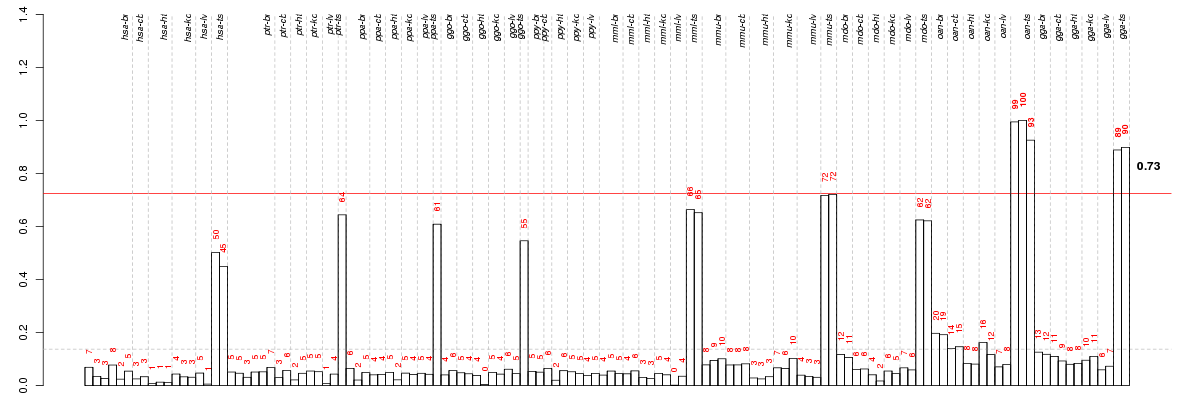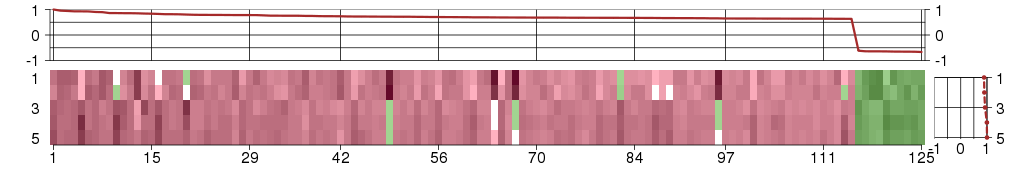

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

reproduction
The production by an organism of new individuals that contain some portion of their genetic material inherited from that organism.
chromosome segregation
The process by which genetic material, in the form of chromosomes, is organized into specific structures and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets.
M phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which mitosis takes place.
microtubule cytoskeleton organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising microtubules and their associated proteins.
mitotic cell cycle
Progression through the phases of the mitotic cell cycle, the most common eukaryotic cell cycle, which canonically comprises four successive phases called G1, S, G2, and M and includes replication of the genome and the subsequent segregation of chromosomes into daughter cells. In some variant cell cycles nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division, or G1 and G2 phases may be absent.
M phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the cell cycle comprising nuclear division.
nuclear division
A process by which a cell nucleus is divided into two nuclei, with DNA and other nuclear contents distributed between the daughter nuclei.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
cytoskeleton organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
DNA metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving deoxyribonucleic acid. This is one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
DNA recombination
Any process by which a new genotype is formed by reassortment of genes resulting in gene combinations different from those that were present in the parents. In eukaryotes genetic recombination can occur by chromosome assortment, intrachromosomal recombination, or nonreciprocal interchromosomal recombination. Intrachromosomal recombination occurs by crossing over. In bacteria it may occur by genetic transformation, conjugation, transduction, or F-duction.
DNA packaging
Any process by which DNA and associated proteins are formed into a compact, orderly structure.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
microtubule-based process
Any cellular process that depends upon or alters the microtubule cytoskeleton, that part of the cytoskeleton comprising microtubules and their associated proteins.
cell cycle
The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division.
spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the spindle, the array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during DNA segregation and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
mitotic spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the microtubule spindle during a mitotic cell cycle.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
meiosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the nuclear division phase of a meiotic cell cycle, the specialized nuclear and cell division in which a single diploid cell undergoes two nuclear divisions following a single round of DNA replication in order to produce four daughter cells that contain half the number of chromosomes as the diploid cell. Meiotic division occurs during the formation of gametes from diploid organisms and at the beginning of haplophase in those organisms that alternate between diploid and haploid generations.
meiosis I
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the first phase of meiosis, in which cells divide and homologous chromosomes are paired and segregated from each other, producing two daughter cells.
reciprocal meiotic recombination
The cell cycle process whereby double strand breaks are formed and repaired through a double Holliday junction intermediate. This results in the equal exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids in a pair of homologous chromosomes. These reciprocal recombinant products ensure the proper segregation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I and create genetic diversity.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
cell cycle phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through one of the biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
organelle fission
The creation of two or more organelles by division of one organelle.
meiotic cell cycle
Progression through the phases of the meiotic cell cycle, in which canonically a cell replicates to produce four offspring with half the chromosomal content of the progenitor cell.
M phase of meiotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the meiotic cell cycle during which meiosis takes place.
DNA conformation change
A cellular process that results in a change in the spatial configuration of a DNA molecule. A conformation change can bend DNA, or alter the, twist, writhe, or linking number of a DNA molecule.
nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleic acids.
all
NA
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
DNA packaging
Any process by which DNA and associated proteins are formed into a compact, orderly structure.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
microtubule cytoskeleton organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising microtubules and their associated proteins.
mitotic spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the microtubule spindle during a mitotic cell cycle.
DNA metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving deoxyribonucleic acid. This is one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
mitotic spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the microtubule spindle during a mitotic cell cycle.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
meiosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the nuclear division phase of a meiotic cell cycle, the specialized nuclear and cell division in which a single diploid cell undergoes two nuclear divisions following a single round of DNA replication in order to produce four daughter cells that contain half the number of chromosomes as the diploid cell. Meiotic division occurs during the formation of gametes from diploid organisms and at the beginning of haplophase in those organisms that alternate between diploid and haploid generations.
M phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which mitosis takes place.
spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the spindle, the array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during DNA segregation and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
M phase of meiotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the meiotic cell cycle during which meiosis takes place.
meiosis I
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the first phase of meiosis, in which cells divide and homologous chromosomes are paired and segregated from each other, producing two daughter cells.
reciprocal meiotic recombination
The cell cycle process whereby double strand breaks are formed and repaired through a double Holliday junction intermediate. This results in the equal exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids in a pair of homologous chromosomes. These reciprocal recombinant products ensure the proper segregation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I and create genetic diversity.
reciprocal meiotic recombination
The cell cycle process whereby double strand breaks are formed and repaired through a double Holliday junction intermediate. This results in the equal exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids in a pair of homologous chromosomes. These reciprocal recombinant products ensure the proper segregation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I and create genetic diversity.

condensed chromosome
A highly compacted molecule of DNA and associated proteins resulting in a cytologically distinct structure.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a chromosome that includes the centromeric DNA and associated proteins. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
condensed chromosome kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of a condensed chromosome and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
condensed chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a condensed chromosome that includes the centromere and associated proteins, including the kinetochore. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
nucleus
A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent.
chromosome
A structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
microtubule
Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle.
microtubule cytoskeleton
The part of the cytoskeleton (the internal framework of a cell) composed of microtubules and associated proteins.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
microtubule
Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
condensed chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a condensed chromosome that includes the centromere and associated proteins, including the kinetochore. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
microtubule
Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle.
condensed chromosome kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of a condensed chromosome and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.

AGBL3ATP/GTP binding protein-like 3 (ENSG00000146856), score: 0.74 AK7adenylate kinase 7 (ENSG00000140057), score: 0.67 ANKRD5ankyrin repeat domain 5 (ENSG00000132623), score: 0.64 ASF1AASF1 anti-silencing function 1 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000111875), score: 0.7 ASPMasp (abnormal spindle) homolog, microcephaly associated (Drosophila) (ENSG00000066279), score: 0.92 ATAD2ATPase family, AAA domain containing 2 (ENSG00000156802), score: 0.68 B3GNT5UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 5 (ENSG00000176597), score: 0.75 C12orf48chromosome 12 open reading frame 48 (ENSG00000185480), score: 0.66 C12orf50chromosome 12 open reading frame 50 (ENSG00000165805), score: 0.65 C13orf34chromosome 13 open reading frame 34 (ENSG00000136122), score: 0.72 C14orf39chromosome 14 open reading frame 39 (ENSG00000179008), score: 0.9 C14orf50chromosome 14 open reading frame 50 (ENSG00000165807), score: 0.68 C1orf100chromosome 1 open reading frame 100 (ENSG00000173728), score: 0.64 C1orf111chromosome 1 open reading frame 111 (ENSG00000171722), score: 0.69 C1orf158chromosome 1 open reading frame 158 (ENSG00000157330), score: 0.74 C1orf9chromosome 1 open reading frame 9 (ENSG00000094975), score: 0.76 C20orf85chromosome 20 open reading frame 85 (ENSG00000124237), score: 0.64 C4orf47chromosome 4 open reading frame 47 (ENSG00000205129), score: 0.72 C5orf51chromosome 5 open reading frame 51 (ENSG00000205765), score: 0.69 C7orf57chromosome 7 open reading frame 57 (ENSG00000164746), score: 0.7 C7orf60chromosome 7 open reading frame 60 (ENSG00000164603), score: 0.64 CCDC27coiled-coil domain containing 27 (ENSG00000162592), score: 0.7 CCDC67coiled-coil domain containing 67 (ENSG00000165325), score: 0.68 CDC42EP4CDC42 effector protein (Rho GTPase binding) 4 (ENSG00000179604), score: -0.64 CENPIcentromere protein I (ENSG00000102384), score: 0.95 CENPKcentromere protein K (ENSG00000123219), score: 0.71 CHAF1Bchromatin assembly factor 1, subunit B (p60) (ENSG00000159259), score: 0.68 CNGA2cyclic nucleotide gated channel alpha 2 (ENSG00000183862), score: 0.83 CNGB1cyclic nucleotide gated channel beta 1 (ENSG00000070729), score: 0.68 COL17A1collagen, type XVII, alpha 1 (ENSG00000065618), score: 0.71 CPA1carboxypeptidase A1 (pancreatic) (ENSG00000091704), score: 0.71 CRY2cryptochrome 2 (photolyase-like) (ENSG00000121671), score: -0.62 CRYBA1crystallin, beta A1 (ENSG00000108255), score: 0.69 CXorf22chromosome X open reading frame 22 (ENSG00000165164), score: 0.85 CXorf30chromosome X open reading frame 30 (ENSG00000205081), score: 0.9 CYP11A1cytochrome P450, family 11, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000140459), score: 0.76 DMC1DMC1 dosage suppressor of mck1 homolog, meiosis-specific homologous recombination (yeast) (ENSG00000100206), score: 0.68 DMRT3doublesex and mab-3 related transcription factor 3 (ENSG00000064218), score: 0.82 DNAI1dynein, axonemal, intermediate chain 1 (ENSG00000122735), score: 0.64 DNAI2dynein, axonemal, intermediate chain 2 (ENSG00000171595), score: 0.63 EFCAB1EF-hand calcium binding domain 1 (ENSG00000034239), score: 0.79 EFCAB5EF-hand calcium binding domain 5 (ENSG00000176927), score: 0.66 ERCC6Lexcision repair cross-complementing rodent repair deficiency, complementation group 6-like (ENSG00000186871), score: 0.93 ESYT2extended synaptotagmin-like protein 2 (ENSG00000117868), score: -0.66 EXO1exonuclease 1 (ENSG00000174371), score: 0.71 EXOSC10exosome component 10 (ENSG00000171824), score: 0.67 FANCBFanconi anemia, complementation group B (ENSG00000181544), score: 0.93 FBXO47F-box protein 47 (ENSG00000204952), score: 0.86 GEMC1geminin coiled-coil domain-containing protein 1 (ENSG00000205835), score: 0.78 GPATCH2G patch domain containing 2 (ENSG00000092978), score: 0.77 GPR20G protein-coupled receptor 20 (ENSG00000204882), score: 0.67 HORMAD1HORMA domain containing 1 (ENSG00000143452), score: 0.76 HORMAD2HORMA domain containing 2 (ENSG00000176635), score: 0.67 ING3inhibitor of growth family, member 3 (ENSG00000071243), score: 0.67 IQUBIQ motif and ubiquitin domain containing (ENSG00000164675), score: 0.76 KIF11kinesin family member 11 (ENSG00000138160), score: 0.67 KIF14kinesin family member 14 (ENSG00000118193), score: 0.72 KIF2Bkinesin family member 2B (ENSG00000141200), score: 0.72 KIF6kinesin family member 6 (ENSG00000164627), score: 0.64 KLHL10kelch-like 10 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000161594), score: 0.7 LCORLligand dependent nuclear receptor corepressor-like (ENSG00000178177), score: 0.69 LCTlactase (ENSG00000115850), score: 0.84 LHCGRluteinizing hormone/choriogonadotropin receptor (ENSG00000138039), score: 0.86 LIN28Blin-28 homolog B (C. elegans) (ENSG00000187772), score: 0.85 LRGUKleucine-rich repeats and guanylate kinase domain containing (ENSG00000155530), score: 0.72 LRRC18leucine rich repeat containing 18 (ENSG00000165383), score: 0.64 LRRC43leucine rich repeat containing 43 (ENSG00000158113), score: 0.69 LRRC52leucine rich repeat containing 52 (ENSG00000162763), score: 0.76 LRRC67leucine rich repeat containing 67 (ENSG00000178125), score: 0.79 LRRIQ4leucine-rich repeats and IQ motif containing 4 (ENSG00000188306), score: 0.79 MAP9microtubule-associated protein 9 (ENSG00000164114), score: 0.66 MELKmaternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase (ENSG00000165304), score: 0.82 MLLT6myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia (trithorax homolog, Drosophila); translocated to, 6 (ENSG00000108292), score: -0.65 MTF2metal response element binding transcription factor 2 (ENSG00000143033), score: 0.72 MYBL1v-myb myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog (avian)-like 1 (ENSG00000185697), score: 0.79 MYF5myogenic factor 5 (ENSG00000111049), score: 0.72 NCAPGnon-SMC condensin I complex, subunit G (ENSG00000109805), score: 0.68 NPRL2nitrogen permease regulator-like 2 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000114388), score: -0.64 NR5A1nuclear receptor subfamily 5, group A, member 1 (ENSG00000136931), score: 0.68 ORC1Lorigin recognition complex, subunit 1-like (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000085840), score: 0.73 OXTRoxytocin receptor (ENSG00000180914), score: 0.66 PAX5paired box 5 (ENSG00000196092), score: 0.65 PAX9paired box 9 (ENSG00000198807), score: 0.63 PIWIL1piwi-like 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000125207), score: 0.65 POLD3polymerase (DNA-directed), delta 3, accessory subunit (ENSG00000077514), score: 0.65 RAD54BRAD54 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000197275), score: 0.78 RBM46RNA binding motif protein 46 (ENSG00000151962), score: 0.81 RBP2retinol binding protein 2, cellular (ENSG00000114113), score: 0.8 RFX6regulatory factor X, 6 (ENSG00000185002), score: 0.69 RIBC2RIB43A domain with coiled-coils 2 (ENSG00000128408), score: 0.68 RNF17ring finger protein 17 (ENSG00000132972), score: 0.69 SGOL1shugoshin-like 1 (S. pombe) (ENSG00000129810), score: 0.84 SLC6A14solute carrier family 6 (amino acid transporter), member 14 (ENSG00000087916), score: 0.86 SMC1Bstructural maintenance of chromosomes 1B (ENSG00000077935), score: 0.65 SNX16sorting nexin 16 (ENSG00000104497), score: 0.63 SPACA1sperm acrosome associated 1 (ENSG00000118434), score: 0.64 SPATS2spermatogenesis associated, serine-rich 2 (ENSG00000123352), score: 0.64 SPC25SPC25, NDC80 kinetochore complex component, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000152253), score: 0.78 SPTBN1spectrin, beta, non-erythrocytic 1 (ENSG00000115306), score: -0.64 SQSTM1sequestosome 1 (ENSG00000161011), score: -0.67 STRA8stimulated by retinoic acid gene 8 homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000146857), score: 0.94 SYCP1synaptonemal complex protein 1 (ENSG00000198765), score: 0.67 TBX4T-box 4 (ENSG00000121075), score: 1 TDRD1tudor domain containing 1 (ENSG00000095627), score: 0.66 TEKT3tektin 3 (ENSG00000125409), score: 0.72 TEKT5tektin 5 (ENSG00000153060), score: 0.64 TLX1T-cell leukemia homeobox 1 (ENSG00000107807), score: 0.65 TOP2Atopoisomerase (DNA) II alpha 170kDa (ENSG00000131747), score: 0.73 TRPC6transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 6 (ENSG00000137672), score: 0.79 TSGA14testis specific, 14 (ENSG00000106477), score: 0.78 TTC25tetratricopeptide repeat domain 25 (ENSG00000204815), score: 0.72 TTKTTK protein kinase (ENSG00000112742), score: 0.68 UBE4Aubiquitination factor E4A (UFD2 homolog, yeast) (ENSG00000110344), score: 0.68 WDHD1WD repeat and HMG-box DNA binding protein 1 (ENSG00000198554), score: 0.65 WDR16WD repeat domain 16 (ENSG00000166596), score: 0.66 WDR76WD repeat domain 76 (ENSG00000092470), score: 0.66 WDR78WD repeat domain 78 (ENSG00000152763), score: 0.78 YOD1YOD1 OTU deubiquinating enzyme 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000180667), score: 0.74 ZC3H7Bzinc finger CCCH-type containing 7B (ENSG00000100403), score: -0.65 ZDHHC7zinc finger, DHHC-type containing 7 (ENSG00000153786), score: -0.65 ZMYND11zinc finger, MYND domain containing 11 (ENSG00000015171), score: -0.64 ZNRF4zinc and ring finger 4 (ENSG00000105428), score: 0.64 ZPBPzona pellucida binding protein (ENSG00000042813), score: 0.68
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gga_ts_m1_ca1 | gga | ts | m | 1 |
| gga_ts_m2_ca1 | gga | ts | m | 2 |
| oan_ts_m2_ca1 | oan | ts | m | 2 |
| oan_ts_m3_ca1 | oan | ts | m | 3 |
| oan_ts_m1_ca1 | oan | ts | m | 1 |