Difference between revisions of "Cellophane"
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
The plugin is available under a GPL license and the code is available [[Media:Cellophane.zip | here]]. This zip files contains two .java files containing the semi-automated and manual versions of Cellophane, as well as the necessary java library file. | The plugin is available under a GPL license and the code is available [[Media:Cellophane.zip | here]]. This zip files contains two .java files containing the semi-automated and manual versions of Cellophane, as well as the necessary java library file. | ||
| − | You can also download the short [[Media:CellophaneManual.pdf | manual]]. If you have | + | You can also download the short [[Media:CellophaneManual.pdf | manual]]. If you have additional questions, you can contact [[User:Micha | Micha]] |
== Credits== | == Credits== | ||
Revision as of 16:40, 11 April 2014
Introduction
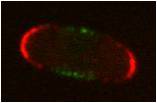
Cellophane is an ImageJ plugin for the semi-automated quantification of a protein profile along the cell membrane. It allows for the quantification along two channels. The plugin also has a manual mode which has a lower throughput but allows for higher precision.
Download
The plugin is available under a GPL license and the code is available here. This zip files contains two .java files containing the semi-automated and manual versions of Cellophane, as well as the necessary java library file.
You can also download the short manual. If you have additional questions, you can contact Micha
Credits
This plugin was developed by Micha Hersch in collaboration with the lab of Sophie Martin at the University of Lausanne, in particular with Olivier Hachet. Sascha Dalessi helped testing the software. It uses the imagescience library written by Erik Meijering. If you use Cellophane for your published work, please acknowledge it by citing the following paper:
Bhatia P, Hachet O, Hersch M, Rincon SA, Berthelot-Grosjean M, Dalessi S, Basterra L, Bergmann S, Paoletti A, Martin SG
Distinct levels in Pom1 gradients limit Cdr2 activity and localization to time and position division.
Cell Cycle: 2014, 13(4);538-52
[PubMed:24316795]
[WorldCat.org:
ISSN
ESSN
]
[DOI]
( o)