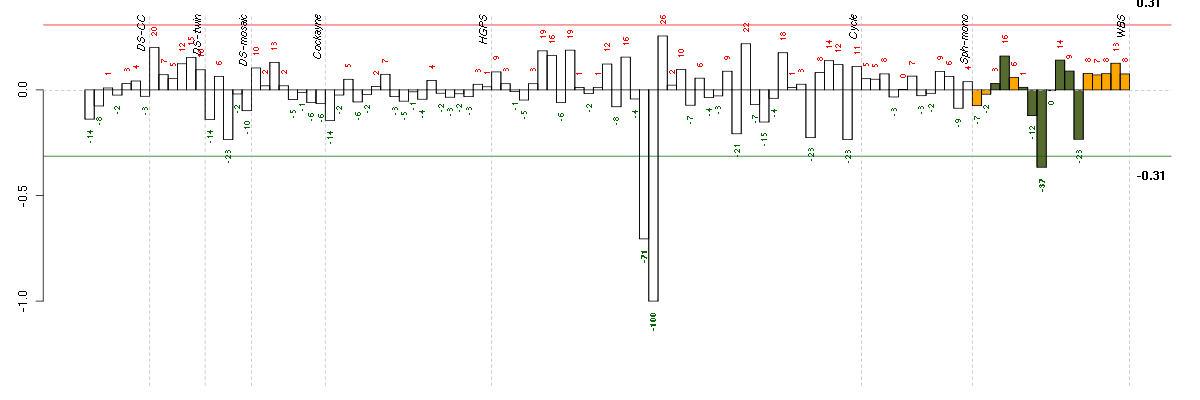

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
transcription
The synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription, DNA-dependent
The synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
gene expression
The process by which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
mesenchymal cell development
The process aimed at the progression of a mesenchymal cell over time, from initial commitment of the cell to its specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
RNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
RNA biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage. Includes polymerization of ribonucleotide monomers.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
mesenchymal cell differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a mesenchymal cell.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
transcription
The synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription, DNA-dependent
The synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
RNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
RNA biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage. Includes polymerization of ribonucleotide monomers.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
mesenchymal cell development
The process aimed at the progression of a mesenchymal cell over time, from initial commitment of the cell to its specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.
transcription
The synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.


molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
nucleic acid binding
Interacting selectively with any nucleic acid.
DNA binding
Interacting selectively with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
transcription factor activity
The function of binding to a specific DNA sequence in order to modulate transcription. The transcription factor may or may not also interact selectively with a protein or macromolecular complex.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
transcription regulator activity
Plays a role in regulating transcription; may bind a promoter or enhancer DNA sequence or interact with a DNA-binding transcription factor.
all
This term is the most general term possible
transcription factor activity
The function of binding to a specific DNA sequence in order to modulate transcription. The transcription factor may or may not also interact selectively with a protein or macromolecular complex.
ADAMTS6ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 6 (220866_at), score: -0.58 ADNP2ADNP homeobox 2 (203321_s_at), score: -0.57 ALPPL2alkaline phosphatase, placental-like 2 (216377_x_at), score: 0.64 AMELXamelogenin (amelogenesis imperfecta 1, X-linked) (208410_x_at), score: 0.64 ARHGEF11Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 11 (202914_s_at), score: -0.61 ATF3activating transcription factor 3 (202672_s_at), score: -0.54 BANPBTG3 associated nuclear protein (219966_x_at), score: 0.65 BCL2B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2 (203685_at), score: 0.66 BRPF1bromodomain and PHD finger containing, 1 (204481_at), score: -0.54 C10orf59chromosome 10 open reading frame 59 (220564_at), score: -0.61 C16orf7chromosome 16 open reading frame 7 (205781_at), score: -0.67 C1orf109chromosome 1 open reading frame 109 (218712_at), score: 0.67 C1orf159chromosome 1 open reading frame 159 (219337_at), score: -0.57 C8orf17chromosome 8 open reading frame 17 (208266_at), score: -0.68 CCDC25coiled-coil domain containing 25 (218125_s_at), score: 0.58 CDADC1cytidine and dCMP deaminase domain containing 1 (221015_s_at), score: 0.59 CELSR2cadherin, EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 2 (flamingo homolog, Drosophila) (204029_at), score: 0.58 CLCF1cardiotrophin-like cytokine factor 1 (219500_at), score: -0.99 CLEC1AC-type lectin domain family 1, member A (219761_at), score: -0.59 CPZcarboxypeptidase Z (211062_s_at), score: -0.64 CRELD1cysteine-rich with EGF-like domains 1 (203368_at), score: -0.55 CROCCL1ciliary rootlet coiled-coil, rootletin-like 1 (211038_s_at), score: 0.57 CYTH1cytohesin 1 (202880_s_at), score: -0.64 DDIT4DNA-damage-inducible transcript 4 (202887_s_at), score: 0.57 DGCR2DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 2 (214198_s_at), score: 0.59 DLX4distal-less homeobox 4 (208216_at), score: -0.6 DNAJC24DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 24 (213853_at), score: 0.64 DNM3dynamin 3 (209839_at), score: -0.62 DNMBPdynamin binding protein (212838_at), score: 0.62 DUSP6dual specificity phosphatase 6 (208892_s_at), score: -0.6 EDN1endothelin 1 (218995_s_at), score: -0.78 EGR2early growth response 2 (Krox-20 homolog, Drosophila) (205249_at), score: -0.99 EGR3early growth response 3 (206115_at), score: -0.97 EIF3Leukaryotic translation initiation factor 3, subunit L (217719_at), score: 0.56 EPHA2EPH receptor A2 (203499_at), score: -0.6 FAM131Bfamily with sequence similarity 131, member B (205368_at), score: 0.65 FGFR3fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (204379_s_at), score: -0.68 FOXC2forkhead box C2 (MFH-1, mesenchyme forkhead 1) (214520_at), score: -0.58 FURINfurin (paired basic amino acid cleaving enzyme) (201945_at), score: -0.58 GABRG3gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, gamma 3 (216895_at), score: 0.56 GIPC2GIPC PDZ domain containing family, member 2 (219970_at), score: -0.55 HERC3hect domain and RLD 3 (206183_s_at), score: -0.57 HINFPhistone H4 transcription factor (206495_s_at), score: 0.6 HISPPD2Ahistidine acid phosphatase domain containing 2A (204578_at), score: 0.67 HOXA9homeobox A9 (214651_s_at), score: 0.6 IER2immediate early response 2 (202081_at), score: -0.59 IER3immediate early response 3 (201631_s_at), score: -0.76 IPPKinositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate 2-kinase (219092_s_at), score: -0.57 JUNBjun B proto-oncogene (201473_at), score: -1 KIAA0907KIAA0907 (202220_at), score: 0.67 KIAA1598KIAA1598 (221802_s_at), score: 0.57 KLHL26kelch-like 26 (Drosophila) (219354_at), score: -0.56 KLHL5kelch-like 5 (Drosophila) (220682_s_at), score: 0.58 LAIR2leukocyte-associated immunoglobulin-like receptor 2 (207509_s_at), score: -0.65 LIFleukemia inhibitory factor (cholinergic differentiation factor) (205266_at), score: -0.91 LRRC37B2leucine rich repeat containing 37, member B2 (216149_at), score: 0.56 MAP3K14mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 14 (205192_at), score: -0.65 MCOLN1mucolipin 1 (219952_s_at), score: -0.62 MGAMAX gene associated (212945_s_at), score: 0.57 MTMR3myotubularin related protein 3 (202197_at), score: -0.62 MYH15myosin, heavy chain 15 (215331_at), score: 0.64 MYST2MYST histone acetyltransferase 2 (200049_at), score: -0.57 NFATC4nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 4 (205897_at), score: -0.59 NTRK3neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type 3 (217033_x_at), score: -0.55 NUDT2nudix (nucleoside diphosphate linked moiety X)-type motif 2 (218609_s_at), score: 0.59 OCLMoculomedin (208274_at), score: 0.77 OSBPoxysterol binding protein (201800_s_at), score: 0.69 PEX13peroxisomal biogenesis factor 13 (205246_at), score: -0.57 PHF16PHD finger protein 16 (204866_at), score: 0.56 PKD1polycystic kidney disease 1 (autosomal dominant) (202328_s_at), score: -0.59 PLK3polo-like kinase 3 (Drosophila) (204958_at), score: -0.79 PRKCHprotein kinase C, eta (218764_at), score: -0.55 PTCD1pentatricopeptide repeat domain 1 (218956_s_at), score: 0.62 PYGO1pygopus homolog 1 (Drosophila) (215517_at), score: -0.54 R3HDM2R3H domain containing 2 (203831_at), score: 0.6 RABL3RAB, member of RAS oncogene family-like 3 (213970_at), score: 0.89 RARAretinoic acid receptor, alpha (203749_s_at), score: -0.77 RBPJrecombination signal binding protein for immunoglobulin kappa J region (211974_x_at), score: 0.57 RIPK1receptor (TNFRSF)-interacting serine-threonine kinase 1 (209941_at), score: -0.64 RPGRIP1LRPGRIP1-like (213959_s_at), score: 0.57 RPL10Lribosomal protein L10-like (217559_at), score: 0.64 RSBN1round spermatid basic protein 1 (213694_at), score: 0.96 SAPS2SAPS domain family, member 2 (202792_s_at), score: 0.56 SERPINB3serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 3 (209719_x_at), score: 0.57 SETMARSET domain and mariner transposase fusion gene (206554_x_at), score: 0.62 SLC24A1solute carrier family 24 (sodium/potassium/calcium exchanger), member 1 (206081_at), score: 0.56 SLC25A21solute carrier family 25 (mitochondrial oxodicarboxylate carrier), member 21 (220474_at), score: 0.58 SLC25A28solute carrier family 25, member 28 (221432_s_at), score: -0.69 SLC2A8solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 8 (218985_at), score: -0.76 SMAD7SMAD family member 7 (204790_at), score: -0.65 SPAG1sperm associated antigen 1 (210117_at), score: -0.56 SPAG6sperm associated antigen 6 (210033_s_at), score: -0.6 SPRY4sprouty homolog 4 (Drosophila) (221489_s_at), score: -0.55 SRD5A1steroid-5-alpha-reductase, alpha polypeptide 1 (3-oxo-5 alpha-steroid delta 4-dehydrogenase alpha 1) (204675_at), score: 0.59 STAP2signal transducing adaptor family member 2 (221610_s_at), score: 0.62 TACC2transforming, acidic coiled-coil containing protein 2 (202289_s_at), score: 0.7 TCF3transcription factor 3 (E2A immunoglobulin enhancer binding factors E12/E47) (209153_s_at), score: 0.63 TLE2transducin-like enhancer of split 2 (E(sp1) homolog, Drosophila) (40837_at), score: -0.56 TRIB1tribbles homolog 1 (Drosophila) (202241_at), score: -0.64 ULBP1UL16 binding protein 1 (221323_at), score: -0.75 UPF2UPF2 regulator of nonsense transcripts homolog (yeast) (203519_s_at), score: 0.57 VAMP1vesicle-associated membrane protein 1 (synaptobrevin 1) (213326_at), score: 0.7 WDR5BWD repeat domain 5B (219538_at), score: 0.8 ZBTB24zinc finger and BTB domain containing 24 (205340_at), score: 0.76 ZC3H12Azinc finger CCCH-type containing 12A (218810_at), score: -0.72 ZFAND5zinc finger, AN1-type domain 5 (217741_s_at), score: -0.58 ZKSCAN4zinc finger with KRAB and SCAN domains 4 (213625_at), score: 0.71 ZNF133zinc finger protein 133 (216960_s_at), score: 0.59 ZNF280Dzinc finger protein 280D (221213_s_at), score: 0.71 ZNF3zinc finger protein 3 (212684_at), score: 0.57 ZNF337zinc finger protein 337 (37860_at), score: 0.82 ZNF480zinc finger protein 480 (222283_at), score: 0.63 ZNF510zinc finger protein 510 (206053_at), score: 0.63 ZNF606zinc finger protein 606 (219635_at), score: 0.68 ZNF75Dzinc finger protein 75D (213659_at), score: 0.58
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485991.cel | 18 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485971.cel | 17 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| 5850_CNTL.CEL | 8 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | none | WBS 1 |