
Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

DNA replication
The process whereby new strands of DNA are synthesized. The template for replication can either be an existing DNA molecule or RNA.
DNA synthesis during DNA repair
Synthesis of DNA that proceeds from the broken 3' single-strand DNA end uses the homologous intact duplex as the template.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
temperature homeostasis
A homeostatic process by which an organism modulates its internal body temperature.
cytokine production
The appearance of a cytokine due to biosynthesis or secretion following a cellular stimulus, resulting in an increase in its intracellular or extracellular levels.
regulation of cytokine production
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of production of a cytokine.
regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups into an amino acid in a protein.
positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
DNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
DNA-dependent DNA replication
The process whereby new strands of DNA are synthesized, using parental DNA as a template for the DNA-dependent DNA polymerases that synthesize the new strands.
DNA repair
The process of restoring DNA after damage. Genomes are subject to damage by chemical and physical agents in the environment (e.g. UV and ionizing radiations, chemical mutagens, fungal and bacterial toxins, etc.) and by free radicals or alkylating agents endogenously generated in metabolism. DNA is also damaged because of errors during its replication. A variety of different DNA repair pathways have been reported that include direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, photoreactivation, bypass, double-strand break repair pathway, and mismatch repair pathway.
protein modification process
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in proteins, peptides and nascent polypeptides (co-translational, post-translational modifications). Includes the modification of charged tRNAs that are destined to occur in a protein (pre-translation modification).
protein amino acid phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein.
lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent. Includes fatty acids; neutral fats, other fatty-acid esters, and soaps; long-chain (fatty) alcohols and waxes; sphingoids and other long-chain bases; glycolipids, phospholipids and sphingolipids; and carotenes, polyprenols, sterols, terpenes and other isoprenoids.
steroid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus; includes de novo formation and steroid interconversion by modification.
phosphorus metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving the nonmetallic element phosphorus or compounds that contain phosphorus, usually in the form of a phosphate group (PO4).
phosphate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving the phosphate group, the anion or salt of any phosphoric acid.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
response to DNA damage stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism.
cell cycle
The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division.
regulation of steroid biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
steroid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus.
cell proliferation
The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population.
lipid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
positive regulation of phosphorus metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphorus or compounds containing phosphorus.
vascular endothelial growth factor production
The appearance of vascular endothelial growth factor production due to biosynthesis or secretion following a cellular stimulus, resulting in an increase in its intracellular or extracellular levels.
regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of production of vascular endothelial growth factor.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group into a molecule, usually with the formation of a phosphoric ester, a phosphoric anhydride or a phosphoric amide.
regulation of lipid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids.
regulation of steroid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving steroids.
regulation of phosphate metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphates.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
cell cycle phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through one of the biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of protein modification process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
positive regulation of protein modification process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
cellular response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating the organism is under stress. The stress is usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular response to DNA damage stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism.
regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation.
regulation of phosphorylation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups into a molecule.
positive regulation of phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to a molecule.
homeostatic process
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal equilibrium.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
biopolymer modification
The covalent alteration of one or more monomeric units in a polypeptide, polynucleotide, polysaccharide, or other biological polymer, resulting in a change in its properties.
post-translational protein modification
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in a protein after the protein has been completely translated and released from the ribosome.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
positive regulation of phosphate metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphates.
regulation of lipid biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of lipids.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of phosphorus metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphorus or compounds containing phosphorus.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
positive regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
cellular response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
cellular response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of cytokine production
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of production of a cytokine.
cellular response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating the organism is under stress. The stress is usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
regulation of lipid biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of lipids.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of lipid biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of lipids.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of phosphorus metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphorus or compounds containing phosphorus.
regulation of phosphorus metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphorus or compounds containing phosphorus.
steroid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus.
lipid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
regulation of lipid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids.
cellular lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
positive regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of production of vascular endothelial growth factor.
cellular response to DNA damage stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism.
temperature homeostasis
A homeostatic process by which an organism modulates its internal body temperature.
regulation of steroid biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of steroid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving steroids.
steroid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus; includes de novo formation and steroid interconversion by modification.
regulation of steroid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving steroids.
positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
regulation of steroid biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus.
positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of phosphorus metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphorus or compounds containing phosphorus.
regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
DNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
regulation of phosphate metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphates.
positive regulation of phosphate metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphates.
protein modification process
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in proteins, peptides and nascent polypeptides (co-translational, post-translational modifications). Includes the modification of charged tRNAs that are destined to occur in a protein (pre-translation modification).
regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
DNA repair
The process of restoring DNA after damage. Genomes are subject to damage by chemical and physical agents in the environment (e.g. UV and ionizing radiations, chemical mutagens, fungal and bacterial toxins, etc.) and by free radicals or alkylating agents endogenously generated in metabolism. DNA is also damaged because of errors during its replication. A variety of different DNA repair pathways have been reported that include direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, photoreactivation, bypass, double-strand break repair pathway, and mismatch repair pathway.
DNA replication
The process whereby new strands of DNA are synthesized. The template for replication can either be an existing DNA molecule or RNA.
positive regulation of protein modification process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
positive regulation of phosphate metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphates.
regulation of protein modification process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
positive regulation of protein modification process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
DNA synthesis during DNA repair
Synthesis of DNA that proceeds from the broken 3' single-strand DNA end uses the homologous intact duplex as the template.
regulation of phosphorylation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups into a molecule.
positive regulation of phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to a molecule.
positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein.
positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein.
regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups into an amino acid in a protein.
positive regulation of phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to a molecule.
protein amino acid phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein.
regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups into an amino acid in a protein.
positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein.

nuclear chromosome
A chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
nucleus
A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent.
replication fork
The Y-shaped region of a replicating DNA molecule, resulting from the separation of the DNA strands and in which the synthesis of new strands takes place. Also includes associated protein complexes.
chromosome
A structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
replisome
A multi-component enzymatic machine at the replication fork which mediates DNA replication. Includes DNA primase, one or more DNA polymerases, DNA helicases, and other proteins.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
protein-DNA complex
A macromolecular complex containing both protein and DNA molecules.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
nuclear replication fork
The Y-shaped region of a nuclear replicating DNA molecule, resulting from the separation of the DNA strands and in which the synthesis of new strands takes place. Also includes associated protein complexes.
nuclear replisome
A multi-component enzymatic machine at the nuclear replication fork, which mediates DNA replication. Includes DNA primase, one or more DNA polymerases, DNA helicases, and other proteins.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
nuclear part
Any constituent part of the nucleus, a membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
nuclear chromosome part
Any constituent part of a nuclear chromosome, a chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
This term is the most general term possible
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
replisome
A multi-component enzymatic machine at the replication fork which mediates DNA replication. Includes DNA primase, one or more DNA polymerases, DNA helicases, and other proteins.
nuclear chromosome part
Any constituent part of a nuclear chromosome, a chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
nuclear part
Any constituent part of the nucleus, a membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated.
nuclear chromosome
A chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
replisome
A multi-component enzymatic machine at the replication fork which mediates DNA replication. Includes DNA primase, one or more DNA polymerases, DNA helicases, and other proteins.
nuclear replication fork
The Y-shaped region of a nuclear replicating DNA molecule, resulting from the separation of the DNA strands and in which the synthesis of new strands takes place. Also includes associated protein complexes.
nuclear replisome
A multi-component enzymatic machine at the nuclear replication fork, which mediates DNA replication. Includes DNA primase, one or more DNA polymerases, DNA helicases, and other proteins.
nuclear chromosome part
Any constituent part of a nuclear chromosome, a chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
nuclear replisome
A multi-component enzymatic machine at the nuclear replication fork, which mediates DNA replication. Includes DNA primase, one or more DNA polymerases, DNA helicases, and other proteins.

protein binding
Interacting selectively with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
receptor binding
Interacting selectively with one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function.
cytokine activity
Functions to control the survival, growth, differentiation and effector function of tissues and cells.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
growth factor activity
The function that stimulates a cell to grow or proliferate. Most growth factors have other actions besides the induction of cell growth or proliferation.
all
This term is the most general term possible
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 03030 | 2.425e-03 | 0.5893 | 6 | 33 | DNA replication |
| 04060 | 4.324e-02 | 2.054 | 8 | 115 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction |
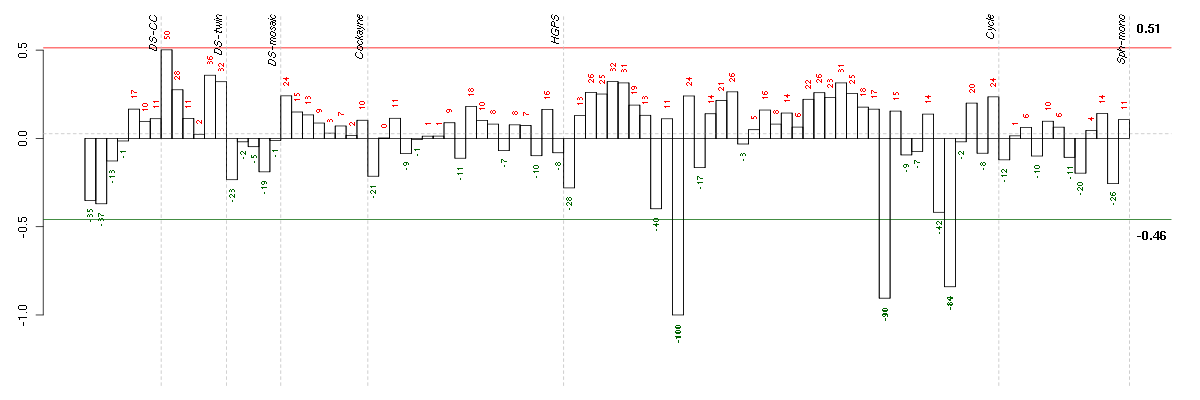
ANGPTL4angiopoietin-like 4 (221009_s_at), score: -0.89 AQP3aquaporin 3 (Gill blood group) (39248_at), score: -0.77 AREGamphiregulin (205239_at), score: -0.97 ASAP2ArfGAP with SH3 domain, ankyrin repeat and PH domain 2 (206414_s_at), score: -0.77 ASF1BASF1 anti-silencing function 1 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (218115_at), score: 0.62 ATP6V0A2ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal V0 subunit a2 (205704_s_at), score: -0.75 B3GNT2UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 2 (219326_s_at), score: -0.97 BCL2A1BCL2-related protein A1 (205681_at), score: -0.72 BMP2bone morphogenetic protein 2 (205289_at), score: -1 BMP6bone morphogenetic protein 6 (206176_at), score: -0.84 C17orf91chromosome 17 open reading frame 91 (214696_at), score: -0.77 C18orf24chromosome 18 open reading frame 24 (217640_x_at), score: 0.62 CBR3carbonyl reductase 3 (205379_at), score: 0.65 CCNE2cyclin E2 (205034_at), score: 0.62 CCNG2cyclin G2 (202769_at), score: 0.68 CCNJcyclin J (219470_x_at), score: -0.68 CDC6cell division cycle 6 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (203967_at), score: 0.65 CDC7cell division cycle 7 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (204510_at), score: 0.7 CDYLchromodomain protein, Y-like (203100_s_at), score: -0.72 CENPIcentromere protein I (214804_at), score: 0.63 CENPMcentromere protein M (218741_at), score: 0.66 CHAF1Achromatin assembly factor 1, subunit A (p150) (214426_x_at), score: 0.62 CKAP2cytoskeleton associated protein 2 (218252_at), score: 0.64 CPA3carboxypeptidase A3 (mast cell) (205624_at), score: -0.68 CXCL3chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 3 (207850_at), score: -0.7 CXCR7chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 7 (212977_at), score: -0.78 DSN1DSN1, MIND kinetochore complex component, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (219512_at), score: 0.66 DTLdenticleless homolog (Drosophila) (218585_s_at), score: 0.65 ENTPD7ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 7 (220153_at), score: -0.97 EZH2enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (Drosophila) (203358_s_at), score: 0.65 FAM108B1family with sequence similarity 108, member B1 (220285_at), score: -0.7 FBXW7F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7 (218751_s_at), score: -0.68 FGF1fibroblast growth factor 1 (acidic) (205117_at), score: -0.75 FGF7fibroblast growth factor 7 (keratinocyte growth factor) (205782_at), score: -0.7 GALNT4UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 4 (GalNAc-T4) (220442_at), score: -0.86 GFPT2glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase 2 (205100_at), score: -0.82 GINS2GINS complex subunit 2 (Psf2 homolog) (221521_s_at), score: 0.65 GPR183G protein-coupled receptor 183 (205419_at), score: -0.97 HLXH2.0-like homeobox (214438_at), score: -0.67 HMGB2high-mobility group box 2 (208808_s_at), score: 0.69 HOXA10homeobox A10 (213150_at), score: 0.7 HTR2A5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2A (207135_at), score: -0.72 ICAM1intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (202638_s_at), score: -0.85 IDI2isopentenyl-diphosphate delta isomerase 2 (217631_at), score: -0.71 IL1Ainterleukin 1, alpha (210118_s_at), score: -0.73 IL1Binterleukin 1, beta (39402_at), score: -0.89 IL6interleukin 6 (interferon, beta 2) (205207_at), score: -0.72 IL8interleukin 8 (211506_s_at), score: -0.75 INSIG1insulin induced gene 1 (201627_s_at), score: -0.73 JARID2jumonji, AT rich interactive domain 2 (203297_s_at), score: -0.79 JHDM1Djumonji C domain containing histone demethylase 1 homolog D (S. cerevisiae) (221778_at), score: -0.75 KCNG1potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily G, member 1 (214595_at), score: -0.8 KIAA1644KIAA1644 (52837_at), score: -0.69 KIF11kinesin family member 11 (204444_at), score: 0.63 KIF18Bkinesin family member 18B (222039_at), score: 0.63 LAMC2laminin, gamma 2 (202267_at), score: -0.86 LIFleukemia inhibitory factor (cholinergic differentiation factor) (205266_at), score: -0.75 LUZP1leucine zipper protein 1 (221832_s_at), score: -0.7 MAD2L1MAD2 mitotic arrest deficient-like 1 (yeast) (203362_s_at), score: 0.62 MAMLD1mastermind-like domain containing 1 (205088_at), score: -0.68 MCM10minichromosome maintenance complex component 10 (220651_s_at), score: 0.65 MCM2minichromosome maintenance complex component 2 (202107_s_at), score: 0.62 MDM1Mdm1 nuclear protein homolog (mouse) (213761_at), score: 0.67 MTSS1metastasis suppressor 1 (203037_s_at), score: -0.78 MYBL1v-myb myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog (avian)-like 1 (213906_at), score: 0.63 MYO1Emyosin IE (203072_at), score: -0.72 NR3C1nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 1 (glucocorticoid receptor) (201866_s_at), score: -0.69 PIK3CDphosphoinositide-3-kinase, catalytic, delta polypeptide (203879_at), score: -0.8 PLCXD1phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C, X domain containing 1 (218951_s_at), score: -0.71 PMEPA1prostate transmembrane protein, androgen induced 1 (217875_s_at), score: -0.86 POLA1polymerase (DNA directed), alpha 1, catalytic subunit (204835_at), score: 0.64 POLD1polymerase (DNA directed), delta 1, catalytic subunit 125kDa (203422_at), score: 0.63 POLD3polymerase (DNA-directed), delta 3, accessory subunit (212836_at), score: 0.63 PPP3CCprotein phosphatase 3 (formerly 2B), catalytic subunit, gamma isoform (207000_s_at), score: -0.85 PRIM1primase, DNA, polypeptide 1 (49kDa) (205053_at), score: 0.68 PTHLHparathyroid hormone-like hormone (211756_at), score: -0.82 RASGRP1RAS guanyl releasing protein 1 (calcium and DAG-regulated) (205590_at), score: -0.87 RASSF8Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain family (N-terminal) member 8 (207754_at), score: -0.67 RELBv-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog B (205205_at), score: -0.84 RFC3replication factor C (activator 1) 3, 38kDa (204128_s_at), score: 0.62 RICSRho GTPase-activating protein (203431_s_at), score: -0.69 SC4MOLsterol-C4-methyl oxidase-like (209146_at), score: -0.69 SEC14L2SEC14-like 2 (S. cerevisiae) (204541_at), score: -0.76 SIM1single-minded homolog 1 (Drosophila) (206876_at), score: 0.69 SLC19A2solute carrier family 19 (thiamine transporter), member 2 (209681_at), score: -0.69 SMOXspermine oxidase (210357_s_at), score: -0.68 SOX9SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 9 (202935_s_at), score: -0.76 SPATA2Lspermatogenesis associated 2-like (214965_at), score: -0.73 ST3GAL1ST3 beta-galactoside alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase 1 (208322_s_at), score: -0.73 STK38Lserine/threonine kinase 38 like (212572_at), score: -0.82 TACSTD2tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (202286_s_at), score: -0.76 TGFBR1transforming growth factor, beta receptor 1 (206943_at), score: -0.74 THBDthrombomodulin (203887_s_at), score: -0.91 TMEM194Atransmembrane protein 194A (212621_at), score: 0.69 TNFAIP3tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 3 (202644_s_at), score: -0.74 TP53BP2tumor protein p53 binding protein, 2 (203120_at), score: -0.68 TRAF4TNF receptor-associated factor 4 (202871_at), score: -0.69 TRPC6transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 6 (217287_s_at), score: -0.8 TTC17tetratricopeptide repeat domain 17 (218972_at), score: -0.88 TTKTTK protein kinase (204822_at), score: 0.65 TXNIPthioredoxin interacting protein (201008_s_at), score: 0.7 VCLvinculin (200930_s_at), score: -0.7 WEE1WEE1 homolog (S. pombe) (212533_at), score: 0.82 YOD1YOD1 OTU deubiquinating enzyme 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (215150_at), score: -0.67 YRDCyrdC domain containing (E. coli) (218647_s_at), score: -0.78 ZBED4zinc finger, BED-type containing 4 (204799_at), score: -0.76 ZFP36L2zinc finger protein 36, C3H type-like 2 (201367_s_at), score: 0.67 ZNF222zinc finger protein 222 (206175_x_at), score: -0.69 ZNF672zinc finger protein 672 (218068_s_at), score: -0.83
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485851.cel | 11 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486231.cel | 30 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486351.cel | 36 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |