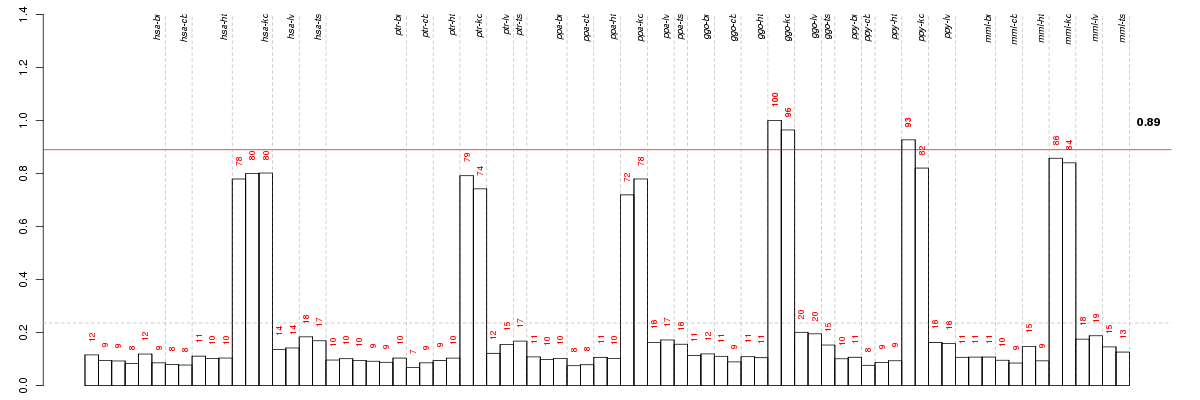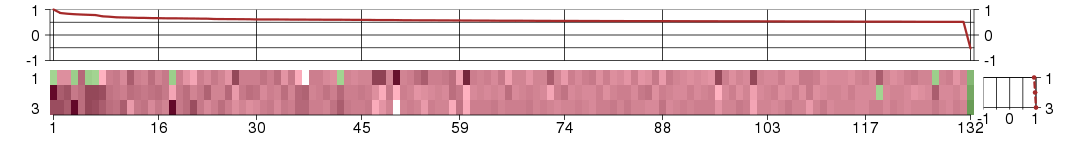

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

regionalization
The pattern specification process by which an axis or axes is subdivided in space to define an area or volume in which specific patterns of cell differentiation will take place or in which cells interpret a specific environment.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
secretion
The controlled release of a substance by a cell, a group of cells, or a tissue.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
ion transport
The directed movement of charged atoms or small charged molecules into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cation transport
The directed movement of cations, atoms or small molecules with a net positive charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
sodium ion transport
The directed movement of sodium ions (Na+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
anion transport
The directed movement of anions, atoms or small molecules with a net negative charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
metal ion transport
The directed movement of metal ions, any metal ion with an electric charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
pattern specification process
Any developmental process that results in the creation of defined areas or spaces within an organism to which cells respond and eventually are instructed to differentiate.
excretion
The elimination by an organism of the waste products that arise as a result of metabolic activity. These products include water, carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrogenous compounds.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
anterior/posterior pattern formation
The regionalization process by which specific areas of cell differentiation are determined along the anterior-posterior axis. The anterior-posterior axis is defined by a line that runs from the head or mouth of an organism to the tail or opposite end of the organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
monovalent inorganic cation transport
The directed movement of inorganic cations with a valency of one into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Inorganic cations are atoms or small molecules with a positive charge which do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
organic anion transport
The directed movement of organic anions into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Organic anions are atoms or small molecules with a negative charge which contain carbon in covalent linkage.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
homeostatic process
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state.
ion homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of ions within an organism or cell.
chemical homeostasis
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of a chemical.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
cation homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of cations within an organism or cell.
transmembrane transport
The process whereby a solute is transported from one side of a membrane to the other. This process includes the actual movement of the solute, and any regulation and preparatory steps, such as reduction of the solute.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
all
NA
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
pattern specification process
Any developmental process that results in the creation of defined areas or spaces within an organism to which cells respond and eventually are instructed to differentiate.
transmembrane transport
The process whereby a solute is transported from one side of a membrane to the other. This process includes the actual movement of the solute, and any regulation and preparatory steps, such as reduction of the solute.
excretion
The elimination by an organism of the waste products that arise as a result of metabolic activity. These products include water, carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrogenous compounds.
sodium ion transport
The directed movement of sodium ions (Na+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
brush border
Dense covering of microvilli on the apical surface of epithelial cells in tissues such as the intestine, kidney, and choroid plexus; the microvilli aid absorption by increasing the surface area of the cell.
basolateral plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane that includes the basal end and sides of the cell. Often used in reference to animal polarized epithelial membranes, where the basal membrane is the part attached to the extracellular matrix, or in plant cells, where the basal membrane is defined with respect to the zygotic axis.
apical plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
cell projection
A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
apical part of cell
The region of a polarized cell that forms a tip or is distal to a base. For example, in a polarized epithelial cell, the apical region has an exposed surface and lies opposite to the basal lamina that separates the epithelium from other tissue.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
apical plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
organic acid transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage, from one side of the membrane to the other.
secondary active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of a membrane to the other, up its concentration gradient. The transporter binds the solute and undergoes a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction and is driven by a chemiosmotic source of energy. Chemiosmotic sources of energy include uniport, symport or antiport.
inorganic anion exchanger activity
NA
cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of cation from one side of the membrane to the other.
anion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a negatively charged ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
organic anion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of organic anions from one side of a membrane to the other. Organic anions are atoms or small molecules with a negative charge which contain carbon in covalent linkage.
ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
inorganic anion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of inorganic anions from one side of a membrane to the other. Inorganic anions are atoms or small molecules with a negative charge which do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
symporter activity
Enables the active transport of a solute across a membrane by a mechanism whereby two or more species are transported together in the same direction in a tightly coupled process not directly linked to a form of energy other than chemiosmotic energy.
solute:cation symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: solute(out) + cation(out) = solute(in) + cation(in).
anion:cation symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: anion(out) + cation(out) = anion(in) + cation(in).
antiporter activity
Enables the active transport of a solute across a membrane by a mechanism whereby two or more species are transported in opposite directions in a tightly coupled process not directly linked to a form of energy other than chemiosmotic energy.
solute:solute antiporter activity
Catalysis of the reaction: solute A(out) + solute B(in) = solute A(in) + solute B(out).
anion:anion antiporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: anion A(out) + anion B(in) = anion A(in) + anion B(out).
anion exchanger activity
NA
active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a specific substance or related group of substances from one side of a membrane to the other, up the solute's concentration gradient. The transporter binds the solute and undergoes a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction.
inorganic cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of inorganic cations from one side of a membrane to the other. Inorganic cations are atoms or small molecules with a positive charge that do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
all
NA
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
solute:cation symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: solute(out) + cation(out) = solute(in) + cation(in).
anion:cation symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: anion(out) + cation(out) = anion(in) + cation(in).
anion:anion antiporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: anion A(out) + anion B(in) = anion A(in) + anion B(out).
ACPPacid phosphatase, prostate (ENSG00000014257), score: 0.55 AGR2anterior gradient homolog 2 (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000106541), score: 0.66 ALDH3A1aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, member A1 (ENSG00000108602), score: 0.51 ARHGEF38Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 38 (ENSG00000138784), score: 0.54 ATP2C2ATPase, Ca++ transporting, type 2C, member 2 (ENSG00000064270), score: 0.67 ATP6V1B1ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 56/58kDa, V1 subunit B1 (ENSG00000116039), score: 0.52 ATP6V1G3ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 13kDa, V1 subunit G3 (ENSG00000151418), score: 0.55 ATP8B4ATPase, class I, type 8B, member 4 (ENSG00000104043), score: 0.61 B4GALNT2beta-1,4-N-acetyl-galactosaminyl transferase 2 (ENSG00000167080), score: 0.69 C12orf59chromosome 12 open reading frame 59 (ENSG00000165685), score: 0.57 C14orf149chromosome 14 open reading frame 149 (ENSG00000126790), score: 0.56 C1orf106chromosome 1 open reading frame 106 (ENSG00000163362), score: 0.58 C1orf85chromosome 1 open reading frame 85 (ENSG00000198715), score: 0.54 C9orf71chromosome 9 open reading frame 71 (ENSG00000181778), score: 0.61 C9orf84chromosome 9 open reading frame 84 (ENSG00000165181), score: 0.55 CA12carbonic anhydrase XII (ENSG00000074410), score: 0.53 CARD14caspase recruitment domain family, member 14 (ENSG00000141527), score: 0.52 CASRcalcium-sensing receptor (ENSG00000036828), score: 0.53 CCL11chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 11 (ENSG00000172156), score: 0.6 CDH16cadherin 16, KSP-cadherin (ENSG00000166589), score: 0.53 CDH17cadherin 17, LI cadherin (liver-intestine) (ENSG00000079112), score: 0.57 CDH3cadherin 3, type 1, P-cadherin (placental) (ENSG00000062038), score: 0.6 CDH6cadherin 6, type 2, K-cadherin (fetal kidney) (ENSG00000113361), score: 0.53 CETN2centrin, EF-hand protein, 2 (ENSG00000147400), score: 0.51 CIRH1Acirrhosis, autosomal recessive 1A (cirhin) (ENSG00000141076), score: 0.61 CLCNKAchloride channel Ka (ENSG00000186510), score: 0.54 CLDN16claudin 16 (ENSG00000113946), score: 0.61 CLDN8claudin 8 (ENSG00000156284), score: 0.52 CLNKcytokine-dependent hematopoietic cell linker (ENSG00000109684), score: 0.6 COL4A3collagen, type IV, alpha 3 (Goodpasture antigen) (ENSG00000169031), score: 0.54 CUBNcubilin (intrinsic factor-cobalamin receptor) (ENSG00000107611), score: 0.54 CWH43cell wall biogenesis 43 C-terminal homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000109182), score: 0.65 CXCL13chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 13 (ENSG00000156234), score: 0.79 CYP24A1cytochrome P450, family 24, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000019186), score: 0.62 DNTTdeoxynucleotidyltransferase, terminal (ENSG00000107447), score: 0.81 DOCK8dedicator of cytokinesis 8 (ENSG00000107099), score: 0.55 EAF2ELL associated factor 2 (ENSG00000145088), score: 0.53 EDARectodysplasin A receptor (ENSG00000135960), score: 0.59 EGFepidermal growth factor (ENSG00000138798), score: 0.52 ENAMenamelin (ENSG00000132464), score: 0.66 ESRP1epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1 (ENSG00000104413), score: 0.52 F2RL1coagulation factor II (thrombin) receptor-like 1 (ENSG00000164251), score: 0.53 FADS2fatty acid desaturase 2 (ENSG00000134824), score: -0.52 FERMT1fermitin family member 1 (ENSG00000101311), score: 0.62 FGFBP1fibroblast growth factor binding protein 1 (ENSG00000137440), score: 0.58 FMO1flavin containing monooxygenase 1 (ENSG00000010932), score: 0.57 FOXI1forkhead box I1 (ENSG00000168269), score: 0.53 FXYD2FXYD domain containing ion transport regulator 2 (ENSG00000137731), score: 0.55 GCET2germinal center expressed transcript 2 (ENSG00000174500), score: 0.73 GHRHRgrowth hormone releasing hormone receptor (ENSG00000106128), score: 0.83 GNPDA1glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase 1 (ENSG00000113552), score: 0.57 GP2glycoprotein 2 (zymogen granule membrane) (ENSG00000169347), score: 0.58 GPR160G protein-coupled receptor 160 (ENSG00000173890), score: 0.54 GRAMD2GRAM domain containing 2 (ENSG00000175318), score: 0.55 HEPACAM2HEPACAM family member 2 (ENSG00000188175), score: 0.54 HOXA10homeobox A10 (ENSG00000153807), score: 0.54 HOXA11homeobox A11 (ENSG00000005073), score: 0.72 HOXA5homeobox A5 (ENSG00000106004), score: 0.55 HOXA9homeobox A9 (ENSG00000078399), score: 0.55 HOXB7homeobox B7 (ENSG00000120087), score: 0.63 HOXC8homeobox C8 (ENSG00000037965), score: 0.62 HOXC9homeobox C9 (ENSG00000180806), score: 0.52 HOXD3homeobox D3 (ENSG00000128652), score: 0.54 HOXD4homeobox D4 (ENSG00000170166), score: 0.55 HSD11B2hydroxysteroid (11-beta) dehydrogenase 2 (ENSG00000176387), score: 0.53 ISXintestine-specific homeobox (ENSG00000175329), score: 1 KCNH6potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily H (eag-related), member 6 (ENSG00000173826), score: 0.57 KCNJ1potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 1 (ENSG00000151704), score: 0.57 KLklotho (ENSG00000133116), score: 0.59 KLHDC7Akelch domain containing 7A (ENSG00000179023), score: 0.53 LGALS2lectin, galactoside-binding, soluble, 2 (ENSG00000100079), score: 0.54 LRRC19leucine rich repeat containing 19 (ENSG00000184434), score: 0.52 LRRN4leucine rich repeat neuronal 4 (ENSG00000125872), score: 0.68 LTFlactotransferrin (ENSG00000012223), score: 0.56 MIOXmyo-inositol oxygenase (ENSG00000100253), score: 0.53 MYO3Bmyosin IIIB (ENSG00000071909), score: 0.62 NLRC4NLR family, CARD domain containing 4 (ENSG00000091106), score: 0.65 NPHS2nephrosis 2, idiopathic, steroid-resistant (podocin) (ENSG00000116218), score: 0.53 OLFM4olfactomedin 4 (ENSG00000102837), score: 0.78 OXGR1oxoglutarate (alpha-ketoglutarate) receptor 1 (ENSG00000165621), score: 0.54 PDZK1IP1PDZK1 interacting protein 1 (ENSG00000162366), score: 0.56 PLA2G4Fphospholipase A2, group IVF (ENSG00000168907), score: 0.56 PLA2R1phospholipase A2 receptor 1, 180kDa (ENSG00000153246), score: 0.55 RAB7L1RAB7, member RAS oncogene family-like 1 (ENSG00000117280), score: 0.54 SCTRsecretin receptor (ENSG00000080293), score: 0.53 SLC10A2solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 2 (ENSG00000125255), score: 0.8 SLC12A1solute carrier family 12 (sodium/potassium/chloride transporters), member 1 (ENSG00000074803), score: 0.55 SLC12A3solute carrier family 12 (sodium/chloride transporters), member 3 (ENSG00000070915), score: 0.55 SLC13A1solute carrier family 13 (sodium/sulfate symporters), member 1 (ENSG00000081800), score: 0.59 SLC16A4solute carrier family 16, member 4 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 5) (ENSG00000168679), score: 0.59 SLC17A3solute carrier family 17 (sodium phosphate), member 3 (ENSG00000124564), score: 0.52 SLC22A11solute carrier family 22 (organic anion/urate transporter), member 11 (ENSG00000168065), score: 0.51 SLC22A12solute carrier family 22 (organic anion/urate transporter), member 12 (ENSG00000197891), score: 0.6 SLC22A2solute carrier family 22 (organic cation transporter), member 2 (ENSG00000112499), score: 0.59 SLC22A6solute carrier family 22 (organic anion transporter), member 6 (ENSG00000197901), score: 0.52 SLC22A8solute carrier family 22 (organic anion transporter), member 8 (ENSG00000149452), score: 0.54 SLC26A7solute carrier family 26, member 7 (ENSG00000147606), score: 0.6 SLC2A9solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 9 (ENSG00000109667), score: 0.55 SLC34A1solute carrier family 34 (sodium phosphate), member 1 (ENSG00000131183), score: 0.58 SLC36A3solute carrier family 36 (proton/amino acid symporter), member 3 (ENSG00000186334), score: 0.6 SLC44A4solute carrier family 44, member 4 (ENSG00000204385), score: 0.56 SLC47A2solute carrier family 47, member 2 (ENSG00000180638), score: 0.64 SLC4A1solute carrier family 4, anion exchanger, member 1 (erythrocyte membrane protein band 3, Diego blood group) (ENSG00000004939), score: 0.52 SLC4A9solute carrier family 4, sodium bicarbonate cotransporter, member 9 (ENSG00000113073), score: 0.56 SLC5A12solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter), member 12 (ENSG00000148942), score: 0.6 SLC7A13solute carrier family 7, (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system) member 13 (ENSG00000164893), score: 0.52 SLC7A8solute carrier family 7 (amino acid transporter, L-type), member 8 (ENSG00000092068), score: 0.55 SLC9A4solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 4 (ENSG00000180251), score: 0.65 SLCO4C1solute carrier organic anion transporter family, member 4C1 (ENSG00000173930), score: 0.6 STRA6stimulated by retinoic acid gene 6 homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000137868), score: 0.53 SULT2B1sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 2B, member 1 (ENSG00000088002), score: 0.64 SYT10synaptotagmin X (ENSG00000110975), score: 0.54 TBC1D23TBC1 domain family, member 23 (ENSG00000036054), score: 0.52 TBX10T-box 10 (ENSG00000167800), score: 0.86 TFECtranscription factor EC (ENSG00000105967), score: 0.67 TINAGtubulointerstitial nephritis antigen (ENSG00000137251), score: 0.61 TM7SF4transmembrane 7 superfamily member 4 (ENSG00000164935), score: 0.6 TMEM106Atransmembrane protein 106A (ENSG00000184988), score: 0.52 TMEM171transmembrane protein 171 (ENSG00000157111), score: 0.55 TMEM174transmembrane protein 174 (ENSG00000164325), score: 0.69 TMIGD1transmembrane and immunoglobulin domain containing 1 (ENSG00000182271), score: 0.54 TNFSF15tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 15 (ENSG00000181634), score: 0.58 TPH1tryptophan hydroxylase 1 (ENSG00000129167), score: 0.65 UMODuromodulin (ENSG00000169344), score: 0.52 UNC5CLunc-5 homolog C (C. elegans)-like (ENSG00000124602), score: 0.54 UPP2uridine phosphorylase 2 (ENSG00000007001), score: 0.62 VDRvitamin D (1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D3) receptor (ENSG00000111424), score: 0.65 WNK4WNK lysine deficient protein kinase 4 (ENSG00000126562), score: 0.56 WNT8Bwingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 8B (ENSG00000075290), score: 0.57
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppy_kd_m_ca1 | ppy | kd | m | _ |
| ggo_kd_f_ca1 | ggo | kd | f | _ |
| ggo_kd_m_ca1 | ggo | kd | m | _ |