
Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
embryonic development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an embryo from its formation until the end of its embryonic life stage. The end of the embryonic stage is organism-specific. For example, for mammals, the process would begin with zygote formation and end with birth. For insects, the process would begin at zygote formation and end with larval hatching. For plant zygotic embryos, this would be from zygote formation to the end of seed dormancy. For plant vegetative embryos, this would be from the initial determination of the cell or group of cells to form an embryo until the point when the embryo becomes independent of the parent plant.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
embryonic limb morphogenesis
The process, occurring in the embryo, by which the anatomical structures of the limb are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. A limb is an appendage of an animal used for locomotion or grasping.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
appendage morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of appendages are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. An appendage is an organ or part that is attached to the trunk of an organism. For example a limb or a branch.
limb morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of limb are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. A limb is an appendage of an animal used for locomotion or grasping. For example a leg, arm or some types of fin.
embryonic appendage morphogenesis
The process, occurring in the embryo, by which the anatomical structures of the appendage are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. An appendage is an organ or part that is attached to the trunk of an organism. For example a limb or a branch.
embryonic morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The embryonic phase begins with zygote formation. The end of the embryonic phase is organism-specific. For example, it would be at birth for mammals, larval hatching for insects and seed dormancy in plants.
appendage development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an appendage over time, from its formation to the mature structure. An appendage is an organ or part that is attached to the trunk of an organism. For example a limb or a branch.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
limb development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a limb over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A limb is an appendage of an animal used for locomotion or grasping. For example a leg, arm or some types of fin.
all
This term is the most general term possible
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
embryonic development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an embryo from its formation until the end of its embryonic life stage. The end of the embryonic stage is organism-specific. For example, for mammals, the process would begin with zygote formation and end with birth. For insects, the process would begin at zygote formation and end with larval hatching. For plant zygotic embryos, this would be from zygote formation to the end of seed dormancy. For plant vegetative embryos, this would be from the initial determination of the cell or group of cells to form an embryo until the point when the embryo becomes independent of the parent plant.
embryonic morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The embryonic phase begins with zygote formation. The end of the embryonic phase is organism-specific. For example, it would be at birth for mammals, larval hatching for insects and seed dormancy in plants.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
appendage development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an appendage over time, from its formation to the mature structure. An appendage is an organ or part that is attached to the trunk of an organism. For example a limb or a branch.
appendage morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of appendages are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. An appendage is an organ or part that is attached to the trunk of an organism. For example a limb or a branch.
embryonic appendage morphogenesis
The process, occurring in the embryo, by which the anatomical structures of the appendage are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. An appendage is an organ or part that is attached to the trunk of an organism. For example a limb or a branch.
limb morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of limb are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. A limb is an appendage of an animal used for locomotion or grasping. For example a leg, arm or some types of fin.
embryonic limb morphogenesis
The process, occurring in the embryo, by which the anatomical structures of the limb are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. A limb is an appendage of an animal used for locomotion or grasping.

extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
all
This term is the most general term possible

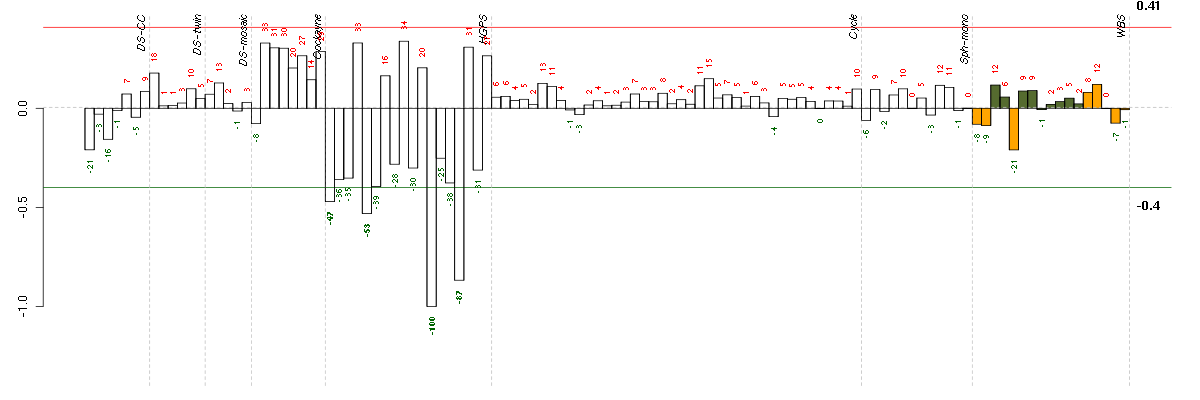
ADAMTS5ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 5 (219935_at), score: -0.55 ADCY7adenylate cyclase 7 (203741_s_at), score: -0.44 ADD2adducin 2 (beta) (205268_s_at), score: -0.49 AHRaryl hydrocarbon receptor (202820_at), score: 0.56 ANTXR1anthrax toxin receptor 1 (220092_s_at), score: -0.54 ARNTLaryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like (209824_s_at), score: -0.44 ATP5DATP synthase, H+ transporting, mitochondrial F1 complex, delta subunit (213041_s_at), score: -0.49 BBXbobby sox homolog (Drosophila) (213016_at), score: 0.58 BIN3bridging integrator 3 (222199_s_at), score: -0.47 BNC1basonuclin 1 (206581_at), score: -0.46 C1orf54chromosome 1 open reading frame 54 (219506_at), score: 0.6 C4orf31chromosome 4 open reading frame 31 (219747_at), score: -0.7 CAMK2N1calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II inhibitor 1 (218309_at), score: -0.44 CAPGcapping protein (actin filament), gelsolin-like (201850_at), score: -0.53 CD44CD44 molecule (Indian blood group) (210916_s_at), score: -0.49 CDH4cadherin 4, type 1, R-cadherin (retinal) (206866_at), score: -0.51 CGBchorionic gonadotropin, beta polypeptide (205387_s_at), score: -1 CH25Hcholesterol 25-hydroxylase (206932_at), score: -0.49 CKBcreatine kinase, brain (200884_at), score: -0.6 CLEC2BC-type lectin domain family 2, member B (209732_at), score: -0.63 CNIH3cornichon homolog 3 (Drosophila) (214841_at), score: -0.47 COL8A2collagen, type VIII, alpha 2 (221900_at), score: -0.54 COMPcartilage oligomeric matrix protein (205713_s_at), score: -0.7 CYP26B1cytochrome P450, family 26, subfamily B, polypeptide 1 (219825_at), score: -0.6 DICER1dicer 1, ribonuclease type III (213229_at), score: 0.57 ELL2elongation factor, RNA polymerase II, 2 (214446_at), score: -0.44 EMX2empty spiracles homeobox 2 (221950_at), score: -0.5 EPB41L3erythrocyte membrane protein band 4.1-like 3 (206710_s_at), score: -0.43 FAM46Afamily with sequence similarity 46, member A (221766_s_at), score: -0.49 GABARAPL3GABA(A) receptors associated protein like 3 (pseudogene) (211458_s_at), score: -0.45 GABRA5gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 5 (206456_at), score: -0.54 GATA2GATA binding protein 2 (209710_at), score: -0.53 GFRA1GDNF family receptor alpha 1 (205696_s_at), score: -0.46 GOLIM4golgi integral membrane protein 4 (204324_s_at), score: 0.56 GRAMD4GRAM domain containing 4 (212856_at), score: -0.44 HMOX1heme oxygenase (decycling) 1 (203665_at), score: -0.53 HOXA10homeobox A10 (213150_at), score: -0.48 HOXA11homeobox A11 (213823_at), score: -0.55 HOXA9homeobox A9 (214651_s_at), score: -0.59 HS3ST3A1heparan sulfate (glucosamine) 3-O-sulfotransferase 3A1 (219985_at), score: -0.51 IER3immediate early response 3 (201631_s_at), score: 0.59 IMAASLC7A5 pseudogene (208118_x_at), score: -0.52 INHBBinhibin, beta B (205258_at), score: -0.65 IRX5iroquois homeobox 5 (210239_at), score: -0.6 ISLRimmunoglobulin superfamily containing leucine-rich repeat (207191_s_at), score: -0.58 KBTBD11kelch repeat and BTB (POZ) domain containing 11 (204301_at), score: -0.52 LAPTM5lysosomal multispanning membrane protein 5 (201721_s_at), score: -0.48 LOC100129652hypothetical protein LOC100129652 (208622_s_at), score: -0.44 LRRC15leucine rich repeat containing 15 (213909_at), score: -0.54 MBPmyelin basic protein (210136_at), score: 0.56 MEGF6multiple EGF-like-domains 6 (213942_at), score: -0.58 MLPHmelanophilin (218211_s_at), score: -0.46 MMP3matrix metallopeptidase 3 (stromelysin 1, progelatinase) (205828_at), score: -0.46 MSL2male-specific lethal 2 homolog (Drosophila) (218733_at), score: -0.48 MSX1msh homeobox 1 (205932_s_at), score: -0.56 MXRA5matrix-remodelling associated 5 (209596_at), score: -0.48 NBL1neuroblastoma, suppression of tumorigenicity 1 (37005_at), score: -0.57 NCAM1neural cell adhesion molecule 1 (212843_at), score: -0.65 NCLNnicalin homolog (zebrafish) (222206_s_at), score: -0.54 NDNnecdin homolog (mouse) (209550_at), score: -0.5 NRG1neuregulin 1 (206343_s_at), score: -0.5 NTF3neurotrophin 3 (206706_at), score: -0.45 ODZ4odz, odd Oz/ten-m homolog 4 (Drosophila) (213273_at), score: -0.46 PALLDpalladin, cytoskeletal associated protein (200906_s_at), score: 0.55 PBX1pre-B-cell leukemia homeobox 1 (212148_at), score: -0.5 PLA2G4Aphospholipase A2, group IVA (cytosolic, calcium-dependent) (210145_at), score: 0.61 PLAC8placenta-specific 8 (219014_at), score: -0.53 PLEC1plectin 1, intermediate filament binding protein 500kDa (216971_s_at), score: -0.43 POLR2J2polymerase (RNA) II (DNA directed) polypeptide J2 (216242_x_at), score: -0.45 POMZP3POM (POM121 homolog, rat) and ZP3 fusion (204148_s_at), score: -0.47 PRPS1phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase 1 (208447_s_at), score: -0.43 PSG2pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 2 (208134_x_at), score: -0.53 PSG5pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 5 (204830_x_at), score: -0.51 PSG6pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 6 (209738_x_at), score: -0.46 PSG9pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 9 (209594_x_at), score: -0.51 PTPLBprotein tyrosine phosphatase-like (proline instead of catalytic arginine), member b (212640_at), score: -0.48 PTPRBprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, B (205846_at), score: -0.66 PTPRRprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, R (210675_s_at), score: -0.48 RAB11BRAB11B, member RAS oncogene family (34478_at), score: -0.48 RAB31RAB31, member RAS oncogene family (217763_s_at), score: -0.46 RASIP1Ras interacting protein 1 (220027_s_at), score: -0.56 RELNreelin (205923_at), score: 0.55 RUNX3runt-related transcription factor 3 (204198_s_at), score: -0.63 SALL1sal-like 1 (Drosophila) (206893_at), score: -0.51 SGCDsarcoglycan, delta (35kDa dystrophin-associated glycoprotein) (213543_at), score: -0.49 SIRPAsignal-regulatory protein alpha (202897_at), score: -0.51 SLC16A5solute carrier family 16, member 5 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 6) (206600_s_at), score: -0.58 SLC7A1solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 1 (212295_s_at), score: -0.43 SLC9A3R2solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 3 regulator 2 (209830_s_at), score: -0.47 SOCS2suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 (203373_at), score: -0.53 STMN2stathmin-like 2 (203000_at), score: -0.55 TACSTD2tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (202286_s_at), score: -0.66 TBX5T-box 5 (207155_at), score: -0.53 TIMP2TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 2 (203167_at), score: -0.55 TMEM158transmembrane protein 158 (213338_at), score: -0.53 TMEM8transmembrane protein 8 (five membrane-spanning domains) (221882_s_at), score: -0.43 TSPAN13tetraspanin 13 (217979_at), score: -0.49 TSPAN4tetraspanin 4 (209264_s_at), score: -0.44 UNC5Bunc-5 homolog B (C. elegans) (213100_at), score: -0.59 WNT5Bwingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 5B (221029_s_at), score: -0.49 ZNF423zinc finger protein 423 (214761_at), score: 0.6 ZNF711zinc finger protein 711 (207781_s_at), score: -0.44
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690360.cel | 12 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690416.cel | 15 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690248.cel | 5 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11513 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690199.cel | 1 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |