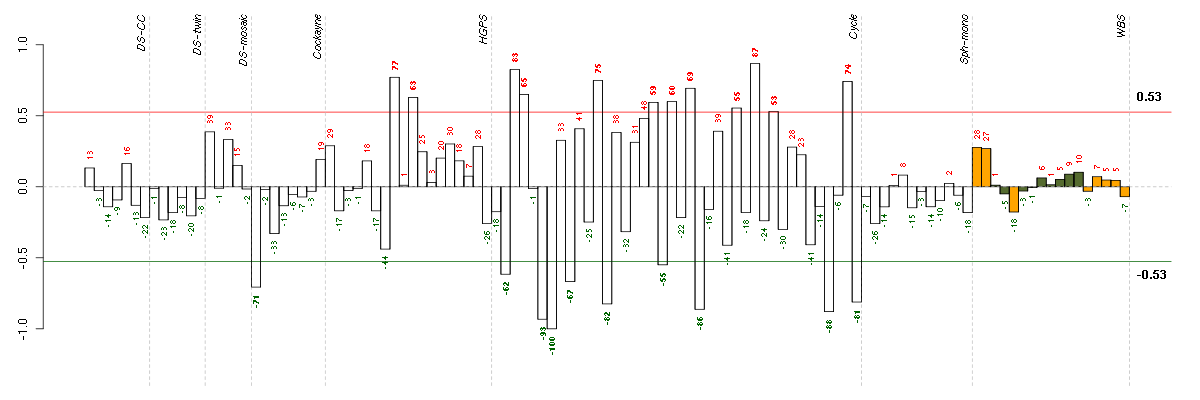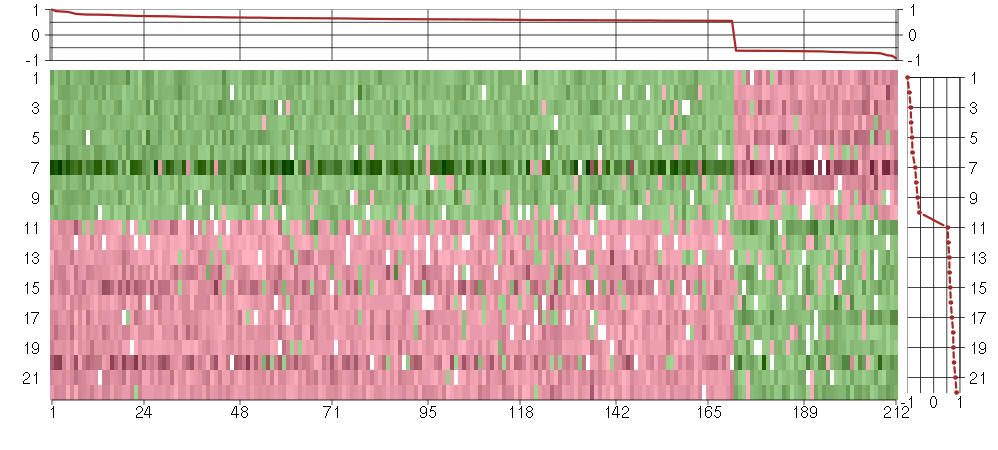

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

chromosome organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level that results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of chromosomes, structures composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins that carries hereditary information.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
establishment or maintenance of chromatin architecture
Any process that results in the specification, formation or maintenance of the physical structure of eukaryotic chromatin.
chromatin remodeling
Dynamic structural changes to eukaryotic chromatin occurring throughout the cell division cycle. These changes range from the local changes necessary for transcriptional regulation to global changes necessary for chromosome segregation.
chromatin-mediated maintenance of transcription
Maintenance of transcription by remodelling of chromatin into an 'open configuration'. Once established, this regulation is mitotically stable and is maintained over many cell divisions. It is also heritable.
transcription
The synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription, DNA-dependent
The synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
positive regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
gene expression
The process by which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of gene expression
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
RNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
chromatin modification
The alteration of DNA or protein in chromatin, which may result in changing the chromatin structure.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
RNA biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage. Includes polymerization of ribonucleotide monomers.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of gene expression, epigenetic
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression; the process is mitotically or meiotically heritable, or is stably self-propagated in the cytoplasm of a resting cell, and does not entail a change in DNA sequence.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
positive regulation of gene expression, epigenetic
Any epigenetic process that activates or increases the rate of gene expression.
positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.
positive regulation of transcription
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
positive regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
positive regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
positive regulation of gene expression
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
transcription
The synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
positive regulation of transcription
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription.
positive regulation of transcription
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription.
positive regulation of transcription
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription.
positive regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
positive regulation of gene expression
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
positive regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
transcription, DNA-dependent
The synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
positive regulation of transcription
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription.
RNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
RNA biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage. Includes polymerization of ribonucleotide monomers.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
positive regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.
positive regulation of transcription
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription.
positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.
transcription
The synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.
positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.
chromatin-mediated maintenance of transcription
Maintenance of transcription by remodelling of chromatin into an 'open configuration'. Once established, this regulation is mitotically stable and is maintained over many cell divisions. It is also heritable.
positive regulation of gene expression, epigenetic
Any epigenetic process that activates or increases the rate of gene expression.
positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of DNA-dependent transcription.
chromatin-mediated maintenance of transcription
Maintenance of transcription by remodelling of chromatin into an 'open configuration'. Once established, this regulation is mitotically stable and is maintained over many cell divisions. It is also heritable.


ABCD1ATP-binding cassette, sub-family D (ALD), member 1 (205142_x_at), score: 0.65 ADCK2aarF domain containing kinase 2 (221893_s_at), score: 0.71 AGPAT11-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase 1 (lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase, alpha) (215535_s_at), score: 0.65 AGRNagrin (217419_x_at), score: 0.58 AKAP2A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein 2 (202759_s_at), score: 0.68 ALDH1L1aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family, member L1 (215798_at), score: -0.66 AP2A2adaptor-related protein complex 2, alpha 2 subunit (212159_x_at), score: 0.56 ARID1AAT rich interactive domain 1A (SWI-like) (210649_s_at), score: 0.57 ARSAarylsulfatase A (204443_at), score: 0.71 ATF5activating transcription factor 5 (204999_s_at), score: 0.56 ATN1atrophin 1 (40489_at), score: 0.83 B3GAT3beta-1,3-glucuronyltransferase 3 (glucuronosyltransferase I) (203452_at), score: 0.77 BACE2beta-site APP-cleaving enzyme 2 (217867_x_at), score: 0.6 BAIAP2BAI1-associated protein 2 (209502_s_at), score: 0.58 BAP1BRCA1 associated protein-1 (ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase) (201419_at), score: 0.67 BAT2HLA-B associated transcript 2 (212081_x_at), score: 0.82 BAT2LHLA-B associated transcript 2-like (212068_s_at), score: 0.74 BRD4bromodomain containing 4 (202102_s_at), score: 0.56 BTBD2BTB (POZ) domain containing 2 (207722_s_at), score: 0.69 C16orf57chromosome 16 open reading frame 57 (218060_s_at), score: 0.71 C19orf61chromosome 19 open reading frame 61 (221335_x_at), score: 0.59 C4orf43chromosome 4 open reading frame 43 (218513_at), score: -0.63 C5orf44chromosome 5 open reading frame 44 (218674_at), score: -0.66 CABIN1calcineurin binding protein 1 (37652_at), score: 0.64 CDC25Bcell division cycle 25 homolog B (S. pombe) (201853_s_at), score: 0.58 CDC42BPBCDC42 binding protein kinase beta (DMPK-like) (217849_s_at), score: 0.91 CDC42EP1CDC42 effector protein (Rho GTPase binding) 1 (204693_at), score: 0.66 CDC42EP4CDC42 effector protein (Rho GTPase binding) 4 (214721_x_at), score: 0.62 CENPTcentromere protein T (218148_at), score: 0.65 CHMP1Achromatin modifying protein 1A (201933_at), score: 0.58 CHMP5chromatin modifying protein 5 (218085_at), score: -0.67 CICcapicua homolog (Drosophila) (212784_at), score: 0.8 CITcitron (rho-interacting, serine/threonine kinase 21) (212801_at), score: 0.57 CIZ1CDKN1A interacting zinc finger protein 1 (205516_x_at), score: 0.77 CLIP2CAP-GLY domain containing linker protein 2 (211031_s_at), score: 0.62 CNOT3CCR4-NOT transcription complex, subunit 3 (203239_s_at), score: 0.77 CORO2Bcoronin, actin binding protein, 2B (209789_at), score: 0.56 CRTC3CREB regulated transcription coactivator 3 (218648_at), score: 0.74 CScitrate synthase (208660_at), score: 0.68 DCAKDdephospho-CoA kinase domain containing (221224_s_at), score: -0.62 DNM2dynamin 2 (202253_s_at), score: 0.6 DOK4docking protein 4 (209691_s_at), score: 0.61 DOPEY1dopey family member 1 (40612_at), score: -0.69 DSPPdentin sialophosphoprotein (221681_s_at), score: -0.62 EHBP1L1EH domain binding protein 1-like 1 (221755_at), score: 0.61 EPHA4EPH receptor A4 (206114_at), score: -0.63 ERBB2IPerbb2 interacting protein (217941_s_at), score: -0.64 EVLEnah/Vasp-like (217838_s_at), score: 0.62 FAM18Bfamily with sequence similarity 18, member B (218446_s_at), score: -0.65 FAM3Afamily with sequence similarity 3, member A (38043_at), score: 0.57 FAM62Afamily with sequence similarity 62 (C2 domain containing), member A (208858_s_at), score: 0.55 FBXL11F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 11 (208989_s_at), score: 0.56 FBXL14F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 14 (213145_at), score: 0.68 FBXO17F-box protein 17 (220233_at), score: 0.67 FCF1FCF1 small subunit (SSU) processome component homolog (S. cerevisiae) (219927_at), score: -0.75 FHOD1formin homology 2 domain containing 1 (218530_at), score: 0.63 FKSG2apoptosis inhibitor (208588_at), score: -0.64 FLJ12529pre-mRNA cleavage factor I, 59 kDa subunit (217866_at), score: 0.76 FOSL1FOS-like antigen 1 (204420_at), score: 0.59 FOXC2forkhead box C2 (MFH-1, mesenchyme forkhead 1) (214520_at), score: 0.61 FOXK2forkhead box K2 (203064_s_at), score: 0.91 FURINfurin (paired basic amino acid cleaving enzyme) (201945_at), score: 0.67 GABARAPL3GABA(A) receptors associated protein like 3 (pseudogene) (211458_s_at), score: -0.63 GRINAglutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate-associated protein 1 (glutamate binding) (212090_at), score: 0.65 GTPBP1GTP binding protein 1 (219357_at), score: 0.56 H1FXH1 histone family, member X (204805_s_at), score: 0.69 HAB1B1 for mucin (215778_x_at), score: -0.68 HBS1LHBS1-like (S. cerevisiae) (209314_s_at), score: -0.62 HECTD3HECT domain containing 3 (218632_at), score: 0.56 HMGA1high mobility group AT-hook 1 (210457_x_at), score: 0.7 HNRNPH2heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein H2 (H') (201132_at), score: -0.71 HNRNPUL1heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U-like 1 (209675_s_at), score: 0.68 HSD17B6hydroxysteroid (17-beta) dehydrogenase 6 homolog (mouse) (37512_at), score: -0.7 HSF1heat shock transcription factor 1 (202344_at), score: 0.61 HSPA12Aheat shock 70kDa protein 12A (214434_at), score: 0.59 IDUAiduronidase, alpha-L- (205059_s_at), score: 0.8 IGFBP4insulin-like growth factor binding protein 4 (201508_at), score: 0.56 INTS1integrator complex subunit 1 (212212_s_at), score: 0.55 JUNDjun D proto-oncogene (203751_x_at), score: 0.58 JUPjunction plakoglobin (201015_s_at), score: 0.67 KAL1Kallmann syndrome 1 sequence (205206_at), score: -0.71 KCTD13potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 13 (45653_at), score: 0.56 KIAA1305KIAA1305 (220911_s_at), score: 0.58 KLHL23kelch-like 23 (Drosophila) (213610_s_at), score: -0.62 KPNA6karyopherin alpha 6 (importin alpha 7) (212101_at), score: 0.59 LEPREL2leprecan-like 2 (204854_at), score: 0.7 LMF2lipase maturation factor 2 (212682_s_at), score: 0.67 LOC100133105hypothetical protein LOC100133105 (214237_x_at), score: -0.62 LOC339047hypothetical protein LOC339047 (221501_x_at), score: 0.61 LOC90379hypothetical protein BC002926 (221849_s_at), score: 0.68 LPGAT1lysophosphatidylglycerol acyltransferase 1 (202651_at), score: -0.62 LRDDleucine-rich repeats and death domain containing (221640_s_at), score: 0.66 LRFN4leucine rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 4 (219491_at), score: 0.57 MAGOH2mago-nashi homolog 2, proliferation-associated (Drosophila) (217693_x_at), score: -0.67 MAP1Smicrotubule-associated protein 1S (218522_s_at), score: 0.94 MAP3K6mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 6 (219278_at), score: 0.75 MAP4microtubule-associated protein 4 (200836_s_at), score: 0.62 MAP7D1MAP7 domain containing 1 (217943_s_at), score: 0.74 MAPK7mitogen-activated protein kinase 7 (35617_at), score: 0.59 MAST2microtubule associated serine/threonine kinase 2 (211593_s_at), score: 0.68 MAST4microtubule associated serine/threonine kinase family member 4 (40016_g_at), score: 0.62 MBD3methyl-CpG binding domain protein 3 (41160_at), score: 0.56 MED15mediator complex subunit 15 (222175_s_at), score: 0.63 MGAT1mannosyl (alpha-1,3-)-glycoprotein beta-1,2-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (201126_s_at), score: 0.65 MINK1misshapen-like kinase 1 (zebrafish) (214246_x_at), score: 0.65 MLL4myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia 4 (203419_at), score: 0.58 MUL1mitochondrial E3 ubiquitin ligase 1 (218246_at), score: 0.71 MYL4myosin, light chain 4, alkali; atrial, embryonic (210088_x_at), score: -0.63 MYO1Bmyosin IB (212364_at), score: -0.62 MYO9Bmyosin IXB (217297_s_at), score: 0.56 NBL1neuroblastoma, suppression of tumorigenicity 1 (37005_at), score: 0.7 NCDNneurochondrin (209556_at), score: 0.58 NCKAP1NCK-associated protein 1 (217465_at), score: -0.8 NCOR2nuclear receptor co-repressor 2 (207760_s_at), score: 0.6 NDPNorrie disease (pseudoglioma) (206022_at), score: 0.58 NEFMneurofilament, medium polypeptide (205113_at), score: -0.69 NFATC4nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 4 (205897_at), score: 0.66 NFKBIAnuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha (201502_s_at), score: 0.6 NPDC1neural proliferation, differentiation and control, 1 (218086_at), score: 0.58 NPIPnuclear pore complex interacting protein (204538_x_at), score: 0.62 OLFML2Bolfactomedin-like 2B (213125_at), score: 0.58 OLR1oxidized low density lipoprotein (lectin-like) receptor 1 (210004_at), score: -0.64 PARVBparvin, beta (204629_at), score: 0.79 PCDHG@protocadherin gamma cluster (215836_s_at), score: 0.73 PCDHGA1protocadherin gamma subfamily A, 1 (209079_x_at), score: 0.78 PCDHGC3protocadherin gamma subfamily C, 3 (211066_x_at), score: 0.61 PDE7Bphosphodiesterase 7B (220343_at), score: -0.63 PHF7PHD finger protein 7 (215622_x_at), score: -0.67 PIP5K1Cphosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase, type I, gamma (212518_at), score: 0.93 PKN1protein kinase N1 (202161_at), score: 0.71 PLAUplasminogen activator, urokinase (211668_s_at), score: 0.56 PNPLA6patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 6 (203718_at), score: 0.62 POLR2Apolymerase (RNA) II (DNA directed) polypeptide A, 220kDa (202725_at), score: 0.76 POLRMTpolymerase (RNA) mitochondrial (DNA directed) (203782_s_at), score: 0.56 POLSpolymerase (DNA directed) sigma (202466_at), score: 0.66 POM121POM121 membrane glycoprotein (rat) (212178_s_at), score: 0.74 POM121CPOM121 membrane glycoprotein C (213360_s_at), score: 0.61 POMZP3POM (POM121 homolog, rat) and ZP3 fusion (204148_s_at), score: 0.69 PRKACAprotein kinase, cAMP-dependent, catalytic, alpha (202801_at), score: 0.64 PRKCDprotein kinase C, delta (202545_at), score: 0.63 PTDSS1phosphatidylserine synthase 1 (201433_s_at), score: 0.61 PTOV1prostate tumor overexpressed 1 (212032_s_at), score: 0.57 PTPN9protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 9 (202958_at), score: 0.6 PTPROprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, O (211600_at), score: 0.62 PXNpaxillin (211823_s_at), score: 0.58 RAB1ARAB1A, member RAS oncogene family (213440_at), score: -0.62 RAD54L2RAD54-like 2 (S. cerevisiae) (213205_s_at), score: 0.73 RBM15BRNA binding motif protein 15B (202689_at), score: 0.63 REREarginine-glutamic acid dipeptide (RE) repeats (200940_s_at), score: 0.69 RNF11ring finger protein 11 (208924_at), score: -0.68 RNF220ring finger protein 220 (219988_s_at), score: 0.74 RNF24ring finger protein 24 (204669_s_at), score: 0.59 RNF40ring finger protein 40 (206845_s_at), score: 0.58 RPL18AP6ribosomal protein L18a pseudogene 6 (216383_at), score: -0.91 RPRD2regulation of nuclear pre-mRNA domain containing 2 (212553_at), score: 0.65 RPS17P5ribosomal protein S17 pseudogene 5 (216348_at), score: -0.81 RPS6KA4ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 90kDa, polypeptide 4 (204632_at), score: 0.6 SBF1SET binding factor 1 (39835_at), score: 0.58 SBNO2strawberry notch homolog 2 (Drosophila) (204166_at), score: 0.7 SCAMP1secretory carrier membrane protein 1 (206667_s_at), score: -0.64 SCAMP4secretory carrier membrane protein 4 (213244_at), score: 1 SDAD1SDA1 domain containing 1 (218607_s_at), score: 0.63 SEMA3Fsema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), short basic domain, secreted, (semaphorin) 3F (35666_at), score: -0.62 SF1splicing factor 1 (208313_s_at), score: 0.81 SF3A2splicing factor 3a, subunit 2, 66kDa (37462_i_at), score: 0.67 SIN3BSIN3 homolog B, transcription regulator (yeast) (209352_s_at), score: 0.59 SIPA1signal-induced proliferation-associated 1 (204164_at), score: 0.57 SLC25A28solute carrier family 25, member 28 (221432_s_at), score: 0.58 SLC43A3solute carrier family 43, member 3 (213113_s_at), score: 0.56 SLC4A2solute carrier family 4, anion exchanger, member 2 (erythrocyte membrane protein band 3-like 1) (202111_at), score: 0.55 SMARCD1SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily d, member 1 (209518_at), score: 0.61 SMG6Smg-6 homolog, nonsense mediated mRNA decay factor (C. elegans) (214940_s_at), score: 0.73 SMG7Smg-7 homolog, nonsense mediated mRNA decay factor (C. elegans) (201794_s_at), score: 0.68 SMYD5SMYD family member 5 (209516_at), score: 0.62 SOLHsmall optic lobes homolog (Drosophila) (204275_at), score: 0.79 SORBS3sorbin and SH3 domain containing 3 (209253_at), score: 0.56 SPG7spastic paraplegia 7 (pure and complicated autosomal recessive) (202104_s_at), score: 0.64 SPRY4sprouty homolog 4 (Drosophila) (221489_s_at), score: 0.62 SSBP3single stranded DNA binding protein 3 (217991_x_at), score: 0.66 STRN4striatin, calmodulin binding protein 4 (217903_at), score: 0.75 SUPT6Hsuppressor of Ty 6 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (208831_x_at), score: 0.61 TAF13TAF13 RNA polymerase II, TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factor, 18kDa (205966_at), score: -0.63 TAPBPTAP binding protein (tapasin) (208829_at), score: 0.8 TBC1D10BTBC1 domain family, member 10B (220947_s_at), score: 0.62 TERF2telomeric repeat binding factor 2 (203611_at), score: 0.61 TIAF1TGFB1-induced anti-apoptotic factor 1 (202039_at), score: 0.62 TICAM2toll-like receptor adaptor molecule 2 (214658_at), score: -0.69 TLE4transducin-like enhancer of split 4 (E(sp1) homolog, Drosophila) (204872_at), score: -0.63 TMEM123transmembrane protein 123 (211967_at), score: -0.62 TMSB4Ythymosin beta 4, Y-linked (206769_at), score: -0.7 TRIM21tripartite motif-containing 21 (204804_at), score: 0.61 TSC2tuberous sclerosis 2 (215735_s_at), score: 0.63 TSKUtsukushin (218245_at), score: 0.64 TXLNAtaxilin alpha (212300_at), score: 0.74 TYRO3TYRO3 protein tyrosine kinase (211432_s_at), score: 0.57 UBE2Zubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2Z (217750_s_at), score: 0.58 UBTD1ubiquitin domain containing 1 (219172_at), score: 0.66 ULK1unc-51-like kinase 1 (C. elegans) (209333_at), score: 0.57 USF2upstream transcription factor 2, c-fos interacting (202152_x_at), score: 0.66 VAT1vesicle amine transport protein 1 homolog (T. californica) (208626_s_at), score: 0.57 VCPIP1valosin containing protein (p97)/p47 complex interacting protein 1 (219810_at), score: -0.62 VEGFBvascular endothelial growth factor B (203683_s_at), score: 0.87 VPS37Bvacuolar protein sorting 37 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (221704_s_at), score: 0.8 WDR42AWD repeat domain 42A (202249_s_at), score: 0.6 WDR6WD repeat domain 6 (217734_s_at), score: 0.72 WIZwidely interspaced zinc finger motifs (52005_at), score: 0.57 XAB2XPA binding protein 2 (218110_at), score: 0.7 YES1v-yes-1 Yamaguchi sarcoma viral oncogene homolog 1 (202932_at), score: 0.58 ZDHHC18zinc finger, DHHC-type containing 18 (212860_at), score: 0.57 ZFP36L1zinc finger protein 36, C3H type-like 1 (211965_at), score: 0.66 ZNF318zinc finger protein 318 (203521_s_at), score: 0.62 ZNF580zinc finger protein 580 (220748_s_at), score: 0.56
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485771.cel | 7 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485751.cel | 6 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486371.cel | 37 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486091.cel | 23 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485891.cel | 13 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486431.cel | 40 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949557.cel | 1 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485811.cel | 9 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485671.cel | 2 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486011.cel | 19 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486251.cel | 31 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486171.cel | 27 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485991.cel | 18 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486031.cel | 20 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690344.cel | 10 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM00038C |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485711.cel | 4 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486071.cel | 22 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486411.cel | 39 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485871.cel | 12 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690304.cel | 8 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GMO8398C |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485691.cel | 3 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486211.cel | 29 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |