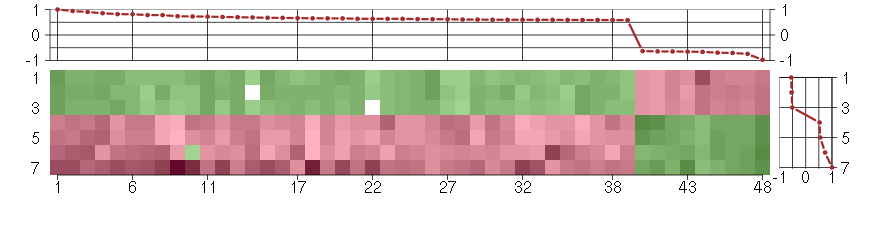

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
cellular aldehyde metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving aldehydes, any organic compound with the formula R-CH=O, as carried out by individual cells.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
salivary gland development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the salivary gland over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Salivary glands include any of the saliva-secreting exocrine glands of the oral cavity.
salivary gland morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of the salivary gland are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
gland morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a gland are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
exocrine system development
Progression of the exocrine system over time, from its formation to a mature structure. The exocrine system is a system of hormones and glands, where the glands secrete straight to a target site via ducts or tubes. The human exocrine system includes the salivary glands, sweat glands and many glands of the digestive system.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
gland development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a gland over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A gland is an organ specialised for secretion.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
salivary gland development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the salivary gland over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Salivary glands include any of the saliva-secreting exocrine glands of the oral cavity.
gland morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a gland are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
salivary gland morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of the salivary gland are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.


molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
aldo-keto reductase activity
Catalysis of the NADPH-dependent reduction of carbonyl compounds.
aryl sulfotransferase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate + a phenol = adenosine 3',5'-bisphosphate + an aryl sulfate.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
oxidoreductase activity
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction, a reversible chemical reaction in which the oxidation state of an atom or atoms within a molecule is altered. One substrate acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and becomes oxidized, while the other acts as hydrogen or electron acceptor and becomes reduced.
sulfotransferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a sulfate group from 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate to the hydroxyl group of an acceptor, producing the sulfated derivative and 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphate.
steroid dehydrogenase activity
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which one substrate is a sterol derivative.
oxidoreductase activity, acting on CH-OH group of donors
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-OH group act as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces a hydrogen or electron acceptor.
oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-OH group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces NAD+ or NADP.
oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-CH group of donors
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-CH group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces a hydrogen or electron acceptor.
oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-CH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-CH group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces NAD or NADP.
transferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from one compound (generally regarded as the donor) to another compound (generally regarded as the acceptor). Transferase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 2.
transferase activity, transferring sulfur-containing groups
Catalysis of the transfer of a sulfur-containing group from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor).
carboxylic acid binding
Interacting selectively with a carboxylic acid, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
bile acid binding
Interacting selectively with bile acids, any of a group of steroid carboxylic acids occurring in bile.
steroid dehydrogenase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-OH group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces NAD+ or NADP, and in which one substrate is a sterol derivative.
3-alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (A-specific) activity
Catalysis of the reaction: NAD(P)+ + androsterone = NAD(P)H + H+ + 5-alpha-androstane-3,17-dione. The reaction is A-specific (i.e. the pro-R hydrogen is transferred from the 4-position of reduced nicotinamide cofactor) with respect to NAD(P)+.
trans-1,2-dihydrobenzene-1,2-diol dehydrogenase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: NADP+ + trans-1,2-dihydrobenzene-1,2-diol = NADPH + catechol.
all
This term is the most general term possible
steroid dehydrogenase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-OH group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces NAD+ or NADP, and in which one substrate is a sterol derivative.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00980 | 1.694e-02 | 0.3122 | 4 | 37 | Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 |
| 00120 | 2.328e-02 | 0.1434 | 3 | 17 | Bile acid biosynthesis |
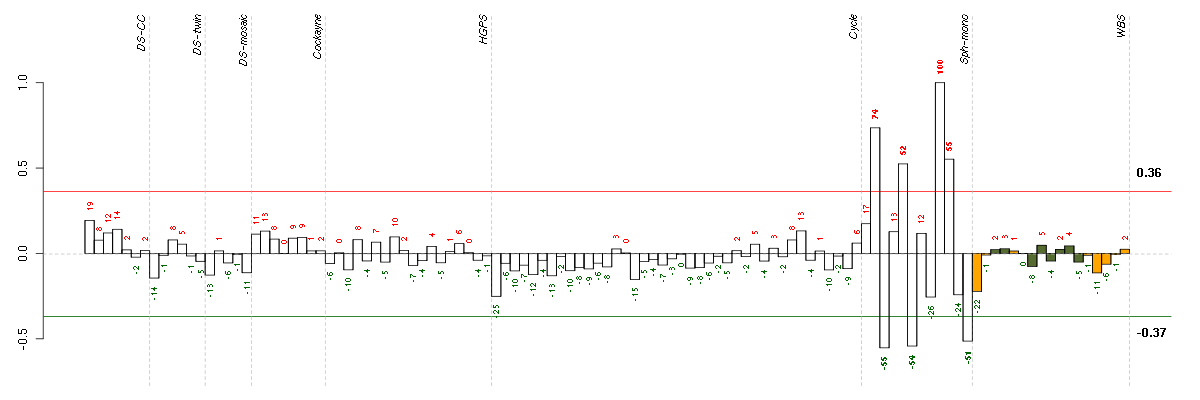
ABCG2ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 2 (209735_at), score: 0.59 ACSL5acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 5 (218322_s_at), score: 0.64 AKAP2A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein 2 (202759_s_at), score: -0.65 AKR1B10aldo-keto reductase family 1, member B10 (aldose reductase) (206561_s_at), score: 0.94 AKR1C1aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C1 (dihydrodiol dehydrogenase 1; 20-alpha (3-alpha)-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase) (204151_x_at), score: 0.59 AKR1C2aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C2 (dihydrodiol dehydrogenase 2; bile acid binding protein; 3-alpha hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, type III) (209699_x_at), score: 0.64 AKR1C3aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C3 (3-alpha hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, type II) (209160_at), score: 0.63 ALDH3A1aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, memberA1 (205623_at), score: 0.71 ALDH3A2aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, member A2 (202053_s_at), score: 0.58 ASB9ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing 9 (205673_s_at), score: 0.61 BMP7bone morphogenetic protein 7 (209590_at), score: 0.67 C14orf169chromosome 14 open reading frame 169 (219526_at), score: -0.71 C20orf39chromosome 20 open reading frame 39 (219310_at), score: 0.78 CELSR1cadherin, EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 1 (flamingo homolog, Drosophila) (41660_at), score: 0.81 CELSR3cadherin, EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 3 (flamingo homolog, Drosophila) (40020_at), score: 0.72 CFIcomplement factor I (203854_at), score: 0.6 DGKDdiacylglycerol kinase, delta 130kDa (208072_s_at), score: 0.62 DLX4distal-less homeobox 4 (208216_at), score: 0.6 EGLN3egl nine homolog 3 (C. elegans) (219232_s_at), score: 0.65 EMP1epithelial membrane protein 1 (201325_s_at), score: -0.64 FAM174Bfamily with sequence similarity 174, member B (51158_at), score: -0.66 FCGR2AFc fragment of IgG, low affinity IIa, receptor (CD32) (203561_at), score: 0.78 FGF13fibroblast growth factor 13 (205110_s_at), score: 0.62 GABRA2gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 2 (207014_at), score: 0.74 GREM1gremlin 1, cysteine knot superfamily, homolog (Xenopus laevis) (218469_at), score: -0.97 HHIPL2HHIP-like 2 (220283_at), score: 0.59 HLA-DRB1major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 1 (209312_x_at), score: 0.65 IGSF3immunoglobulin superfamily, member 3 (202421_at), score: 0.85 KYNUkynureninase (L-kynurenine hydrolase) (217388_s_at), score: 1 LAPTM5lysosomal multispanning membrane protein 5 (201721_s_at), score: 0.63 LEF1lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (221558_s_at), score: 0.82 LUMlumican (201744_s_at), score: -0.69 MPPED2metallophosphoesterase domain containing 2 (205413_at), score: 0.9 MYO1Bmyosin IB (212364_at), score: -0.74 NDRG1N-myc downstream regulated 1 (200632_s_at), score: 0.59 NPTX1neuronal pentraxin I (204684_at), score: 0.65 RARBretinoic acid receptor, beta (205080_at), score: 0.69 RBM47RNA binding motif protein 47 (218035_s_at), score: 0.6 RIPK4receptor-interacting serine-threonine kinase 4 (221215_s_at), score: 0.7 RND3Rho family GTPase 3 (212724_at), score: -0.63 SH3BGRSH3 domain binding glutamic acid-rich protein (204979_s_at), score: 0.59 SPANXCSPANX family, member C (220217_x_at), score: 0.66 SULT1A1sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1A, phenol-preferring, member 1 (203615_x_at), score: 0.67 SULT1A2sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1A, phenol-preferring, member 2 (207122_x_at), score: 0.61 TEStestis derived transcript (3 LIM domains) (202720_at), score: -0.65 TGFB2transforming growth factor, beta 2 (220407_s_at), score: 0.6 TGIF2TGFB-induced factor homeobox 2 (216262_s_at), score: 0.62 VAV3vav 3 guanine nucleotide exchange factor (218807_at), score: 0.73
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956178.cel | 6 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956358.cel | 10 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956824.cel | 24 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956321.cel | 9 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956614.cel | 18 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956138.cel | 4 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956457.cel | 14 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |