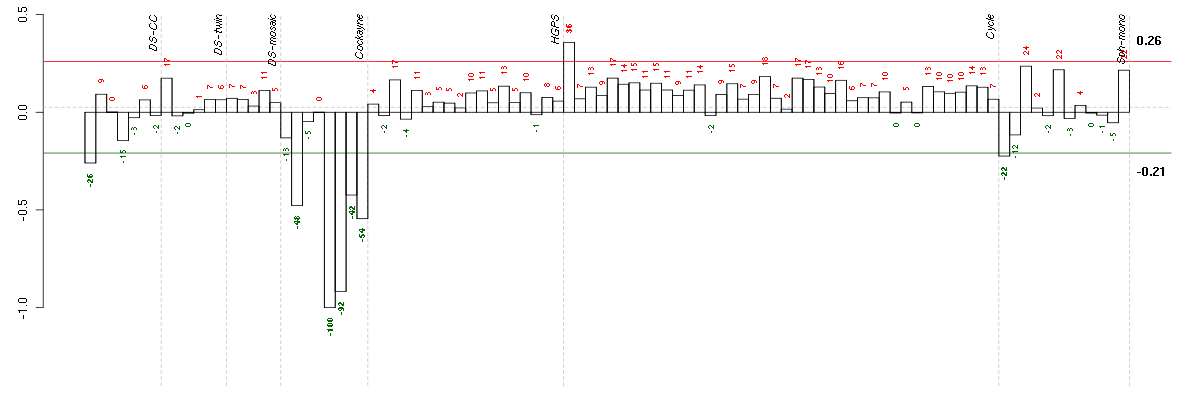

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
xenobiotic metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a xenobiotic compound, a compound foreign to living organisms. Used of chemical compounds, e.g. a xenobiotic chemical, such as a pesticide.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
response to xenobiotic stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a xenobiotic compound stimulus. Xenobiotic compounds are compounds foreign to living organisms.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
xenobiotic metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a xenobiotic compound, a compound foreign to living organisms. Used of chemical compounds, e.g. a xenobiotic chemical, such as a pesticide.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
endomembrane system
A collection of membranous structures involved in transport within the cell. The main components of the endomembrane system are endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, vesicles, cell membrane and nuclear envelope. Members of the endomembrane system pass materials through each other or though the use of vesicles.
vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding any membrane-bounded vesicle in the cell.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cytoplasmic vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a cytoplasmic vesicle.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by membrane or protein.
membrane-bounded vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by a lipid bilayer.
melanosome membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a melanosome.
melanosome
A tissue-specific, membrane-bounded cytoplasmic organelle within which melanin pigments are synthesized and stored. Melanosomes are synthesized in melanocyte cells.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
chitosome
An intracellular membrane-bounded particle found in fungi and containing chitin synthase; it synthesizes chitin microfibrils. Chitin synthase activity exists in chitosomes and they are proposed to act as a reservoir for regulated transport of chitin synthase enzymes to the division septum.
pigment granule
A small, subcellular membrane-bounded vesicle containing pigment and/or pigment precursor molecules. Pigment granule biogenesis is poorly understood, as pigment granules are derived from multiple sources including the endoplasmic reticulum, coated vesicles, lysosomes, and endosomes.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding any membrane-bounded vesicle in the cell.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding any membrane-bounded vesicle in the cell.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cytoplasmic vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a cytoplasmic vesicle.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoplasmic vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a cytoplasmic vesicle.
melanosome membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a melanosome.
melanosome membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a melanosome.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
UDP-glycosyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a glycosyl group from a UDP-sugar to a small hydrophobic molecule.
glucuronosyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: UDP-glucuronate + acceptor = UDP + acceptor beta-D-glucuronoside.
transferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from one compound (generally regarded as the donor) to another compound (generally regarded as the acceptor). Transferase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 2.
transferase activity, transferring glycosyl groups
Catalysis of the transfer of a glycosyl group from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor).
transferase activity, transferring hexosyl groups
Catalysis of the transfer of a hexosyl group from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor).
all
This term is the most general term possible
glucuronosyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: UDP-glucuronate + acceptor = UDP + acceptor beta-D-glucuronoside.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00040 | 6.001e-03 | 0.08222 | 3 | 13 | Pentose and glucuronate interconversions |
| 00150 | 1.959e-02 | 0.1328 | 3 | 21 | Androgen and estrogen metabolism |
| 00830 | 1.959e-02 | 0.1328 | 3 | 21 | Retinol metabolism |
| 00500 | 2.574e-02 | 0.1518 | 3 | 24 | Starch and sucrose metabolism |
| 00860 | 2.574e-02 | 0.1518 | 3 | 24 | Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism |
| 00983 | 3.956e-02 | 0.1834 | 3 | 29 | Drug metabolism - other enzymes |
A2Malpha-2-macroglobulin (217757_at), score: -0.69 ABCB1ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP), member 1 (209993_at), score: -1 AIM2absent in melanoma 2 (206513_at), score: -0.6 ANK3ankyrin 3, node of Ranvier (ankyrin G) (206385_s_at), score: -0.54 ATP6V1B2ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 56/58kDa, V1 subunit B2 (201089_at), score: -0.53 C5orf30chromosome 5 open reading frame 30 (221823_at), score: 0.72 CD24CD24 molecule (266_s_at), score: -0.59 CRTAPcartilage associated protein (201380_at), score: 0.79 DDX17DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 17 (208151_x_at), score: -0.68 DIO2deiodinase, iodothyronine, type II (203700_s_at), score: -0.6 DKFZP564O0823DKFZP564O0823 protein (204687_at), score: -0.52 EPHB2EPH receptor B2 (209589_s_at), score: -0.53 FAM169Afamily with sequence similarity 169, member A (213954_at), score: -0.58 FKBP9FK506 binding protein 9, 63 kDa (212169_at), score: 0.8 FZD3frizzled homolog 3 (Drosophila) (219683_at), score: -0.54 GABREgamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, epsilon (204537_s_at), score: -0.54 GAGE4G antigen 4 (207086_x_at), score: -0.96 GAGE6G antigen 6 (208155_x_at), score: -0.89 GATA3GATA binding protein 3 (209604_s_at), score: -0.89 HERC5hect domain and RLD 5 (219863_at), score: -0.68 HGSNATheparan-alpha-glucosaminide N-acetyltransferase (218017_s_at), score: 0.77 HLA-DPA1major histocompatibility complex, class II, DP alpha 1 (211990_at), score: -0.61 HRASLSHRAS-like suppressor (219983_at), score: -0.54 MAFv-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog (avian) (209348_s_at), score: -0.54 MARK1MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 1 (221047_s_at), score: -0.76 NCRNA00084non-protein coding RNA 84 (214657_s_at), score: -0.62 NEFLneurofilament, light polypeptide (221805_at), score: -0.59 NMUneuromedin U (206023_at), score: -0.63 NRGNneurogranin (protein kinase C substrate, RC3) (204081_at), score: -0.66 OASL2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase-like (210797_s_at), score: -0.94 PCLOpiccolo (presynaptic cytomatrix protein) (213558_at), score: -0.63 PDE10Aphosphodiesterase 10A (205501_at), score: -0.68 PILRBpaired immunoglobin-like type 2 receptor beta (220954_s_at), score: -0.54 PLS1plastin 1 (I isoform) (205190_at), score: -0.54 PSMB4proteasome (prosome, macropain) subunit, beta type, 4 (202243_s_at), score: 0.75 QPCTglutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase (205174_s_at), score: 0.72 RABGAP1LRAB GTPase activating protein 1-like (213982_s_at), score: 0.74 RAD23BRAD23 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (201223_s_at), score: 0.77 RARRES3retinoic acid receptor responder (tazarotene induced) 3 (204070_at), score: -0.52 REEP1receptor accessory protein 1 (204364_s_at), score: -0.55 SNCAsynuclein, alpha (non A4 component of amyloid precursor) (204466_s_at), score: -0.65 SYTL2synaptotagmin-like 2 (220613_s_at), score: -0.67 TAC1tachykinin, precursor 1 (206552_s_at), score: -0.57 TBC1D8TBC1 domain family, member 8 (with GRAM domain) (204526_s_at), score: -0.53 TCEAL2transcription elongation factor A (SII)-like 2 (211276_at), score: -0.95 TMOD1tropomodulin 1 (203661_s_at), score: -0.56 TYRP1tyrosinase-related protein 1 (205694_at), score: -0.53 UBL3ubiquitin-like 3 (201535_at), score: 0.72 UGT1A1UDP glucuronosyltransferase 1 family, polypeptide A1 (207126_x_at), score: -0.95 UGT1A6UDP glucuronosyltransferase 1 family, polypeptide A6 (206094_x_at), score: -0.95 UGT1A9UDP glucuronosyltransferase 1 family, polypeptide A9 (204532_x_at), score: -0.94 VWA5Avon Willebrand factor A domain containing 5A (210102_at), score: -0.54 WT1Wilms tumor 1 (206067_s_at), score: -0.75
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949721.cel | 5 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | CSB |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949750.cel | 6 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | CSB |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949938.cel | 8 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | none | CSB |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949579.cel | 2 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | none | CSB |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949854.cel | 7 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |
| ctrl a 08-03.CEL | 1 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956083.cel | 2 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485651.cel | 1 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |