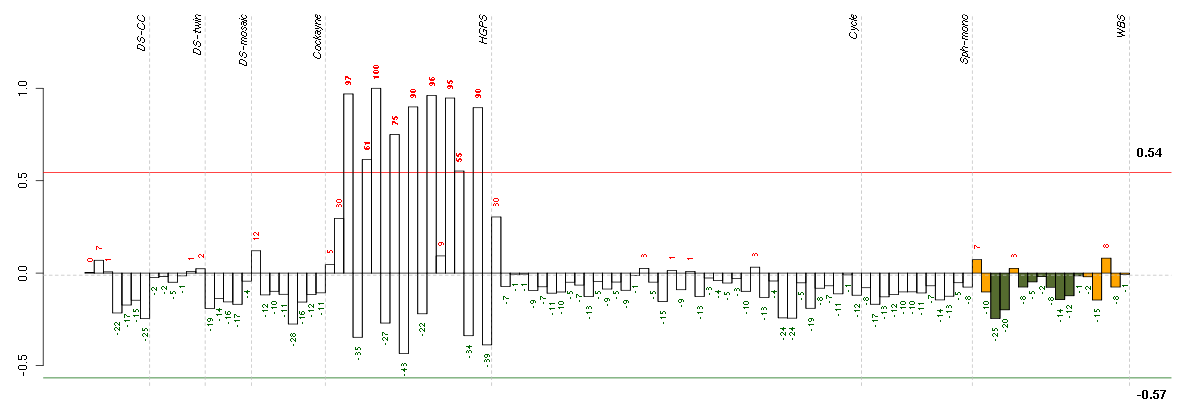
ANKRD1ankyrin repeat domain 1 (cardiac muscle) (206029_at), score: -0.9 AUTS2autism susceptibility candidate 2 (212599_at), score: 0.75 BST1bone marrow stromal cell antigen 1 (205715_at), score: -0.75 C1orf54chromosome 1 open reading frame 54 (219506_at), score: -0.72 C1QTNF3C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 3 (220988_s_at), score: 0.7 CAMK2N1calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II inhibitor 1 (218309_at), score: 0.92 CDH4cadherin 4, type 1, R-cadherin (retinal) (206866_at), score: 0.7 CTSCcathepsin C (201487_at), score: -0.71 CYP1B1cytochrome P450, family 1, subfamily B, polypeptide 1 (202436_s_at), score: -0.72 ENPP1ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1 (205066_s_at), score: 0.69 EPHA5EPH receptor A5 (215664_s_at), score: -0.9 F2Rcoagulation factor II (thrombin) receptor (203989_x_at), score: -0.83 FHOD3formin homology 2 domain containing 3 (218980_at), score: 0.67 FSTfollistatin (204948_s_at), score: -0.72 GABBR2gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) B receptor, 2 (209990_s_at), score: 0.67 GPR116G protein-coupled receptor 116 (212950_at), score: -0.83 HMOX1heme oxygenase (decycling) 1 (203665_at), score: 0.69 HS3ST3A1heparan sulfate (glucosamine) 3-O-sulfotransferase 3A1 (219985_at), score: 0.81 IFI27interferon, alpha-inducible protein 27 (202411_at), score: -0.72 ISLRimmunoglobulin superfamily containing leucine-rich repeat (207191_s_at), score: 0.72 JAG1jagged 1 (Alagille syndrome) (216268_s_at), score: -0.83 KCNN4potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 4 (204401_at), score: 0.74 KRT18keratin 18 (201596_x_at), score: -0.76 LGALS3BPlectin, galactoside-binding, soluble, 3 binding protein (200923_at), score: -0.71 LIPGlipase, endothelial (219181_at), score: -0.8 LMO2LIM domain only 2 (rhombotin-like 1) (204249_s_at), score: -0.81 LPHN2latrophilin 2 (206953_s_at), score: -0.85 LPXNleupaxin (216250_s_at), score: 0.7 LRRC15leucine rich repeat containing 15 (213909_at), score: 0.84 LRRC17leucine rich repeat containing 17 (205381_at), score: -0.76 MBPmyelin basic protein (210136_at), score: -0.79 MEOX2mesenchyme homeobox 2 (206201_s_at), score: -1 MESTmesoderm specific transcript homolog (mouse) (202016_at), score: -0.81 MGPmatrix Gla protein (202291_s_at), score: -0.85 MSX1msh homeobox 1 (205932_s_at), score: 0.67 MT1Mmetallothionein 1M (217546_at), score: 0.65 NBL1neuroblastoma, suppression of tumorigenicity 1 (37005_at), score: 0.72 NDUFA4L2NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex, 4-like 2 (218484_at), score: -0.82 NET1neuroepithelial cell transforming 1 (201830_s_at), score: 0.71 NID2nidogen 2 (osteonidogen) (204114_at), score: -0.72 NKX3-1NK3 homeobox 1 (209706_at), score: 0.77 NRG1neuregulin 1 (206343_s_at), score: 0.68 NRXN3neurexin 3 (205795_at), score: -0.72 PDE10Aphosphodiesterase 10A (205501_at), score: -0.78 PLA2G16phospholipase A2, group XVI (209581_at), score: -0.77 PNMA2paraneoplastic antigen MA2 (209598_at), score: -0.78 PTPRZ1protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor-type, Z polypeptide 1 (204469_at), score: -0.79 RELNreelin (205923_at), score: -0.78 RGS7regulator of G-protein signaling 7 (206290_s_at), score: -0.71 SGCDsarcoglycan, delta (35kDa dystrophin-associated glycoprotein) (213543_at), score: 0.67 SLC7A8solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 8 (216092_s_at), score: 0.81 SRGNserglycin (201859_at), score: -0.75 STMN2stathmin-like 2 (203000_at), score: 0.66 TINAGL1tubulointerstitial nephritis antigen-like 1 (219058_x_at), score: -0.74 TMEM158transmembrane protein 158 (213338_at), score: 0.85 TNXAtenascin XA pseudogene (213451_x_at), score: -0.78 TNXBtenascin XB (216333_x_at), score: -0.77 TUFT1tuftelin 1 (205807_s_at), score: -0.73 ZNF423zinc finger protein 423 (214761_at), score: -0.9 ZNF536zinc finger protein 536 (206403_at), score: 0.73
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690416.cel | 15 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690248.cel | 5 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11513 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690304.cel | 8 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GMO8398C |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690472.cel | 17 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM00038C |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690344.cel | 10 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM00038C |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690392.cel | 14 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GMO8398C |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690360.cel | 12 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690223.cel | 3 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM00038C |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690256.cel | 6 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GMO8398C |