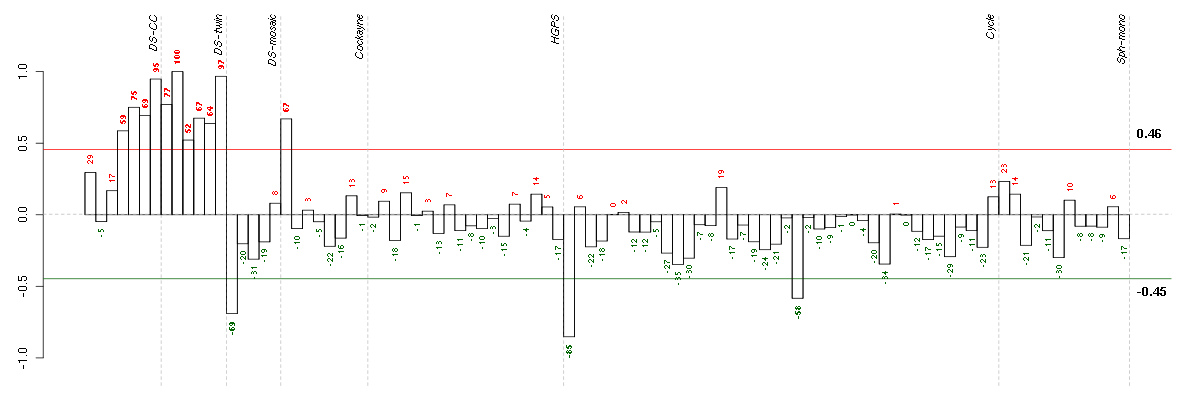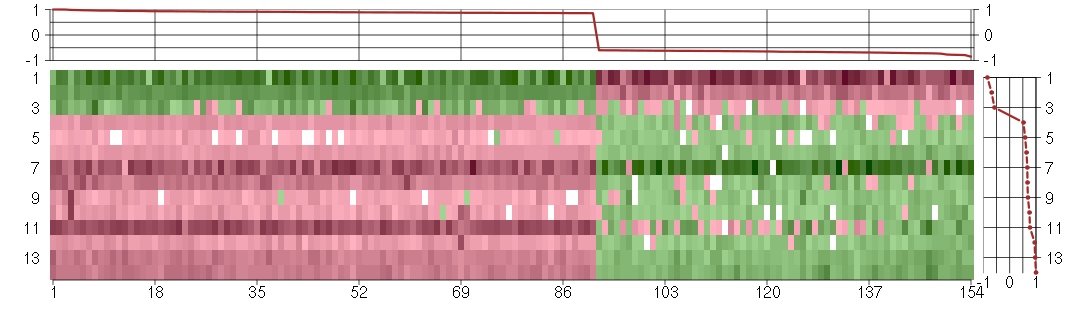

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
cell motion
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
response to external stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an external stimulus.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cell migration
The orderly movement of cells from one site to another, often during the development of a multicellular organism or multicellular structure.
antigen processing and presentation
The process by which an antigen-presenting cell expresses antigen (peptide or lipid) on its cell surface in association with an MHC protein complex.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
locomotion
Self-propelled movement of a cell or organism from one location to another.
antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen
The process by which an antigen-presenting cell expresses peptide antigen in association with an MHC protein complex on its cell surface, including proteolysis and transport steps for the peptide antigen both prior to and following assembly with the MHC protein complex. The peptide antigen is typically, but not always, processed from an endogenous or exogenous protein.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cell motility
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell that results in translocation of the cell from one place to another.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
keratinocyte migration
The directed movement of keratinocytes, epidermal cells which synthesize keratin, from one site to another.
localization of cell
Any process by which a cell is transported to, and/or maintained in, a specific location.
all
This term is the most general term possible
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cell motility
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell that results in translocation of the cell from one place to another.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
cell motion
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
MHC class I protein complex
A transmembrane protein complex composed of a MHC class I alpha chain and an invariant beta2-microglobin chain, and with or without a bound peptide antigen. Class I here refers to classical class I molecules.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
MHC protein complex
A transmembrane protein complex composed of an MHC alpha chain and, in most cases, either an MHC class II beta chain or an invariant beta2-microglobin chain, and with or without a bound peptide, lipid, or polysaccharide antigen.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or carbohydrate groups.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
MHC protein complex
A transmembrane protein complex composed of an MHC alpha chain and, in most cases, either an MHC class II beta chain or an invariant beta2-microglobin chain, and with or without a bound peptide, lipid, or polysaccharide antigen.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
signal transducer activity
Mediates the transfer of a signal from the outside to the inside of a cell by means other than the introduction of the signal molecule itself into the cell.
receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity.
transmembrane receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity, and spanning to the membrane of either the cell or an organelle.
MHC class I receptor activity
Combining with an MHC class I protein complex to initiate a change in cellular activity. Class I here refers to classical class I molecules.
molecular transducer activity
The molecular function that accepts an input of one form and creates an output of a different form.
all
This term is the most general term possible
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05330 | 3.878e-03 | 0.3984 | 5 | 21 | Allograft rejection |
| 05332 | 3.878e-03 | 0.3984 | 5 | 21 | Graft-versus-host disease |
| 05320 | 4.614e-03 | 0.4174 | 5 | 22 | Autoimmune thyroid disease |
| 04514 | 2.044e-02 | 1.328 | 7 | 70 | Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) |
ADAMTS9ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 9 (220287_at), score: 0.88 AGMATagmatine ureohydrolase (agmatinase) (219792_at), score: 0.92 AJAP1adherens junctions associated protein 1 (206460_at), score: -0.68 ALDOBaldolase B, fructose-bisphosphate (214423_x_at), score: 0.92 ANXA2P3annexin A2 pseudogene 3 (211241_at), score: 0.91 APOMapolipoprotein M (205682_x_at), score: 0.96 BCANbrevican (91920_at), score: 0.86 BCL7AB-cell CLL/lymphoma 7A (203795_s_at), score: -0.63 BCORL1BCL6 co-repressor-like 1 (219444_at), score: 0.91 BEND5BEN domain containing 5 (219670_at), score: 0.97 BMP10bone morphogenetic protein 10 (208292_at), score: 0.89 BRD3bromodomain containing 3 (203825_at), score: 0.86 BRS3bombesin-like receptor 3 (207369_at), score: 0.88 BTNL3butyrophilin-like 3 (217207_s_at), score: 0.93 C11orf21chromosome 11 open reading frame 21 (220560_at), score: 0.87 C19orf28chromosome 19 open reading frame 28 (220178_at), score: -0.66 C1orf61chromosome 1 open reading frame 61 (205103_at), score: 1 C8orf17chromosome 8 open reading frame 17 (208266_at), score: 0.89 C9orf33chromosome 9 open reading frame 33 (217130_at), score: 0.9 CASP4caspase 4, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase (209310_s_at), score: -0.66 CASZ1castor zinc finger 1 (220015_at), score: 0.93 CCR9chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 9 (207445_s_at), score: 0.88 CD40CD40 molecule, TNF receptor superfamily member 5 (35150_at), score: 0.93 CDC42SE1CDC42 small effector 1 (218157_x_at), score: -0.66 CDH18cadherin 18, type 2 (206280_at), score: 0.87 CEP152centrosomal protein 152kDa (215170_s_at), score: 0.89 CHST4carbohydrate (N-acetylglucosamine 6-O) sulfotransferase 4 (220446_s_at), score: 0.94 CLEC7AC-type lectin domain family 7, member A (221698_s_at), score: 0.94 COL11A2collagen, type XI, alpha 2 (216993_s_at), score: 0.91 COL15A1collagen, type XV, alpha 1 (203477_at), score: -0.78 CR1complement component (3b/4b) receptor 1 (Knops blood group) (217484_at), score: 0.92 CREG1cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes 1 (201200_at), score: -0.67 CRYGDcrystallin, gamma D (207532_at), score: 0.86 CTSEcathepsin E (205927_s_at), score: 0.9 CTTNBP2NLCTTNBP2 N-terminal like (214731_at), score: 0.88 CYP2A6cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily A, polypeptide 6 (211295_x_at), score: 0.94 CYP2C9cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily C, polypeptide 9 (214421_x_at), score: 0.87 DAOD-amino-acid oxidase (206878_at), score: 0.87 DNASE2deoxyribonuclease II, lysosomal (214992_s_at), score: -0.61 DNTTIP2deoxynucleotidyltransferase, terminal, interacting protein 2 (202776_at), score: -0.68 DPP4dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (211478_s_at), score: -0.79 DRD5dopamine receptor D5 (208486_at), score: 0.87 EDARectodysplasin A receptor (220048_at), score: 0.87 EPHB3EPH receptor B3 (1438_at), score: 0.9 EXD3exonuclease 3'-5' domain containing 3 (220838_at), score: 0.89 F10coagulation factor X (205620_at), score: -0.71 FGF7fibroblast growth factor 7 (keratinocyte growth factor) (205782_at), score: -0.62 FLGfilaggrin (215704_at), score: 0.98 FMO4flavin containing monooxygenase 4 (206263_at), score: 0.94 GNAO1guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), alpha activating activity polypeptide O (204762_s_at), score: 0.87 GNG4guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma 4 (205184_at), score: 0.87 GPNMBglycoprotein (transmembrane) nmb (201141_at), score: -0.72 GPR183G protein-coupled receptor 183 (205419_at), score: -0.61 GSTT1glutathione S-transferase theta 1 (203815_at), score: -0.64 HAO2hydroxyacid oxidase 2 (long chain) (220801_s_at), score: 0.9 HBEGFheparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (203821_at), score: -0.66 HIST1H2BKhistone cluster 1, H2bk (209806_at), score: -0.65 HIST1H4Dhistone cluster 1, H4d (208076_at), score: 0.89 HLA-Amajor histocompatibility complex, class I, A (213932_x_at), score: -0.63 HLA-Amajor histocompatibility complex, class I, A (217436_x_at), score: -0.64 HLA-Cmajor histocompatibility complex, class I, C (211799_x_at), score: -0.66 HLA-Emajor histocompatibility complex, class I, E (200904_at), score: -0.72 HLA-Fmajor histocompatibility complex, class I, F (204806_x_at), score: -0.7 HOXD11homeobox D11 (214604_at), score: 1 HOXD4homeobox D4 (205522_at), score: 0.91 HPCAL1hippocalcin-like 1 (205462_s_at), score: -0.65 IL1RAPinterleukin 1 receptor accessory protein (205227_at), score: -0.62 IL6interleukin 6 (interferon, beta 2) (205207_at), score: -0.69 ITIH2inter-alpha (globulin) inhibitor H2 (204987_at), score: 0.96 KCNMB4potassium large conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily M, beta member 4 (219287_at), score: 1 KLF1Kruppel-like factor 1 (erythroid) (210504_at), score: 0.97 KLHL26kelch-like 26 (Drosophila) (219354_at), score: -0.61 LITAFlipopolysaccharide-induced TNF factor (200706_s_at), score: -0.62 LOC730227hypothetical protein LOC730227 (215756_at), score: 0.93 LONRF3LON peptidase N-terminal domain and ring finger 3 (220009_at), score: 0.89 LYNv-yes-1 Yamaguchi sarcoma viral related oncogene homolog (202625_at), score: -0.69 MADCAM1mucosal vascular addressin cell adhesion molecule 1 (208037_s_at), score: 0.87 MAN1C1mannosidase, alpha, class 1C, member 1 (218918_at), score: -0.73 MAN2B1mannosidase, alpha, class 2B, member 1 (209166_s_at), score: -0.62 MAP2K3mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 (207667_s_at), score: -0.66 MBmyoglobin (204179_at), score: 0.92 MEIS3P1Meis homeobox 3 pseudogene 1 (214077_x_at), score: -0.7 MEOX1mesenchyme homeobox 1 (205619_s_at), score: 0.91 MMP9matrix metallopeptidase 9 (gelatinase B, 92kDa gelatinase, 92kDa type IV collagenase) (203936_s_at), score: 0.88 MUC3Amucin 3A, cell surface associated (217117_x_at), score: 0.9 MYO5Cmyosin VC (218966_at), score: 0.87 NCRNA00093non-protein coding RNA 93 (210723_x_at), score: 0.86 NFIBnuclear factor I/B (209290_s_at), score: 0.86 NFKB1nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1 (209239_at), score: -0.85 NID1nidogen 1 (202008_s_at), score: -0.67 NINJ1ninjurin 1 (203045_at), score: -0.68 NOTCH4Notch homolog 4 (Drosophila) (205247_at), score: 0.87 NOVA1neuro-oncological ventral antigen 1 (205794_s_at), score: 0.92 NPnucleoside phosphorylase (201695_s_at), score: -0.6 OR10C1olfactory receptor, family 10, subfamily C, member 1 (221339_at), score: 0.95 OR7E24olfactory receptor, family 7, subfamily E, member 24 (215463_at), score: 0.91 OVOL2ovo-like 2 (Drosophila) (211778_s_at), score: 0.87 PCDH7protocadherin 7 (205534_at), score: -0.6 PECAM1platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule (208982_at), score: 0.93 PEG3paternally expressed 3 (209242_at), score: 0.98 PER1period homolog 1 (Drosophila) (36829_at), score: 0.92 PGCprogastricsin (pepsinogen C) (205261_at), score: 0.91 PMEPA1prostate transmembrane protein, androgen induced 1 (217875_s_at), score: -0.72 POLR1Cpolymerase (RNA) I polypeptide C, 30kDa (207515_s_at), score: -0.63 POU4F1POU class 4 homeobox 1 (206940_s_at), score: 0.87 PPARDperoxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta (37152_at), score: -0.78 PRB3proline-rich protein BstNI subfamily 3 (206998_x_at), score: 0.93 PRKCBprotein kinase C, beta (209685_s_at), score: 0.91 PROL1proline rich, lacrimal 1 (208004_at), score: 0.9 PROX1prospero homeobox 1 (207401_at), score: 0.87 PTGDSprostaglandin D2 synthase 21kDa (brain) (212187_x_at), score: -0.77 PYHIN1pyrin and HIN domain family, member 1 (216748_at), score: 0.88 RAB26RAB26, member RAS oncogene family (50965_at), score: 0.89 RALGPS2Ral GEF with PH domain and SH3 binding motif 2 (220338_at), score: 0.93 RCAN2regulator of calcineurin 2 (203498_at), score: -0.61 ROS1c-ros oncogene 1 , receptor tyrosine kinase (207569_at), score: 0.86 RPGRIP1retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator interacting protein 1 (206608_s_at), score: 0.91 RPS4Y1ribosomal protein S4, Y-linked 1 (201909_at), score: -0.7 RRADRas-related associated with diabetes (204802_at), score: -0.66 RUNX1runt-related transcription factor 1 (209360_s_at), score: -0.6 S100A12S100 calcium binding protein A12 (205863_at), score: 0.86 S100A14S100 calcium binding protein A14 (218677_at), score: 0.88 SASH3SAM and SH3 domain containing 3 (204923_at), score: 0.86 SERPINA1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 1 (211429_s_at), score: 0.96 SERPINB8serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 8 (206034_at), score: -0.61 SHBSrc homology 2 domain containing adaptor protein B (204657_s_at), score: -0.63 SLC10A1solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 1 (207185_at), score: 0.89 SLC10A2solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 2 (207095_at), score: 0.86 SLC19A2solute carrier family 19 (thiamine transporter), member 2 (209681_at), score: -0.6 SLC1A7solute carrier family 1 (glutamate transporter), member 7 (210923_at), score: 0.89 SLC26A10solute carrier family 26, member 10 (214951_at), score: 0.86 SLC4A5solute carrier family 4, sodium bicarbonate cotransporter, member 5 (204296_at), score: 0.93 SPARCL1SPARC-like 1 (hevin) (200795_at), score: 0.88 SPRY2sprouty homolog 2 (Drosophila) (204011_at), score: -0.62 SPRY4sprouty homolog 4 (Drosophila) (221489_s_at), score: -0.62 STOMstomatin (201060_x_at), score: -0.64 SVEP1sushi, von Willebrand factor type A, EGF and pentraxin domain containing 1 (213247_at), score: -0.71 TAS2R16taste receptor, type 2, member 16 (221444_at), score: 0.9 TEX2testis expressed 2 (218099_at), score: -0.64 TM6SF1transmembrane 6 superfamily member 1 (219892_at), score: -0.67 TMEM39Atransmembrane protein 39A (218615_s_at), score: -0.63 TMEM41Btransmembrane protein 41B (212623_at), score: -0.62 TP53BP2tumor protein p53 binding protein, 2 (203120_at), score: -0.68 TP63tumor protein p63 (209863_s_at), score: 0.91 TPP1tripeptidyl peptidase I (200742_s_at), score: -0.71 TRIB1tribbles homolog 1 (Drosophila) (202241_at), score: -0.62 TRIM45tripartite motif-containing 45 (219923_at), score: 0.96 WDR3WD repeat domain 3 (218882_s_at), score: -0.63 YRDCyrdC domain containing (E. coli) (218647_s_at), score: -0.68 ZNF286Azinc finger protein 286A (220250_at), score: 0.87 ZNF287zinc finger protein 287 (216453_at), score: 0.91 ZNF35zinc finger protein 35 (206096_at), score: -0.64 ZNF362zinc finger protein 362 (214915_at), score: 0.88 ZNF672zinc finger protein 672 (218068_s_at), score: -0.66
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485651.cel | 1 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| 46A.CEL | 1 | 3 | DS-mosaic | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-mosaic 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486071.cel | 22 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| 3Twin.CEL | 3 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 3 |
| t21a 08-03.CEL | 4 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 4 |
| 5CTwin.CEL | 5 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 5 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949557.cel | 1 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |
| 4Twin.CEL | 4 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 4 |
| t21c 08-03.CEL | 6 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 6 |
| t21b 08-03.CEL | 5 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 5 |
| 1Twin.CEL | 1 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 1 |
| t21d 08-03.CEL | 7 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 7 |
| 6Twin.CEL | 6 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 6 |
| 2Twin.CEL | 2 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 2 |