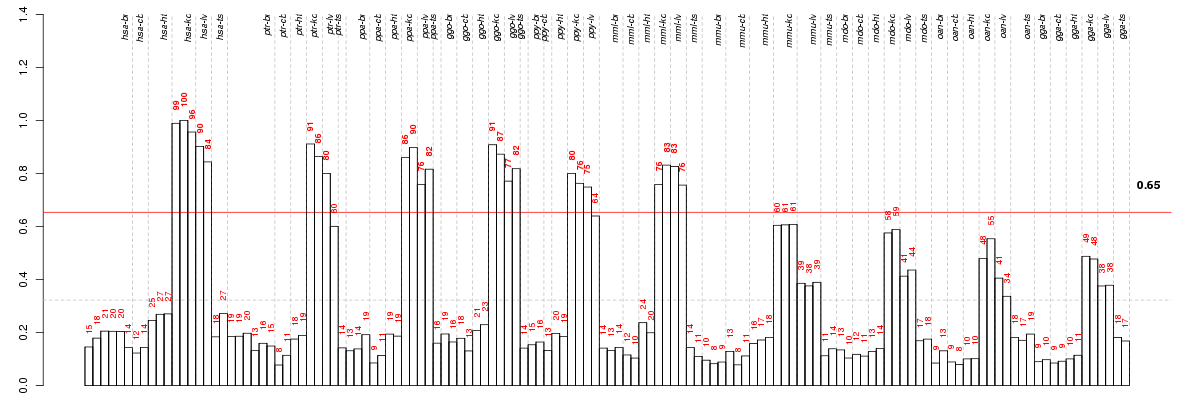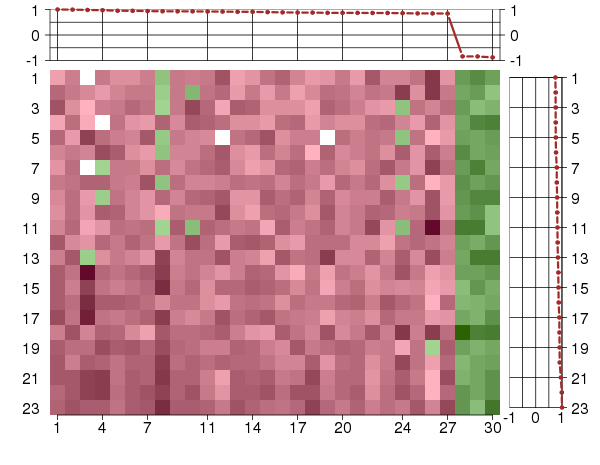

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving compounds derived from amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
cellular biogenic amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways occurring at the level of individual cells involving any of a group of naturally occurring, biologically active amines, such as norepinephrine, histamine, and serotonin, many of which act as neurotransmitters.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
amine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
carboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
gland morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a gland are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
mammary gland development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the mammary gland over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The mammary gland is a large compound sebaceous gland that in female mammals is modified to secrete milk. Its development starts with the formation of the mammary line and ends as the mature gland cycles between nursing and weaning stages.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
cellular amino acid derivative biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of compounds derived from amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
cellular biogenic amine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways occurring at the level of individual cells resulting in the formation of any of a group of naturally occurring, biologically active amines, such as norepinephrine, histamine, and serotonin, many of which act as neurotransmitters.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular nitrogen compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
small molecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
small molecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
gland development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a gland over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A gland is an organ specialised for secretion.
tissue remodeling
The reorganization or renovation of existing tissues. This process can either change the characteristics of a tissue such as in blood vessel remodeling, or result in the dynamic equilibrium of a tissue such as in bone remodeling.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
mammary gland involution
The tissue remodeling that removes differentiated mammary epithelia during weaning.
mammary gland morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures of the mammary gland are generated and organized. Morphogenesis refers to the creation of shape. The mammary gland is a large compound sebaceous gland that in female mammals is modified to secrete milk.
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
small molecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular nitrogen compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
cellular amino acid derivative biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of compounds derived from amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
amine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular biogenic amine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways occurring at the level of individual cells resulting in the formation of any of a group of naturally occurring, biologically active amines, such as norepinephrine, histamine, and serotonin, many of which act as neurotransmitters.
cellular biogenic amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways occurring at the level of individual cells involving any of a group of naturally occurring, biologically active amines, such as norepinephrine, histamine, and serotonin, many of which act as neurotransmitters.
cellular amino acid derivative biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of compounds derived from amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
mammary gland involution
The tissue remodeling that removes differentiated mammary epithelia during weaning.
gland morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a gland are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cellular biogenic amine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways occurring at the level of individual cells resulting in the formation of any of a group of naturally occurring, biologically active amines, such as norepinephrine, histamine, and serotonin, many of which act as neurotransmitters.
mammary gland morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures of the mammary gland are generated and organized. Morphogenesis refers to the creation of shape. The mammary gland is a large compound sebaceous gland that in female mammals is modified to secrete milk.


ACMSDaminocarboxymuconate semialdehyde decarboxylase (ENSG00000153086), score: 0.95 ANXA13annexin A13 (ENSG00000104537), score: 0.86 BBOX1butyrobetaine (gamma), 2-oxoglutarate dioxygenase (gamma-butyrobetaine hydroxylase) 1 (ENSG00000129151), score: 0.87 CLDN14claudin 14 (ENSG00000159261), score: 0.85 CRYAAcrystallin, alpha A (ENSG00000160202), score: 0.93 CRYL1crystallin, lambda 1 (ENSG00000165475), score: 0.93 DBHdopamine beta-hydroxylase (dopamine beta-monooxygenase) (ENSG00000123454), score: 0.92 DDCdopa decarboxylase (aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase) (ENSG00000132437), score: 0.95 DNAJC18DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 18 (ENSG00000170464), score: -0.84 ELF3E74-like factor 3 (ets domain transcription factor, epithelial-specific ) (ENSG00000163435), score: 0.9 ENPEPglutamyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase A) (ENSG00000138792), score: 0.87 ERBB2v-erb-b2 erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 2, neuro/glioblastoma derived oncogene homolog (avian) (ENSG00000141736), score: 0.85 GLYCTKglycerate kinase (ENSG00000168237), score: 0.86 HAO2hydroxyacid oxidase 2 (long chain) (ENSG00000116882), score: 0.92 IMPA2inositol(myo)-1(or 4)-monophosphatase 2 (ENSG00000141401), score: 0.94 LPIN3lipin 3 (ENSG00000132793), score: 0.86 MMP7matrix metallopeptidase 7 (matrilysin, uterine) (ENSG00000137673), score: 0.98 PEPDpeptidase D (ENSG00000124299), score: 0.88 PLCG2phospholipase C, gamma 2 (phosphatidylinositol-specific) (ENSG00000197943), score: 1 RAB17RAB17, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000124839), score: 0.99 SLC22A7solute carrier family 22 (organic anion transporter), member 7 (ENSG00000137204), score: 0.89 SLC5A9solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter), member 9 (ENSG00000117834), score: 0.88 SLC7A9solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 9 (ENSG00000021488), score: 0.91 SPG21spastic paraplegia 21 (autosomal recessive, Mast syndrome) (ENSG00000090487), score: 0.87 SPTLC3serine palmitoyltransferase, long chain base subunit 3 (ENSG00000172296), score: 0.93 TAOK1TAO kinase 1 (ENSG00000160551), score: -0.84 TM7SF3transmembrane 7 superfamily member 3 (ENSG00000064115), score: 0.84 TMPRSS2transmembrane protease, serine 2 (ENSG00000184012), score: 0.91 TNRC6Ctrinucleotide repeat containing 6C (ENSG00000078687), score: -0.88 WDR72WD repeat domain 72 (ENSG00000166415), score: 0.97
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppy_lv_m_ca1 | ppy | lv | m | _ |
| mml_lv_f_ca1 | mml | lv | f | _ |
| mml_kd_m_ca1 | mml | kd | m | _ |
| ppa_lv_m_ca1 | ppa | lv | m | _ |
| ppy_kd_f_ca1 | ppy | kd | f | _ |
| ggo_lv_m_ca1 | ggo | lv | m | _ |
| ptr_lv_m_ca1 | ptr | lv | m | _ |
| ppy_kd_m_ca1 | ppy | kd | m | _ |
| ppa_lv_f_ca1 | ppa | lv | f | _ |
| ggo_lv_f_ca1 | ggo | lv | f | _ |
| mml_lv_m_ca1 | mml | lv | m | _ |
| mml_kd_f_ca1 | mml | kd | f | _ |
| hsa_lv_m2_ca1 | hsa | lv | m | 2 |
| ppa_kd_m_ca1 | ppa | kd | m | _ |
| ptr_kd_f_ca1 | ptr | kd | f | _ |
| ggo_kd_f_ca1 | ggo | kd | f | _ |
| ppa_kd_f_ca1 | ppa | kd | f | _ |
| hsa_lv_m1_ca1 | hsa | lv | m | 1 |
| ggo_kd_m_ca1 | ggo | kd | m | _ |
| ptr_kd_m_ca1 | ptr | kd | m | _ |
| hsa_kd_f_ca1 | hsa | kd | f | _ |
| hsa_kd_m2_ca1 | hsa | kd | m | 2 |
| hsa_kd_m1_ca1 | hsa | kd | m | 1 |