Difference between revisions of "Software"
| (12 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Homepage]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | In addition to studying biological systems through mathematical modeling and analysis of large-scale data sets, the Computational Biology Group also develops tools and methods for such analyses. Like other research groups in the field, we make the software implementation of those methods freely available to encourage their use and comparison with other methods. | ||
| + | == [[Pascal]] == | ||
| + | Pascal efficiently computes gene and pathway scores for GWAS summary statistics '''[[Pascal|See more here]]''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | == [[Metabomatching]] == | ||
| + | Metabomatching is a method to identify compounds from spectral features that jointly associate with genotypes | ||
| + | '''[[Metabomatching|See more here]]''' | ||
| + | |||
== [[ISA|The Iterative Signature Algorithm]] == | == [[ISA|The Iterative Signature Algorithm]] == | ||
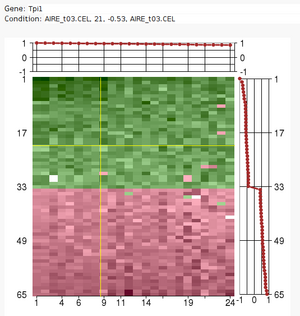
| + | [[image:expmat.png|An ISA transcription module|300px|right|link=ISA]] | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
Large sets of data, like expression profile from many samples, require | Large sets of data, like expression profile from many samples, require | ||
| − | analytic tools to reduce their complexity. | + | analytic tools to reduce their complexity. |
| − | + | The '''Iterative Signature Algorithm (ISA)''' was designed to reduce the | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | The ''' | ||
| − | |||
complexity of very large sets of data by decomposing it into so-called | complexity of very large sets of data by decomposing it into so-called | ||
"modules". In the context of gene expression data these modules consist of | "modules". In the context of gene expression data these modules consist of | ||
| Line 17: | Line 26: | ||
rely on the computation of correlation matrices (like many other tools), it | rely on the computation of correlation matrices (like many other tools), it | ||
is extremely fast even for very large datasets. | is extremely fast even for very large datasets. | ||
| + | '''[[ISA|See more here]]''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
== [[ExpressionView]] == | == [[ExpressionView]] == | ||
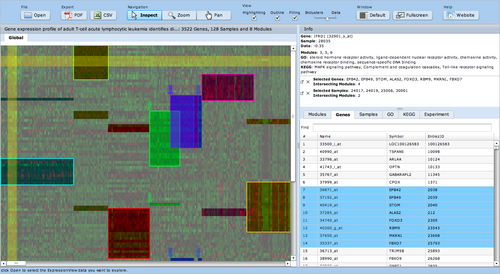
| − | [[image:Expressionview.screenshot.png|Screenshot of the ExpressionView applet|500px|left]] | + | [[image:Expressionview.screenshot.png|Screenshot of the ExpressionView applet|500px|left|link=ExpressionView]] |
<br style="clear: both" /> | <br style="clear: both" /> | ||
| − | <br> | + | <br/> |
[[ExpressionView]] is an R package that provides an interactive environment to explore biclusters identified in gene expression data. A sophisticated ordering algorithm is used to present the biclusters in a visually appealing layout. From this overview, the user can select individual biclusters and access all the biologically relevant data associated with it. The package is aimed to facilitate the collaboration between bioinformaticians and life scientists who are not familiar with the R language. | [[ExpressionView]] is an R package that provides an interactive environment to explore biclusters identified in gene expression data. A sophisticated ordering algorithm is used to present the biclusters in a visually appealing layout. From this overview, the user can select individual biclusters and access all the biologically relevant data associated with it. The package is aimed to facilitate the collaboration between bioinformaticians and life scientists who are not familiar with the R language. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''[[ExpressionView|See more here]]''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == [[Cellophane]] == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cellophane is an ImageJ plugin for the semi-automated quantification of tagged protein profiles along the cortex of ''S. pombe'' cells. | ||
| + | '''[[Cellophane|See more here]]''' | ||
Latest revision as of 12:41, 26 March 2015
In addition to studying biological systems through mathematical modeling and analysis of large-scale data sets, the Computational Biology Group also develops tools and methods for such analyses. Like other research groups in the field, we make the software implementation of those methods freely available to encourage their use and comparison with other methods.
Contents
Pascal
Pascal efficiently computes gene and pathway scores for GWAS summary statistics See more here
Metabomatching
Metabomatching is a method to identify compounds from spectral features that jointly associate with genotypes See more here
The Iterative Signature Algorithm
Large sets of data, like expression profile from many samples, require
analytic tools to reduce their complexity.
The Iterative Signature Algorithm (ISA) was designed to reduce the
complexity of very large sets of data by decomposing it into so-called
"modules". In the context of gene expression data these modules consist of
subsets of genes that exhibit a coherent expression profile only over a
subset of microarray experiments. Genes and arrays may be attributed to
multiple modules and the level of required coherence can be varied resulting
in different "resolutions" of the modular mapping. Since the ISA does not
rely on the computation of correlation matrices (like many other tools), it
is extremely fast even for very large datasets.
See more here
ExpressionView
ExpressionView is an R package that provides an interactive environment to explore biclusters identified in gene expression data. A sophisticated ordering algorithm is used to present the biclusters in a visually appealing layout. From this overview, the user can select individual biclusters and access all the biologically relevant data associated with it. The package is aimed to facilitate the collaboration between bioinformaticians and life scientists who are not familiar with the R language.
Cellophane
Cellophane is an ImageJ plugin for the semi-automated quantification of tagged protein profiles along the cortex of S. pombe cells. See more here